QR code payments have been the driving force behind digital transactions for some time now, enabling contactless, lightning-fast tap-and-go payments.
But there are still a lot of people asking, What are eWallet QR codes? How do they work? Is QR code payment safe?
Well, we are here to answer those questions.
In this guide, we shall be going through all you need to know about eWallet QR code payment, how it works, types, and much more.
So with that being said, let’s get right into it:
QR Code Payment Statistics
Let’s look at some eWallet app statistics showing the increasing use of eWallet QR code payments across the world.
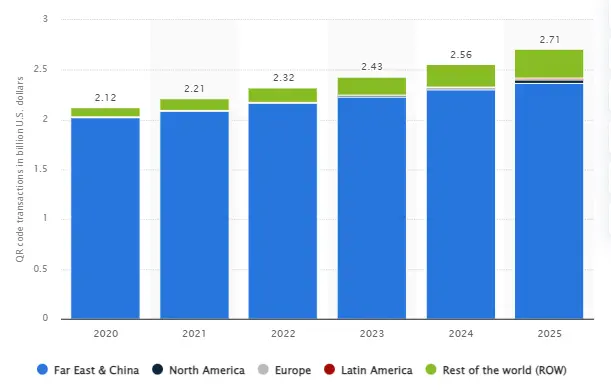
- The QR code payment market is poised for large expansion, with an expected increase from USD 11.2 billion in 2022 to USD 51.58 billion over the next decade, reflecting a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.5%. This is what statistics from Fintech Futures show us.
- In 2022, the dynamic QR code segment took the lead, commanding over 63.00% of the market’s revenue share.
- By 2025, Latin America is projected to surpass Europe in QR code adoption, according to Statista. The Americas, encompassing North America, are expected to lag behind the Far East & China in QR transaction market size.
With these Fintech Statistics out of the way, let’s look overview of what eWallet QR code payment is.
What is a QR code? Understanding QR Code Payment
A QR code, short for Quick Response code, is a two-dimensional code made up of black squares on a square grid against a white background.
Unlike traditional barcodes, QR codes don’t need a specific reader—smartphone cameras can easily scan them.
What sets QR codes apart is their ability to store more data in a smaller space. They are a convenient way to share information quickly and efficiently.
1. eWallet QR Code Payment
So, what are QR Code payments?
In transactional terms, a QR code holds machine-readable transaction-related information that, once scanned, can enable a payment transfer via eWallet. In simple words, Users can make payments by scanning a Quick Response (QR) code displayed by the merchant.
An eWallet QR code payment is a secure and convenient method for conducting transactions using digital wallets.
Unlike traditional methods, eWallet QR code payments streamline the process, offering a quick and efficient way to complete transactions. This method enhances user convenience, promoting a seamless and cashless experience.
The eWallet QR code payment system is designed for simplicity and ease of use, empowering users to make purchases effortlessly while enjoying the benefits of digital wallet technology.
Today, QR codes and QR code scanner features have become integral parts of fintech app development, giving us payment apps with the capacity of QR Code payment. (More on this later.)Top of Form
2. History Behind QR Code
The QR code was invented in the 1990s by a Japanese company called Denso Wave. In its initial time, QR codes were used in the automotive industry for production, shipping, and tracking purposes.
However, as time passed, people started implementing QR codes in several business areas such as item identification and mobile app marketing.
Many experts believe that QR codes didn’t take off at the expected rate in their early life.
However, in countries like China and India, QR code development played a crucial role in mobile payment services’ rapid growth, by enabling QR code-based payments. Especially after its use in UPI payment app development.
Businesses preferred QR-Code eWallet over POS (Point of Sale) terminals as QR codes do not require significant hardware investments.
Moving on from eWallet QR codes, let’s discuss the various types of codes you might encounter.
Types of QR codes
One of the main applications of QR codes lies in eWallet and payment apps in general. There are two categories for the types of QR codes.

Let’s discuss them one by one:
Type 1: Static QR code
In this type, the destination URL is directly placed in the QR code and cannot be edited; thus, the name is static.
