Offline payments in eWallets are emerging as a crucial feature.
This capability is particularly important in regions with limited connectivity, ensuring that everyone can participate in the digital economy seamlessly.
While the name says it all, a lot more questions come to mind.
“How Does It Work?”
“Is There Actually a Need for Offline Payment?”
“Has Anyone Done This Before?”
Well, we have got you covered.
From offline mobile payments to advanced offline payment technology, this blog explores the intricacies of integrating offline payment solutions into eWallets, the benefits they offer, and the challenges involved in their implementation.
Discover how this innovation is paving the way for a more inclusive and accessible financial landscape.
Understanding Offline Payments in eWallets
Offline payments in eWallets are revolutionizing the digital payment landscape, offering users the ability to make transactions without needing a constant internet connection.
But what is it?
Offline Payment allows users to make payment transactions in areas with little to no internet connection.
Offline transactions in eWallets enable users to preload funds into their digital wallets.
This can then be used to make payments even when offline.
This is achieved through advanced offline payment technology that securely stores transaction data and synchronizes it once the device is back online.
The eWallet app’s offline mode is a feature that many mobile wallets with offline payments now include, addressing the needs of users in rural areas or regions with unstable internet connections.
These offline mobile payment solutions enhance the user experience by providing reliability and accessibility, regardless of the connectivity situation.
With offline payment solutions, eWallets offer a versatile payment method that meets the diverse needs of their users.
Understanding how offline digital payments work is crucial for businesses looking to develop an eWallet app.
This mode of payment not only broadens the usability of eWallets but also plays a significant role in promoting financial inclusion, especially in emerging markets.
How do Offline Payments Work in eWallets?
Offline payments work a little differently compared to traditional mobile payments.
Offline payments in eWallet function by enabling transactions without the need for real-time internet connectivity.
This is particularly beneficial in areas with poor or no internet access.
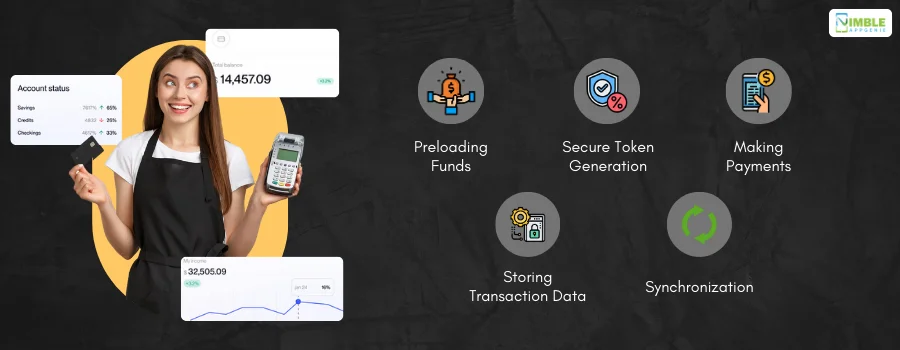
Here’s a breakdown:
1. Preloading Funds
Users preload a certain amount of funds into their mobile wallet’s offline payments system when they have internet access.
This preloaded balance is stored securely within the device.
2. Secure Token Generation
The eWallet app generates secure tokens for each potential transaction.
These tokens are encrypted and stored locally on the device, allowing for safe offline transactions in eWallets.
3. Making Payments
When making an offline payment, the user selects a preloaded balance.
The offline mobile wallet then uses a pre-generated token to authorize the transaction. This process ensures that the payment is secure even without an active internet connection.
4. Storing Transaction Data
All transaction details are stored securely on the user’s device until it reconnects to the internet.
This includes details of offline digital payments made.
5. Synchronization
Once the device reconnects to the internet, the offline wallet transaction data is synchronized with the server.
The eWallet app processes the transaction data, updates the user’s balance, and completes any necessary verifications.
This method ensures that users can continue to make payments seamlessly, regardless of their connectivity situation. This is a crucial feature for offline mobile wallet infrastructure, enhancing the overall user experience by providing continuous access to payment capabilities.
For businesses looking to integrate these capabilities, understanding the intricacies of offline payment technology is essential. Ensuring robust security measures, efficient data synchronization, and user-friendly interfaces are key components in the successful implementation of offline payment systems.
Technologies That Enable Offline Payments
We now know how offline payment works. But what makes it work? Well, let’s find out.
Offline payment technology encompasses a variety of advanced systems and methods designed to facilitate transactions without an active Internet connection.
