Understanding the distinctions between eWallets, payment gateways, and payment processors is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize their payment systems.
These technologies play unique roles in facilitating secure, efficient, and seamless transactions.
Whether you’re an online retailer, service provider, or brick-and-mortar store, choosing the right payment solution can enhance the customer experience and streamline your operations.
This blog delves into the evolution of digital payments, defines each component, and provides a detailed comparison to help you make an informed decision.
So let’s get right into it, starting with:
The Age of Digital Payments: Evolution
The journey to modern digital payments has been marked by significant milestones and innovations.
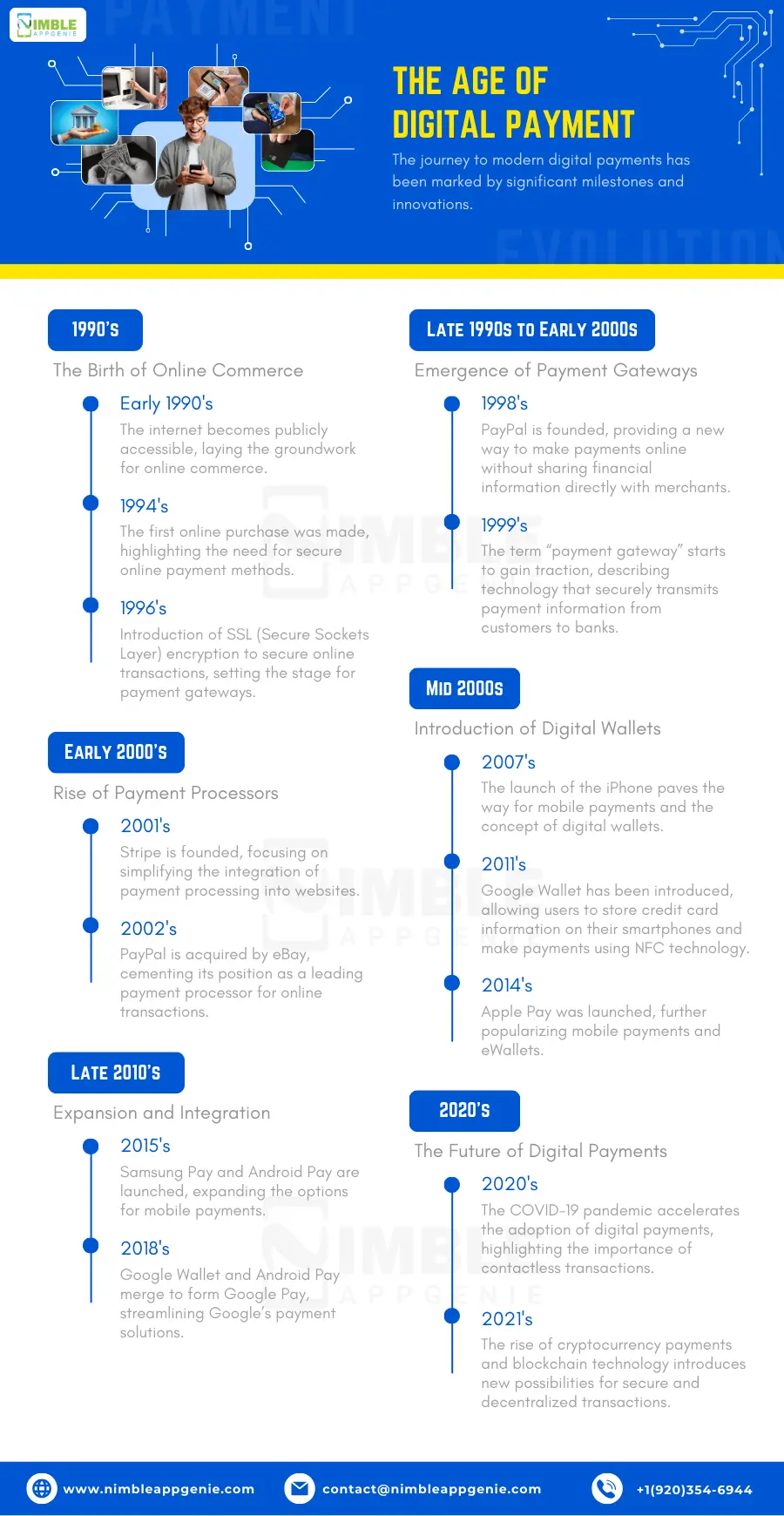
Here’s a timeline highlighting key developments that led to the creation and evolution of payment gateways, processors, and digital wallets.