These eWallet QR codes cannot be tracked, but can be rectified by adding the URL. As the name suggests, the content in these QR codes cannot be edited.
Static QR code payments are fast. That’s why they are used in several industries, like in-store wallet tails, delivery services, cab services, street vendors, in-home services, etc.
To pay for any of these services, all users have to scan the QR code using the in-app camera of their eWallet mobile app and pay. Such payment methods not only increase the speed of payment but also enhance the customer experience.
Type 2: Dynamic QR code
The dynamic QR code is editable.
They also come with advanced features such as password protection, access management and analysis, and device-based redirection.
Dynamic QR codes can generate valuable insights, such as the number of people who scanned the code, the type of device used to scan the code, the user’s location, and more.
Merchants worldwide use dynamic QR code payments, as these QR codes can convey both the payment amount and merchant information.
With this feature, the user has to accept the transaction by scanning the given QR code, and the payment will happen. However, to be noting, the merchants (who send the QR code) will have more control over the payment amount due to this feature.
Other Common Types of QR Codes
Apart from the two types of eWallet payment QR codes we discussed above, there are various other types, such as an email QR code generator, that don’t have a common application in the payment world.
Take a look at them below.
| Type | Description | Examples |
| Model 1 QR Code | General-purpose type for encoding small amounts of data. | URLs, text messages, and contact information. |
| Model 2 QR Code | The most common type offers a larger capacity and improved error correction than the Model 1. | Website links, text descriptions, cards, and SMS messages. |
| Micro QR Code | Designed for small spaces, such as product tags or business cards. | Product codes, brand logos, coupon links. |
| iQR Code | Square-shaped with high density and data capacity. | It is not yet widely used, but it has potential for innovative data encoding. |
| URL QR Code | Directs users to a specific website when scanned. | Landing pages, e-commerce stores, and blog articles. |
| Text QR Code | Stores plain text information for quick access. | Product specifications, recipes, and operating manuals. |
| vCard QR Code | Share your contact information with a single scan. | business cards, personal profiles, and professional contacts. |
| SMS QR Code | Compose and send SMS messages automatically. | customer service interactions, event updates, and appointment reminders. |
| Email QR Code | Open the pre-filled email template with user details. | marketing campaigns, event registration forms, and customer feedback. |
| Wi-Fi QR Code | Connect to a Wi-Fi network without typing passwords. | Hotels, restaurants, conferences, and public spaces. |
| Payment QR Code | Enable quick and secure mobile payments. | Restaurants, retail stores, online purchases, and donations. |
| Event QR Code | Share event details, register attendees, or deliver tickets. | Conference registration, concert tickets, and festival information. |
| Location: QR Code | Navigate users to specific locations on maps. | Tourist attractions, museums, retail stores, and local businesses. |
| App QR Code | Direct users to download apps from app stores. | Mobile games, productivity tools, and social media apps. |
| Social Media QR Code | Link to social media profiles to facilitate sharing. | Personal profiles, company pages, promotional campaigns. |
How Does the QR Code Work?
Now that you know different types of QR codes, it’s time to understand how a QR code wallet works.
There are two primary ways eWallet QR code payments unfold. In this section of the blog, we shall be discussing both of them, starting with:
1. Merchant-Generated QR Code
Step 1: Scan QR Code to Initiate Transaction: The customer walks into a store and sees a unique QR code displayed at the checkout counter. This code, generated by the merchant’s system, encodes crucial information like merchant ID, transaction amount, and currency.
Step 2: eWallet App Reads The Code: The customer whips out their smartphone and opens their preferred eWallet app. Using the app’s built-in camera, they scan the merchant’s QR code.
Step 3: Confirmation & Completion: The eWallet app decodes the information embedded in the QR code and displays it on the customer’s screen. They can then review the transaction details, confirm the amount, and enter their eWallet PIN or fingerprint for biometric authentication.
Step 4: Funds Transferred: Once confirmed, the funds are transferred in real-time from the customer’s eWallet to the merchant’s account. Both parties receive instant notifications, and voila, the payment is complete!