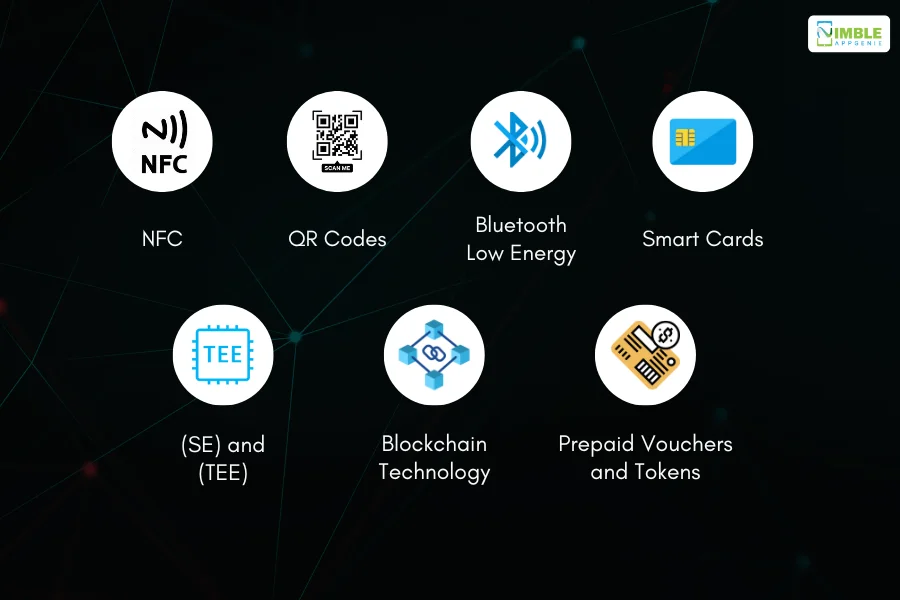
These technologies are crucial for enabling seamless offline transactions in eWallets and ensuring security and efficiency.
♦ NFC (Near Field Communication)
NFC mobile payment technology allows two devices to communicate when they are close to each other.
The technology is widely used in mobile wallets for offline payments, where users can tap their devices to make payments even when offline.
The NFC chip stores the necessary transaction data and completes the payment by generating a secure token.
♦ QR Codes
QR code payments are another popular method for offline digital payments.
Users scan a merchant’s QR code, which contains all the necessary transaction details. The offline mobile wallet can then process this payment using the preloaded funds.
♦ Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
BLE is used for short-range wireless communication.
It is effective in offline payment systems where the mobile wallet can connect with the merchant’s terminal to complete a transaction without needing an internet connection.
♦ Smart Cards
Smart cards with embedded chips can store payment information securely.
These cards can be used to make offline wallet transactions by transferring data to the merchant’s reader.
♦ Secure Elements (SE) and Trusted Execution Environment (TEE)
SE and TEE are critical components of offline payment mobile apps.
They provide a secure area within the device where sensitive data, such as payment credentials and transaction tokens, are stored and processed.
This ensures that offline payment technology remains secure even without real-time connectivity.
♦ Blockchain Technology
Blockchain can play a significant role in offline payment infrastructure.
Using decentralized ledgers, transactions can be securely recorded and verified without an active internet connection.
Once the device reconnects, these transactions are synchronized with the blockchain network.
♦ Prepaid Vouchers and Tokens
Prepaid vouchers or tokens are issued to users, which can be redeemed for goods and services.
These vouchers are particularly useful for offline digital payment options and help in scenarios where connectivity is an issue.
These technologies collectively ensure that offline eWallet payments are secure, efficient, and user-friendly. They enable offline mobile wallet features that enhance the overall user experience, making digital transactions more accessible in various environments.
Where Does Offline Payment Sit in a Modern Digital Wallet Infrastructure?
Offline payments in eWallets are becoming an integral part of modern digital wallet infrastructure, addressing the need for reliable and accessible payment methods in various environments.