♦ 1990s: The Birth of Online Commerce
- Early 1990s: The internet becomes publicly accessible, laying the groundwork for online commerce.
- 1994: The first online purchase was made, highlighting the need for secure online payment methods.
- 1996: Introduction of SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) encryption to secure online transactions, setting the stage for payment gateways.
♦ Late 1990s to Early 2000s: Emergence of Payment Gateways
- 1998: PayPal is founded, providing a new way to make payments online without sharing financial information directly with merchants.
- 1999: The term “payment gateway” starts to gain traction, describing technology that securely transmits payment information from customers to banks.
♦ Early 2000s: Rise of Payment Processors
- 2001: Stripe is founded, focusing on simplifying the integration of payment processing into websites.
- 2002: PayPal is acquired by eBay, cementing its position as a leading payment processor for online transactions.
♦ Mid 2000s: Introduction of Digital Wallets
- 2007: The launch of the iPhone paves the way for mobile payments and the concept of digital wallets.
- 2011: Google Wallet is introduced, allowing users to store credit card information on their smartphones and make payments using NFC (Near Field Communication) technology.
- 2014: Apple Pay was launched, further popularizing mobile payments and eWallets.
♦ Late 2010s: Expansion and Integration
- 2015: Samsung Pay and Android Pay are launched, expanding the options for mobile payments.
- 2018: Google Wallet and Android Pay merge to form Google Pay, streamlining Google’s payment solutions.
♦ 2020s: The Future of Digital Payments
- 2020: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of digital payments, highlighting the importance of contactless transactions.
- 2021: The rise of cryptocurrency payments and blockchain technology introduces new possibilities for secure and decentralized transactions.
The evolution of digital payments has been driven by technological advancements and changing consumer needs.
From the early days of the internet to the sophisticated payment systems we have today, each development has played a crucial role in shaping the digital payment landscape.
Understanding this timeline helps businesses and consumers appreciate the functionalities and advantages of a payment gateway vs wallet, payment processor vs. a gateway, and the integrated ecosystem they create for seamless online transactions.
What is eWallet?
An eWallet, or digital wallet, is a software-based system that securely stores users’ payment information and passwords for numerous payment methods and websites.
Using eWallet, users can complete purchases easily and quickly with near-field communications (NFC) payment technology. eWallets are used for online transactions and in-store purchases, providing a convenient, contactless way to pay.
E-Wallets function by storing the user’s payment information, such as credit card or bank account details, and facilitating payments through encrypted connections.
They offer a layer of security by ensuring that the user’s financial information is not directly shared with merchants.
This reduces the risk of data breaches and fraud.
Moreover, these eWallets are integrated with loyalty programs, allowing users to earn and redeem points effortlessly.
They can store various types of information, including coupons, tickets, and boarding passes.
Thus, making them a versatile tool for both consumers and businesses.
► Key Features
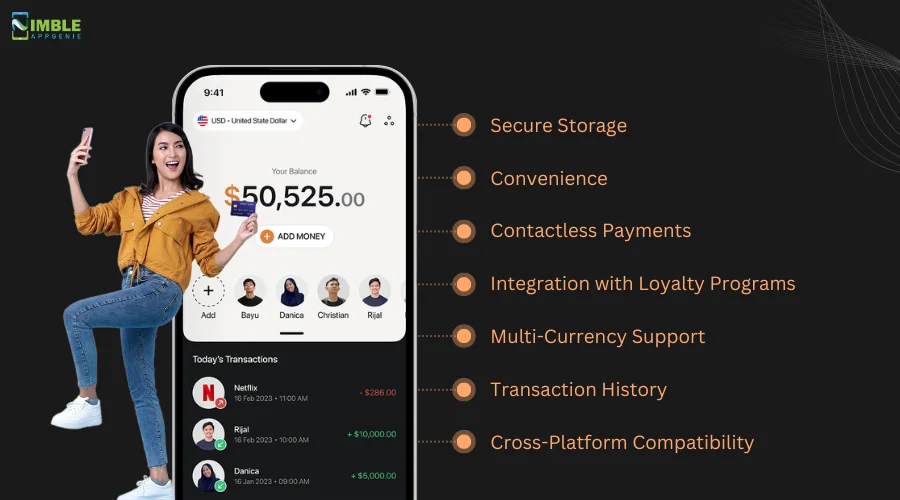
Here are the key features of an eWallet app.