2. Customer-Generated QR Code
Step 1: Payee Gets QR Code: Imagine you’re splitting a restaurant bill with friends. Open your eWallets app and choose the “Generate QR code” option. The app displays a unique payment QR code on your phone screen, containing your eWallet ID and payment details.
Step 2: Scan the Code & Settle: Your friends scan your QR code using their eWallet apps. Once the information is automatically retrieved, they can enter the desired amount to pay you.
Step 3: Funds Transferred: With a tap of confirmation, the money is transferred directly from their eWallet to yours. You’re now the Robin Hood of the bill, dividing the spoils amongst yourselves!
Anatomy, QR Codes Breakdown
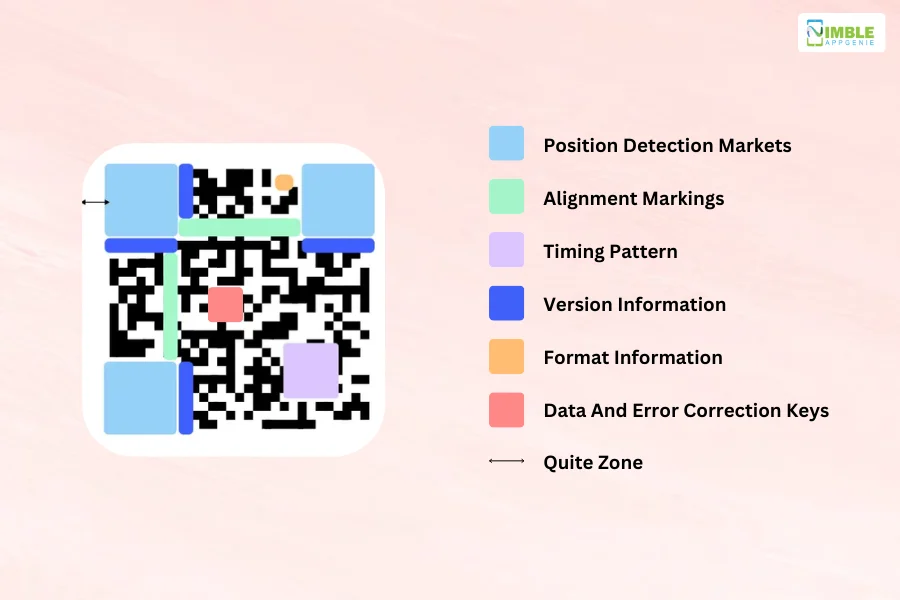
More often than not, eWallet app QR codes seem like random arrangements of white and black boxes, but is it really so?
Well, not really.
As it turns out, payment QR codes, or any QR code for that matter, are specifically created to hold specific information.
To better understand the same, here’s a detailed QR code breakdown.
1. Position Detection Markets
Position detection markets are located at the three corners of each QR code. These markers allow a QR code scanner to quickly and accurately recognize the code. Identification markers are essential to identify the presence and orientation of a QR code in an image.
2. Alignment Markings
These markers are smaller than the position detection markers and help QR code scanners straighten out QR codes, especially when drawn on curved surfaces. It is noted that the more information the QR code stores or the larger the QR code is, the more alignment patterns it requires.
3. Timing Pattern
The timing pattern helps the QR code scanner determine how large the data matrix is by just alternating the black and white modules on the QR-Code eWallet.
4. Version Information
At the present time, QR codes exist in 40 different versions. Version information markers specify which version is being used for a particular QR code. The most common versions used are between 1 to 7.
5. Format Information
The format patterns carry information about data mask patterns and error tolerance, making it easier for the scanner to scan the code.
6. Data and Error Correction Keys
This is where all your data is stored. This space also shares space with error correction blocks that allow up to 30% of the QR code to be damaged.
7. Quiet Zone
Similar to the importance of white space in every design, the quiet zone improves code comprehension by QR code readers. This helps ensure that the QR code is distinguished from the surroundings.
Why Do People (& Businesses) Love eWallet QR Code Payment?
So, what makes QR code-enabled eWallet apps so successful among people?
QR code payments are loved by the masses and businesses alike. In this section of the blog, we shall be discussing how this QR Code payment technology has become a favorite.