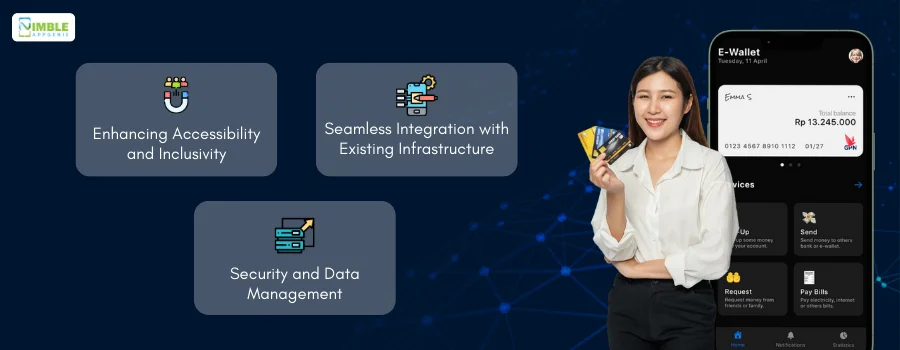
These solutions ensure that transactions can be completed without requiring an active internet connection, which is crucial for users in areas with unstable or no connectivity.
► Enhancing Accessibility and Inclusivity
Offline payments significantly enhance accessibility and inclusivity by allowing users in remote or underserved regions to participate in the digital economy.
This capability is essential for financial empowerment and economic growth in these areas, enabling individuals and businesses to conduct transactions without being hindered by connectivity issues.
Offline mobile wallet features are particularly beneficial in rural areas where internet access is often limited.
By facilitating offline e-wallet transactions, digital wallets promote greater financial inclusion and ensure that everyone can benefit from digital payment technologies.
► Seamless Integration with Existing Infrastructure
The integration of offline payments into existing digital wallet systems is designed to be seamless, ensuring that users can switch between online and offline modes without experiencing any disruption in their payment experience.
Offline payment systems are built to work harmoniously with the current digital wallet infrastructure, ensuring that transactions are processed efficiently and securely.
When the device reconnects to the internet, all offline wallet transactions are synchronized with the central server, validating and updating the user’s transaction history.
This process ensures that the convenience of offline mobile payments is maintained without compromising on security or efficiency.
► Security and Data Management
Security and data management are paramount when implementing offline payment technology.
Advanced security measures such as NFC, QR codes, and blockchain technology are employed to ensure that offline transactions are not only convenient but also secure.
These technologies protect user data and prevent fraud, making offline payment processing a reliable option.
When transactions are made offline, they are securely stored on the device and synchronized with the central server once connectivity is restored.
This ensures the integrity and accuracy of all transactions while maintaining user trust in the eWallet system.
Offline payments in eWallets thus play a crucial role in the modern digital payment ecosystem, enhancing accessibility, ensuring seamless integration with existing systems, and maintaining high-security standards. Businesses looking to develop an eWallet app should consider these aspects to provide a comprehensive and resilient financial solution to their users
Is There a Need for Offline Payments in 2025?
As we advance into 2025, the need for offline payments in eWallets continues to grow, driven by various factors that underscore their importance in the digital payment ecosystem.
Despite the proliferation of internet access globally, significant pockets remain where connectivity is unreliable or non-existent.

Offline mobile payments provide a crucial solution to bridge this gap, ensuring that digital transactions are inclusive and accessible to everyone, regardless of their connectivity status.
1. Bridging the Digital Divide
One of the primary reasons for the necessity of offline digital payments in 2024 is the ongoing digital divide.
According to eWallet market statistics, around 37% of the world’s population, or 2.9 billion people, still do not have access to the internet.
By offering offline payment solutions, eWallets can cater to users in these regions, allowing them to participate in the digital economy.
This is particularly important for achieving financial inclusion, as it enables individuals and businesses in these areas to conduct transactions without the need for a stable internet connection.
2. Enhancing User Convenience
In urban areas where internet connectivity is generally reliable, there are still scenarios where offline payment technology proves invaluable.
For instance, during travel, natural disasters, or network outages, having the ability to make offline transactions in eWallets ensures that users can continue to make payments seamlessly.
This enhances the overall user experience by providing reliability and convenience.
Therefore, ensuring user retention in the fintech app.
3. Support Emerging Markets
In emerging markets, the adoption of offline mobile wallet features is crucial for driving economic growth and financial inclusion.
These markets often face infrastructure challenges that make consistent internet access difficult.
By integrating offline payment systems, digital wallets can support the growth of local economies by enabling transactions even in the absence of internet connectivity.
For instance, a report by the World Bank highlights that only 45% of individuals in Sub-Saharan Africa have access to the internet, underscoring the need for offline payment solutions in these regions.
4. Future-Proofing Digital Wallets
As the digital payment landscape continues to evolve, the integration of offline payment solutions is becoming a standard requirement for modern eWallets.