- Secure Storage: eWallets encrypt and securely store users’ payment information, reducing the risk of fraud.
- Convenience: They enable quick and easy transactions, both online and in physical stores, through a single application.
- Integration with Loyalty Programs: eWallets can store and manage loyalty points, coupons, and rewards, enhancing the shopping experience.
- Multi-Currency Support: Many eWallets support multiple currencies, making them ideal for international transactions.
- Transaction History: Users can track their spending and manage finances more effectively with detailed transaction histories.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: eWallets can be used across various devices, including smartphones, tablets, and wearables.
► Who is it for?

eWallets are designed for a wide range of users, including:
- Consumers: Individuals looking for a convenient and secure way to manage their payments, earn rewards, and keep track of their spending.
- Businesses: Merchants who want to offer their customers an easy and secure payment option, enhance the shopping experience, and leverage loyalty programs.
- Travelers: People who travel frequently and need a secure, multi-currency payment solution.
- Online Shoppers: Individuals who frequently shop online and require a seamless payment method that also offers enhanced security.
► Popular Examples

Now, it’s time to look at some of the popular eWallet platforms.
- PayPal: One of the most widely used digital wallets, PayPal allows users to store multiple payment methods and make transactions online and in-store.
- Apple Pay: Integrated with iOS devices, Apple Pay offers secure, contactless payments using NFC technology.
- Google Pay: Available on Android devices, Google Pay combines payment information storage with loyalty program integration and offers both online and in-store payment capabilities.
- Samsung Pay: Known for its extensive compatibility with various payment terminals, Samsung Pay supports both NFC and MST (Magnetic Secure Transmission) technologies.
- Venmo: A subsidiary of PayPal, Venmo is popular among younger users for its social features and easy peer-to-peer payments.
By understanding the definition, key features, and target audience of eWallets, businesses. Consumers can better appreciate their role in the digital payment ecosystem and make informed decisions about which eWallet solutions best meet their needs.
What is a Payment Gateway?
A payment gateway is a technology that facilitates the transfer of payment information from a customer to a merchant’s bank account.
It acts as an intermediary between the merchant and the financial institution involved in a transaction, ensuring that sensitive payment data is securely transmitted and processed.
Payment gateway integration is essential for online transactions, providing the infrastructure needed to authorize payments and manage the transfer of funds.
Payment gateways work by encrypting sensitive information such as credit card numbers, ensuring that the data is passed securely between the customer, the merchant, and the acquiring bank.
When a customer makes a purchase, the payment gateway validates the payment details, checks for available funds, and processes the transaction.
It then communicates the approval or denial back to the merchant and customer.
► Key Features
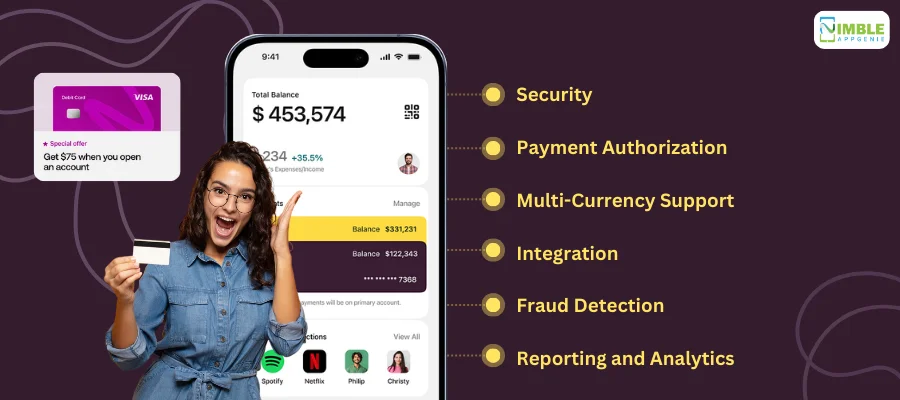
- Security: Payment gateways employ encryption and tokenization to protect sensitive payment information during transmission, reducing the risk of fraud.