Let’s start with people:
► For People
1. Effortless Convenience
Top eWallet apps strive to deliver more convenience to their customers. One of the best ways to do so is via a QR code e-wallet payment system.
The tap-and-go technology makes it that much easier to make a payment. After all, there is no need to fumble with cards or PINs.
QR code payments are lightning-fast, streamlining the checkout process.
But that’s not all, it also has several advanced applications within the digital wallet ecosystem. For instance, splitting bills with friends, generating a QR code on your eWallet, and letting others pay you directly.
2. Enhanced Security
eWallet app security is an area of much importance, with all of the fraud going on. And with the help of QR code payment for eWallet, it is taken to the next level.
eWallets boast robust security features like two-factor authentication, safeguarding your financial information.
Therefore, there is no need to expose your card details at every checkout. QR code payments keep your card information hidden.
In addition to this, a detailed transaction history lets you track your spending and manage your budget effortlessly.
3. A World of Rewards
One of the biggest reasons why people love eWallet payment QR codes is the rewards.
Many eWallets offer cashback, discounts, and exclusive deals when you pay with QR codes. In addition to this, there are loyalty programs integrated with QR code payments that make earning rewards easier than ever.
With that being said, let’s look at the advantages of the eWallet app QR code for businesses.
► For Businesses
1. Faster Checkouts, Happier Customers
The happier the customer, the happier the business. Here’s how QR code payments make that possible.
QR code payments keep the line moving, boosting efficiency and sales, meaning shorter queues
The reduced waiting times lead to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Plus, businesses offer payment options to cater to tech-savvy customers and stay ahead of the curve.
2. Cost-Effective Efficiency
With a QR code for an e-wallet payment generator, a business can eliminate the need for expensive card terminals and physical cash handling, lowering operational costs.
The digital payment system also enables real-time transaction push notifications and streamlined reconciliation to improve cash flow management.
Consequently, businesses can open doors to gain wider reach by attracting customers who prefer cashless payment options.
3. Data-Driven Insights
Even larger businesses love the eWallet QR code since it allows them to track customer spending patterns and preferences through detailed transaction data. Thus, solving one of the biggest eWallet app challenges.
They can offer targeted promotions and personalize customer experiences based on data insights.
Speaking of which, the biggest reason why data-driven insights from QR code systems are valued is that they allow businesses to make informed business decisions based on accurate and real-time data.
These are the reasons why businesses as well as love QR codes in eWallet apps. Moving on, let’s see how to create a QR code for eWallet payments
How To Generate A QR Code For Payment? For User
Now that we know all you need to know about QR code payments, it’s time to discuss how to generate an eWallet QR code.
This is for merchants as well as people who want to receive payment via QR code.
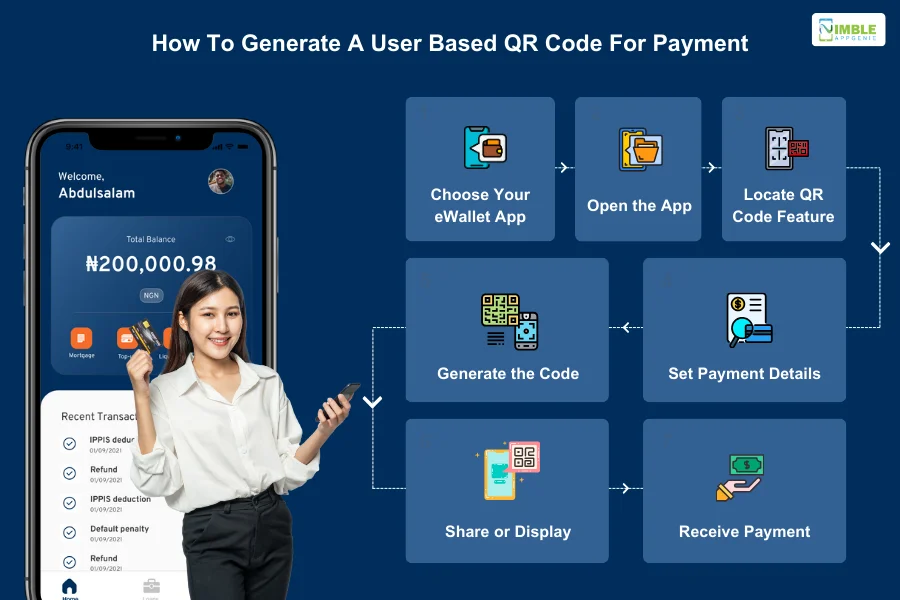
Let’s see how to create a QR code for e-wallet payment:
Step 1. Choose Your eWallet App
The first step is to select a reputable eWallet app that supports QR code payments. This includes popular apps like PayPal, Venmo, and more.