By offering offline payment mobile apps, businesses can future-proof their digital wallets, ensuring that they remain relevant and competitive in an increasingly interconnected world.
This forward-thinking approach helps businesses attract and retain users who prioritize reliability and accessibility in their payment methods.
In conclusion, the need for offline payments in eWallets is evident as we move into 2025.
By addressing connectivity challenges, enhancing user convenience, supporting emerging markets, and future-proofing digital wallets, offline mobile payments play a crucial role in the modern digital payment infrastructure. For businesses looking to stay ahead of the curve, incorporating offline payment technology into their eWallet offerings is essential.
Benefits of Offline Payments (And Why Everyone Would Love It)
The advent of offline payment technology in eWallets has revolutionized the way we think about digital transactions.
As we continue to embrace the digital age, the ability to make payments without an active internet connection is not just a convenience; it’s a necessity.
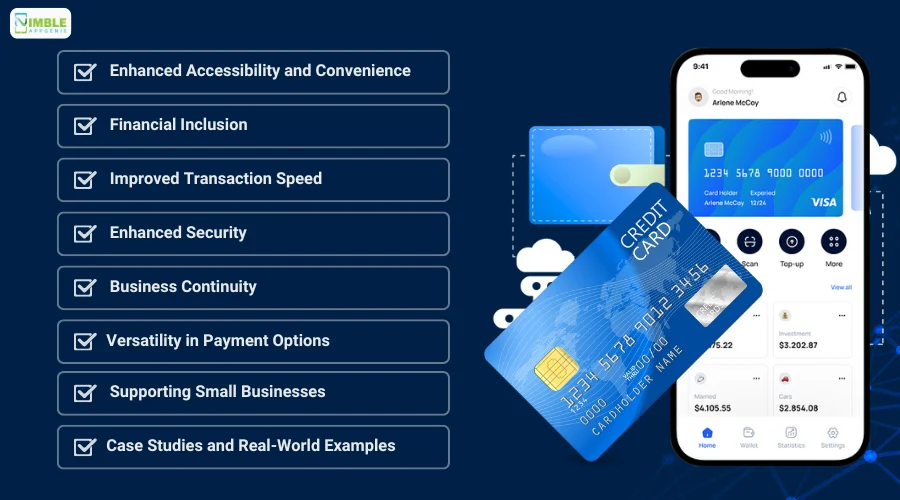
Here are some key benefits of offline payments in eWallets and why everyone would love this feature.
-
Enhanced Accessibility and Convenience
Offline payment eWallet technology ensures that users can make transactions anytime, anywhere, regardless of their internet connectivity.
This is particularly beneficial in regions with poor internet infrastructure or during travel in areas with no network coverage.
By allowing transactions to be processed offline, eWallets significantly enhance user convenience and accessibility.
-
Financial Inclusion
Offline mobile payments play a crucial role in promoting financial inclusion, especially in rural and underserved areas.
According to the World Bank, about 1.7 billion adults remain unbanked, with many of them residing in regions with limited internet access.
Offline eWallets payments can bridge this gap, enabling these individuals to participate in the digital economy, thereby fostering economic growth and reducing poverty.
-
Improved Transaction Speed
One of the standout benefits of offline payment solutions is the speed of transactions.
Since these transactions do not rely on real-time internet connectivity, they are processed almost instantaneously.
This can be a significant advantage in retail environments where quick transaction times can enhance the customer experience and reduce wait times.
-
Enhanced Security
Offline payment systems can enhance transaction ewallet security.
By preloading funds and generating secure tokens for transactions, eWallets can reduce the risk of fraud and data breaches.
Offline mode limits exposure to online threats, making it a secure option for users concerned about the safety of their financial data.
-
Business Continuity
For businesses, especially those in the retail and service industries, the ability to accept offline transactions eWallets ensures continuity during network outages or connectivity issues.
This capability can prevent loss of sales and maintain customer satisfaction even during unexpected downtimes.
-
Versatility in Payment Options
Offline digital payments offer versatility in payment options, supporting various use cases from small peer-to-peer transactions to larger retail purchases.
This flexibility makes offline payment features an attractive option for both consumers and businesses, enhancing the overall utility of eWallets.
-
Supporting Small Businesses
For small businesses, particularly those in emerging markets, offline mobile wallet features can be a game-changer. It allows these businesses to accept digital payments even in areas with unreliable internet, broadening their customer base and improving sales. This is particularly relevant for markets like Sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia, where internet penetration is still growing.