- Payment Authorization: They validate payment information and authorize transactions in real-time, ensuring funds are available and the payment method is valid.
- Multi-Currency Support: Many gateways support multiple currencies, enabling international transactions and global commerce.
- Integration: Payment gateways can integrate with various e-commerce platforms, shopping carts, and point-of-sale systems, offering flexibility and ease of use.
- Fraud Detection: Advanced fraud detection tools and algorithms help identify and prevent fraudulent transactions, protecting both merchants and customers.
- Reporting and Analytics: They provide detailed reports and analytics, helping businesses monitor transactions, manage chargebacks, and gain insights into payment trends.
► Who is it for?

Payment gateways are essential for:
- E-commerce Businesses: Online retailers who need to securely process payments from customers worldwide.
- Brick-and-Mortar Stores: Physical stores that accept card payments and want to ensure secure transactions.
- Service Providers: Businesses offering online services, subscriptions, or digital products that require efficient payment processing.
- Nonprofits and Charities: Organizations that accept donations online and need a secure way to process these transactions.
- Small Businesses: Entrepreneurs and small businesses that sell products or services online and need a reliable payment processing solution.
► Popular Examples

- PayPal: Known for its ease of use and security, PayPal is widely used by businesses of all sizes to process online payments.
- Stripe: A popular choice for developers, Stripe offers robust APIs and tools for integrating payment processing into websites and mobile apps.
- Square: Square provides a comprehensive suite of payment solutions for both online and in-person transactions, making it ideal for small and medium-sized businesses.
- Authorize.Net: A reliable and secure payment gateway that supports a wide range of payment methods and currencies.
- Adyen: Used by many large enterprises, Adyen offers a global payment solution with advanced fraud prevention and multi-currency support.
Understanding what a payment gateway is, along with its key features and target audience, helps businesses choose the right solution for their payment processing needs. This ensures secure, efficient, and smooth transactions, enhancing the overall customer payment experience.
What is a Payment Processor?
The payment processor is a company that handles the technical aspects of processing credit and debit card transactions.
It acts as an intermediary between the merchant and the financial institutions involved in the transaction.
Payment processors are responsible for ensuring that the transaction data is securely transmitted from the merchant to the acquiring bank, and then to the issuing bank for authorization.
They play a crucial role in the completion of electronic transactions, making sure that funds are transferred correctly and efficiently.
Payment processors manage the communication and data transfers involved in the authorization, clearing, and settlement of transactions.
When a customer makes a purchase, the payment processor handles the transaction data, checking for sufficient funds, and ensuring that the transaction is approved by the card issuer.
They also handle the settlement process, which involves transferring the funds from the customer’s bank to the merchant’s account.
► Key Features

- Transaction Authorization: Payment processors verify the validity of the transaction, checking for sufficient funds and approving or declining the transaction based on the card issuer’s response.
- Settlement Services: They manage the settlement process, ensuring that funds are transferred from the customer’s account to the merchant’s account.
- Data Security: Payment processors implement security measures such as encryption and tokenization to protect sensitive transaction data and prevent fraud.
- Compliance: They ensure compliance with industry standards such as PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) to safeguard cardholder information.
- Chargeback Management: Payment processors assist merchants in handling chargebacks, providing tools and support to dispute fraudulent or erroneous transactions.
- Integration: They offer integration capabilities with various point-of-sale systems, e-commerce platforms, and payment gateways to streamline the payment process.
► Who is it for?

Payment processors are essential for:
- E-commerce Businesses: Online retailers who need a reliable solution to handle card transactions and ensure secure payments.
- Brick-and-Mortar Stores: Physical stores that accept card payments and require an efficient transaction processing system.
- Service Providers: Businesses offering services that involve recurring payments or subscriptions, requiring consistent and secure processing.
- Restaurants and Hospitality: Establishments that need to process a high volume of card transactions quickly and efficiently.
- Nonprofits and Charities: Organizations that accept donations via credit or debit cards and need a secure processing solution.