Step 2. Open the App
The next step is to download the app, register, and launch the eWallet app on your smartphone.
Step 3. Locate QR Code Feature
Once inside the app, look for options labeled “Request Money,” “Generate QR Code,” “Receive Payment,” or similar within the app. The exact wording might vary.
Step 4. Set Payment Details
If prompted, enter the amount you wish to receive or specify a payment type (e.g., goods and services, personal).
Step 5. Generate the Code
Tap the button to generate the QR code. The app will display a unique QR code on your screen.
Step 6. Share or Display
Once there, you can either:
- Share the eWallet QR code directly with the person paying you (via messaging apps or by showing them your screen).
- Display the QR code at your storefront or cash counter for customers to scan.
Step 7. Received Payment
Once the payer scans your QR code with their eWallet app, the payment will be initiated. You’ll receive a notification confirming the successful transaction.
How to Generate a QR Code for eWallet Payment? For Merchant
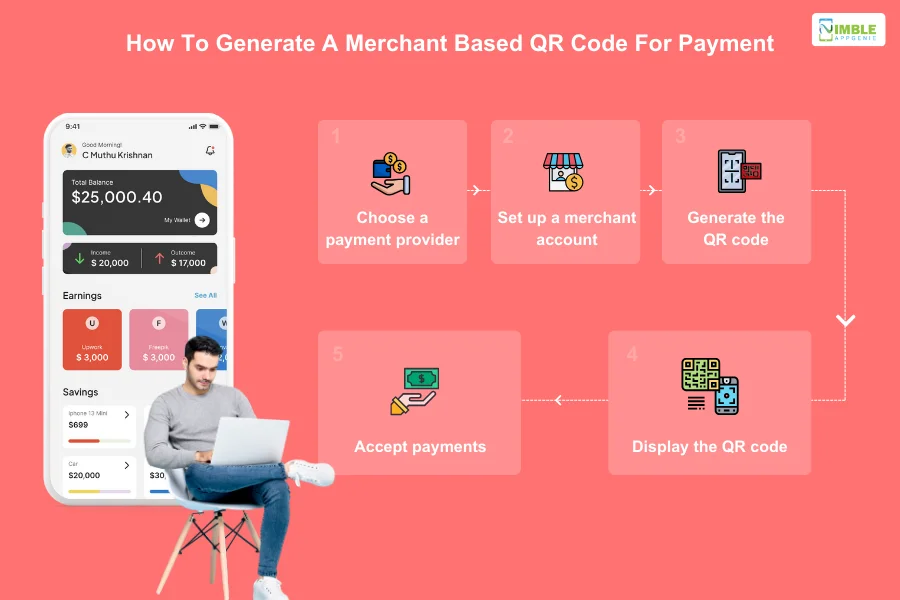
The process for a merchant is also very similar. To make it a complete guide to set up a QR code for e-wallet payments, let’s look at that below.
1. Choose a Payment Provider
Merchants typically partner with a merchant service provider like a bank, payment gateway, or financial technology company to facilitate QR code payments.
Factors to consider here include transaction fees, supported payment methods, and ease of integration when choosing a provider.
2. Set Up a Merchant Account
In this step, merchants will need to create an account with the chosen payment provider.
This involves providing business information, bank account details, and completing the necessary verification process.