-
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Several eWallets have successfully integrated offline payment capabilities, demonstrating the practical benefits of this technology.
For example, M-Pesa, widely used in Kenya, offers offline payment options that have greatly enhanced financial inclusion in rural areas.
Similarly, Alipay’s offline payment solutions have revolutionized transactions in regions with limited connectivity, ensuring that users can always access their funds and make payments.
Challenges in Implementing Offline Payment
Implementing offline payments in eWallets presents several challenges that need to be addressed to ensure a seamless and secure user experience.
Despite the numerous benefits, these challenges can pose significant obstacles if not managed properly.

Here are the main challenges and their potential solutions:
1] Security Concerns
One of the primary challenges in implementing offline payment solutions is ensuring security.
When transactions occur without real-time connectivity, there’s a risk of fraud and data breaches.
Offline transactions rely on pre-generated tokens and stored data, which can be susceptible to tampering if not adequately protected.
Solution: Implement robust encryption methods and secure storage solutions to mitigate these risks. In addition to this, incorporating offline payment security measures such as biometric authentication (fingerprints, facial recognition) can further enhance protection against unauthorized access. Regular security audits and updates can also help in identifying and rectifying vulnerabilities in the system.
2] Limited Transaction Capabilities
Offline payment systems have inherent limitations on transaction amounts and frequency to prevent potential abuse.
This can be a barrier for users who need to make larger or more frequent purchases.
Solution: Develop smart algorithms that dynamically adjust transaction limits based on user behavior and risk profiles. Implement tiered usage policies where verified users with a history of reliable transactions are allowed higher limits. This can balance security and usability, enhancing the offline payment user experience.
3] Data Synchronization
Ensuring accurate and timely data synchronization once the device reconnects to the internet can be complex.
Inconsistencies in synchronization can lead to discrepancies in account balances and transaction histories, undermining user trust.
Solution: Use reliable and efficient synchronization protocols to maintain the integrity of offline wallet transactions. Implement conflict resolution strategies to handle discrepancies, such as timestamping transactions and prioritizing the latest data. Ensure that the app can handle multiple pending transactions efficiently and securely update the central server when connectivity is restored.
4] Infrastructure Requirements
Implementing offline payment technology requires a robust infrastructure capable of handling secure token generation, data storage, and synchronization.
This infrastructure needs to be scalable and resilient to support a large number of users and transactions.
Solution: Invest in scalable cloud infrastructure and edge computing to manage the load and ensure resilience. Utilize microservices architecture to ensure that different components of the eWallet can be updated independently and scaled as needed. Regularly test the infrastructure under various conditions to ensure it can handle peak load and connectivity issues.
5] User Adoption and Education
Users may be unfamiliar with the concept of offline payments and may be hesitant to adopt it due to security concerns or a lack of understanding.
Solution: Provide comprehensive user education and support to encourage adoption. This can include in-app tutorials, FAQs, and customer support. Highlight the security measures in place and the benefits of offline payments, such as accessibility and convenience. Engaging in marketing campaigns and user testimonials can also help in building trust and encouraging adoption.
By addressing these challenges with innovative solutions, businesses can effectively implement offline payments in eWallets, providing a seamless and secure experience for users.
Case Study: Successful eWallet Offline Payment
Implementing offline payment solutions in eWallets has proven successful in various parts of the world, demonstrating both the feasibility and the significant benefits of this technology.

Below are real-world examples of top eWallet apps that have successfully integrated offline payment capabilities.
► M-Pesa: Revolutionizing Mobile Payments in Kenya
M-Pesa, operated by Safaricom in Kenya, is one of the most well-known examples of a mobile payment system that includes offline capabilities.
M-Pesa allows users to deposit, withdraw, transfer money, and pay for goods and services using a mobile device.
The system works even in areas with limited or no internet connectivity, making it highly accessible to users in rural regions.
- Implementation: M-Pesa uses SMS-based transactions to facilitate offline payments. Users can perform transactions using simple text messages, which are then processed by the system once connectivity is available.
- Impact: This capability has significantly enhanced financial inclusion in Kenya, where about 83% of the adult population uses M-Pesa for their financial transactions. It has transformed the lives of millions by providing them access to digital financial services, irrespective of their internet connectivity.