► Popular Examples
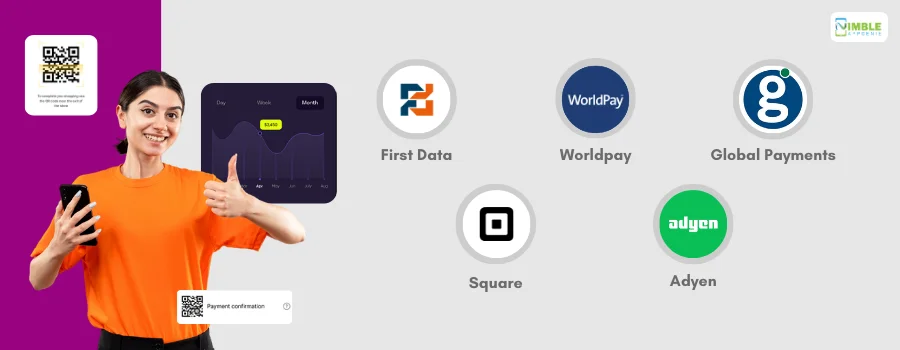
- First Data: One of the largest payment processors offering a range of services including transaction authorization, settlement, and data security.
- Worldpay: Provides comprehensive payment processing solutions for both online and in-person transactions, supporting a wide range of payment methods.
- Global Payments: A leading provider of payment technology services, offering secure and efficient processing for businesses of all sizes.
- Square: Known for its ease of use and versatility, Square provides payment processing solutions for small and medium-sized businesses, both online and offline.
- Adyen: A global payment company offering a seamless payment experience with robust security measures and support for multiple currencies.
By understanding the role, key features, and target audience of payment processors, businesses can choose the right solution to handle their card transactions effectively. This ensures smooth and secure payment processing, enhancing the overall customer experience.
eWallet vs Payment Gateway vs Payment Processor: Complete Comparison
Digital payments have revolutionized how businesses operate and how consumers make purchases.
To fully understand the landscape, it’s crucial to differentiate between eWallets, payment gateways, and payment processors, as each serves a unique function within the digital payment ecosystem.
Here, we compare these three components across various parameters to provide a comprehensive understanding.
| Parameter | eWallet | Payment Gateway | Payment Processor |
| 1. Definition | Software-based payment system | Technology for transmitting payment data | Company handling transaction processing |
| 2. Functionality | Stores and facilitates payments | Authorizes and encrypts transactions | Manages communication and settlement |
| 3. Target Users | Consumers, businesses, travelers | E-commerce businesses and online services | Retailers, service providers, non-profits |
| 4. Key Features | Secure storage and payments | Real-time authorization and fraud detection | Transaction authorization and chargeback management |
| 5. Security | Encryption and biometric authentication | End-to-end encryption and tokenization | Secure data transmission and regular audits |
| 6. Cost | Free for consumers, integration fees | Transaction and setup fees | Transaction fees and additional charges |
| 7. Integration | Mobile apps, websites, POS systems | E-commerce platforms and shopping carts | POS systems and e-commerce platforms |
| 8. Transaction Speed | Instant transactions | Real-time authorization | Real-time authorization and settlement |
Your Partner in Payment Solutions – Nimble AppGenie
At Nimble AppGenie, we specialize in developing cutting-edge payment solutions tailored to your business needs.
Whether you require an eWallet, payment gateway, or a payment processor, our team of experts is here to help you navigate the complexities of digital payments.
With our extensive experience in fintech, we provide secure, scalable, and efficient solutions that enhance your customer’s payment experience and boost your business growth.
As a leading eWallet app development company, we integrate advanced security measures and seamless integration capabilities to ensure your transactions are fast, secure, and reliable.
Partner with Nimble AppGenie to take advantage of the latest technologies and stay ahead in the competitive market.
Let us help you create a payment system that meets your specific requirements and exceeds your expectations.
Conclusion
Navigating the landscape of digital payments requires a clear understanding of the roles and benefits of eWallets, payment gateways, and payment processors. Each serves a specific purpose, from enhancing user convenience to ensuring secure transaction processing. By evaluating your business needs, security requirements, cost implications, and integration capabilities, you can choose the right solution that aligns with your goals.
FAQs

Niketan Sharma is the CTO of Nimble AppGenie, a prominent website and mobile app development company in the USA that is delivering excellence with a commitment to boosting business growth & maximizing customer satisfaction. He is a highly motivated individual who helps SMEs and startups grow in this dynamic market with the latest technology and innovation.
Table of Contents





No Comments
Comments are closed.