3. Generate a QR Code
The specific method for generating the QR code varies depending on the payment provider. Here are some common approaches:
- Online QR code generators: Some providers offer online tools where merchants can input their payment details and create an ewallet QR code payment
- Mobile apps: Many payment providers have mobile apps that allow merchants to generate and manage QR codes.
- Merchant portals: Some providers have web-based portals where merchants can access QR code generation features.
4. Display the QR Code
Once generated, display the QR code prominently at the point of sale, making it easily scannable by customers.
Businesses should post it near the cash register, on product displays, or in print advertisements.
5. Accept Payments
With all said and done, customers can scan the QR code using their mobile payment app.
The payment app will automatically retrieve the merchant’s payment information and allow the customer to initiate the payment.
The merchant receives payment confirmation in real-time or near real-time.
This is how you create an eWallet QR code for merchants.
QR Code Payment vs Traditional Payment Methods
So, what makes eWallet QR code payment better than traditional payment methods?
Apart from the fact that it enables digital payments, QR code transactions offer several other benefits. Let’s compare both of them below:
| Features | QR Code Payment | Traditional Payment Methods (Cash, Cards) |
| Convenience | Scan and pay with just your phone, no need for cash or cards. | Requires carrying cash or cards, sometimes waiting for change. |
| Speed | Transactions are instant, reducing checkout times. | Cash transactions can be slow, and card payments involve entering PINs or signatures. |
| Security | Many QR code systems use two-factor authentication and encrypted data transfer, reducing fraud risk. | Carrying cash poses a theft risk, and card skimming and data breaches are possible. |
| Cost | Lower transaction fees for merchants compared to credit card payments. | Cash purchases have no fees, but card transactions involve merchant fees. |
| Accessibility | Requires a smartphone with a camera and a compatible app. | Works with everyone, regardless of smartphone ownership. |
| Tracking & Data | Transactions are easily tracked in your payment history, providing valuable data for businesses. | Cash transactions leave no digital trace, and card transactions may offer limited data insights. |
| Hygiene | Digital payments reduce the spread of germs compared to handling cash. | Handling cash and cards involves physical contact, which can spread germs. |
| International Use | Widely accepted in many countries, especially in Asia. | Cash and cards may not be universally accepted, and currency exchange is required in some cases. |
| Technology Dependence | Relies on smartphone battery and internet connectivity. | No technology dependence, although cards require active accounts. |
Contactless Payment War: QR Code vs. NFC
Let’s compare the two most popular eWallet app features, namely:
- QR code payments
- NFC mobile payments
Here’s a detailed comparison between the two contactless payment technologies:
| Features | QR Code Payments | NFC Payments |
| How it works | Scan the merchant’s QR code with camera, app confirms and transfers the funds. | Tap NFC-enabled smartphones on payment terminals, secure tokenization and funds transfer. |
| Accessibility | Wider only needs a smartphone with a camera. | Requires NFC-enabled smartphones and terminals. |
| Implementation cost for merchants | Lower only needs to generate QR codes. | higher and require NFC-enabled terminals. |
| Payment speed | Slower, involves scanning and app interaction. | Faster, tap and go with instantaneous communication. |
| Security | Secure encryption, but prone to phishing scams. | Strong encryption and tokenization for enhanced security. |
| Convenience | Requires opening the app and scanning the code. | Simply tap and go, no app interaction needed. |
| Flexibility | In-person, online, bill splitting, peer-to-peer. | Primarily in-person payments at NFC terminals. |
| Additional features | can integrate with loyalty programs and coupons. | No inherent additional features. |
| Best for | Wider accessibility, cost-effective for merchants, and online payments. | Faster transactions, high-traffic environments, and strong security. |
So, how do you like the contrast between QR-based eWallet apps and NFC payment apps? Speaking of which, let’s move on to the next section.
Can You Integrate QR Code Payment in the Existing eWallet?
Whether you want to create an eWallet app or have an existing digital wallet, QR code is an eWallet app feature to ponder over.
And if you are dealing with the latter case, don’t worry, because via application integration, a QR code is added to the platform.
So, the answer to the question above is YES.
But this brings us to a question.