Solution Highlights: Leveraging SMS technology for offline transactions ensures accessibility and broad adoption, especially in areas with poor connectivity.
► AliPay: Expanding Reach with Offline QR Code Payments
AliPay, a major player in the Chinese mobile payment market, has also integrated offline payment features.
AliPay users can make payments by scanning QR codes, even when they are offline. This is particularly useful in busy markets and rural areas where internet connectivity can be inconsistent.
- Implementation: AliPay allows users to generate and scan QR codes that contain payment information. Transaction details are stored securely on the device and processed once the user goes online.
- Impact: Alipay’s offline payment feature has been instrumental in expanding its reach across China, including in less urbanized areas. This has enabled small businesses and street vendors to accept digital payments, enhancing their customer base and revenue.
Solution Highlight: Using QR codes for offline payments simplifies the process and ensures secure transactions without the need for real-time internet access.
► Mastercard PayPass: Enhancing Retail Payments
Mastercard’s PayPass technology is an excellent example of integrating offline capabilities into retail payments.
PayPass enables users to make contactless payments using NFC technology, which works even when there is no active internet connection.
- Implementation: PayPass uses NFC to store transaction details and authorize payments offline. The transaction data is encrypted and stored on the device until it can be synchronized with the server.
- Impact: This technology has been widely adopted in retail environments, allowing for quick and efficient transactions that improve the customer experience. It has also helped retailers reduce queue times and enhance operational efficiency.
Solution Highlights: NFC technology provides a seamless and secure offline payment solution, particularly useful in high-traffic retail environments.
Nimble AppGenie: Your Partner in eWallet Innovation
As a leading eWallet app development company, Nimble AppGenie is at the forefront of transforming digital payment systems with cutting-edge technology and innovative solutions.
We specialize in developing robust, secure, and user-friendly eWallet applications that cater to diverse financial needs, including offline payment capabilities.
Our team of experts leverages the latest advancements in AI, blockchain, and IoT to create eWallets that are not only efficient but also future-proof.
Nimble AppGenie’s comprehensive approach ensures that all aspects of eWallet development, from design and implementation to security and user experience, are meticulously addressed.
Whether you’re looking to start an eWallet business with advanced features, Nimble AppGenie is your ideal partner.
We are committed to delivering excellence and driving innovation in the fintech landscape.
Conclusion
The integration of offline payments in eWallets represents a significant step towards achieving financial inclusion and accessibility.
By leveraging advanced technologies like AI, blockchain, and IoT, offline payment solutions ensure that users can transact seamlessly, regardless of their connectivity status.
As digital wallets continue to evolve, incorporating offline capabilities will be essential in addressing the diverse needs of users worldwide.
Businesses looking to stay ahead in the fintech space must consider the benefits and challenges of offline payment systems to deliver comprehensive and resilient financial solutions.
FAQs
Offline payments in eWallets allow users to complete transactions without an active internet connection. Funds are preloaded and secure tokens are generated for transactions that are synchronized with the server once the device reconnects.
Offline payments enable individuals in areas with limited internet access to participate in the digital economy, fostering financial inclusion and economic growth, particularly in underserved and rural regions.
Technologies such as NFC, QR codes, blockchain, and AI support offline payments by providing secure and efficient methods to process and store transactions until they can be synchronized with the central server.
Yes, offline payments are secure. They use robust encryption, secure token generation, and sometimes biometric authentication to ensure the safety of transactions, even without real-time connectivity.
Challenges include ensuring transaction security, managing data synchronization, and developing a robust infrastructure to support offline capabilities. Addressing these challenges requires advanced technology and strategic planning.
Examples of eWallets supporting offline payments include M-Pesa, AliPay, and Mastercard’s PayPass, each utilizing different technologies like SMS, QR codes, and NFC to facilitate transactions.
Offline payments allow small businesses, especially in regions with poor connectivity, to accept digital payments, expanding their customer base and improving sales without the dependency on a stable internet connection.
Future trends include the integration of AI for enhanced fraud detection, blockchain for secure transaction recording, and IoT for enabling smart devices to independently process payments offline.

Niketan Sharma is the CTO of Nimble AppGenie, a prominent website and mobile app development company in the USA that is delivering excellence with a commitment to boosting business growth & maximizing customer satisfaction. He is a highly motivated individual who helps SMEs and startups grow in this dynamic market with the latest technology and innovation.
Table of Contents





No Comments
Comments are closed.