Should we integrate a QR Code into the eWallet app?
This is an important feature to include, whether you want to create an app like Cash or you want to build a money transfer app.
Here are some reasons to consider this feature as your solution:
- Effortless Payments: No need to fumble with cards or cash. Simply scan a QR code to complete transactions quickly and seamlessly.
- Bill Splitting Made Easy: Conveniently divide bills among friends and family by scanning each other’s QR codes.
- Request Money Easily: Generate a personal QR code to receive payments from others without sharing sensitive account details.
- Secure Data Transmission: QR codes encrypt payment information, reducing the risk of fraud and identity theft. Adding to mobile app security
- Two-Factor Authentication: Many eWallets employ additional security measures for QR code payments, such as PINs or biometrics.
- Streamline Operations: Speed up checkout processes, reduce transaction fees, and simplify reconciliation.
- Wider Customer Reach: Accept payments from a broader range of customers, including those without traditional bank accounts.
- Digital Coupons and Loyalty Programs: Offer scannable QR codes for discounts, rewards, and personalized offers.
- Peer-to-Peer Payments: Facilitate money transfers between individuals directly within the eWallet.
- Offline Payments: Enable transactions even without internet connectivity
- IoT integration: QR code payments enable collaboration with various IoT-based systems.
- Global Acceptance: QR codes are widely adopted worldwide, especially in Asia and Europe.
Speaking of eWallet payment QR code and application integration, this brings us to…
Nimble AppGenie: Here to Help You with Your Payment QR Code Solution
Do you want to tap into the full power of QR code Wallet?
Nimble AppGenie is here to help you.
As a market-leading eWallet app development company, we can help you integrate innovative features like QR code, NFC payments, bill splitting, BNPL, and much more into your app.
Our app developers can make your platform the next best in the market. Don’t believe us?
We have done it before:
- Pay By Check– Pay by Check is a popular e-wallet mobile app in the United States of America. It allows users to transfer, pay, or even exchange currency.
- SatPay – An eWallet platform is a Versatile eWallet Platform that allows users to request, receive, and send payments without hassle.
- CUT– an E-wallet Mobile App, CUT is available in China and Myanmar. It works well with both RMB and MMK currencies.
- SatBorsa – a Currency Exchange Fintech app. SatBorsa is one of the platforms that is available on both platforms, iOS and Android.
Hire mobile app developers with Nimble AppGenie and experience true innovation.
We bring ideas to reality and turn good concepts into great apps. Contact us now.
Conclusion
eWallet QR code payments are experiencing significant global growth, with dynamic QR codes dominating the market.
The historical evolution of QR codes, initially invented by Denso Wave in the 1990s, showcases their transformative journey. Static QR codes excel in quick transactions, while dynamic QR codes offer enhanced security and insights.
The widespread adoption of QR codes in China and India has played a pivotal role in the rise of mobile payment services.
Businesses and users alike benefit from the convenience, security, and efficiency of QR code payments, making them a preferred choice in the evolving landscape of digital transactions.
FAQs
The benefits are plentiful! Here are just a few such as Convenience, Speed, Security, Rewards, and Data-driven insights.
Here’s how:
- Download the eWallet app
- Set up your account
- Explore the QR code features
Yes, eWallet QR code payments are safe when used with reputable providers and practiced with caution. Here are some tips:
- Only scan QR codes from trusted sources, like verified merchants.
- Avoid scanning random codes you find on posters or online.
- Keep your eWallet app updated with the latest security patches.
- Be mindful of your surroundings when making payments in public places.
The adoption of eWallet QR code payments is rapidly growing! You can use them at various places, including:
- Retail stores and supermarkets
- Restaurants and cafes
- Petrol pumps and pharmacies
- Taxis and public transportation
- Online shopping websites and mobile apps

Niketan Sharma is the CTO of Nimble AppGenie, a prominent website and mobile app development company in the USA that is delivering excellence with a commitment to boosting business growth & maximizing customer satisfaction. He is a highly motivated individual who helps SMEs and startups grow in this dynamic market with the latest technology and innovation.
Table of Contents




No Comments