Online payments are the norm of industry 4.0 and our time in general. Whether you talk about full-fledged payment-based fintech mobile apps or others that require payment, PCI compliance is important. So, what’s exactly PCI compliance mobile app?
Well, PCI DSS is a common compliance standard in the world of financial technology. It’s commonly used in all kinds of fintech development.
But it’s not something that we can summarize in one para. Let’s discuss everything regarding PCI compliance. So, without further ado, let’s get right into this:
What is the PCI Compliance Mobile App, Exactly?

To understand what a PCI compliance mobile app is, let’s first read about PCI DSS.
The Term PCI DSS refers to the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard. As such it is “very” prescriptive technical standard. PCI compliance is focused around protecting credit card/debit card details, something also known as “cardholder data” in industrial terms.
So, in layman’s terms, the main goal of PCI DSS compliance is to avoid fraud and financial crimes. This is done by ensuring that all the Fintech development companies who are dealing with this data maintain PCI compliance.
Considering the fact that cyber crimes at increasing at unbelievable rate, resulting in the loss of billions each year, this is more important than ever.
This is also why PCI compliance is mainly based around the tech world. As such, you can often see PCI compliance in mobile app development. To make sure fintech apps and other solutions meet the PCI DSS requirement checklist, a compliance manager is set in place.
PCI Compliance Breakdown: Requirement Levels
So, there are different levels of PCI Compliance. While regardless of level, compliance is an absolute must for PCI development, it’s still a good idea to learn about these PCI development levels. Therefore, with this being said, let’s look at each and every requirement.
► PCI Development Requirement 3: Protect Stored Cardholder Data
PCI DSS Requirement 3 focuses on the protection of stored cardholder data. Organizations must take measures to ensure that this data is kept safe and secure at all times.
3.1: Keep Cardholder Data Storage to a Minimum
Requirement 3.1 states that merchants must keep cardholder data storage to a minimum by implementing data retention and disposal policies. This means that merchants should only store the data they absolutely need, and should dispose of it as soon as it is no longer required. By doing so, merchants can reduce their risk exposure and minimize the amount of data that is at risk in the event of a breach.
3.2: Encrypt All Stored Cardholder Data
Requirement 3.2 states that merchants must encrypt all stored cardholder data. This includes data at rest, as well as data in transit. Encryption is a key component of protecting sensitive data, as it makes the data unreadable and unusable to anyone who does not have the proper decryption key. Merchants should use industry-standard encryption methods to protect their stored cardholder data.
3.3: Mask Cardholder Data
Requirement 3.3 requires merchants to mask all cardholder data, with the exception of the first six and last four digits. This means that merchants must conceal the majority of the cardholder data, while still being able to identify the card for the purpose of transactions. Masking can be accomplished by using an algorithm to replace the middle digits of the card number with asterisks or other symbols.
3.4: Use Strong Cryptography and Security Protocols
Requirement 3.4 requires that merchants use strong cryptography and security protocols, such as SSL/TLS, to protect cardholder data during transmission over open, public networks. This means that merchants should use encryption and other security measures to ensure that data is protected when it is transmitted over the internet or other public networks. Merchants should also ensure that their security protocols are up to date and comply with industry standards.
3.5: Monitor and Test Networks for Vulnerabilities
Requirement 3.5 requires that merchants regularly monitor and test their networks for vulnerabilities. This means that merchants should conduct regular vulnerability scans and penetration tests to identify any weaknesses in their systems. Merchants should also ensure that they have a process in place to remediate any vulnerabilities that are identified.
3.6: Have a Process in Place for Responding to Security Incidents
Requirement 3.6 requires that merchants have a process in place for responding to security incidents. This means that merchants should have a plan in place for detecting and responding to security incidents, including a process for reporting incidents to the appropriate parties. Merchants should also have a plan in place to notify customers and other stakeholders in the event of a breach.
► PCI Development Requirement 4: Encryption
PCI DSS Requirement 4 focuses on encryption.
4.1: Use Strong Encryption for Transmission of Cardholder Data
Requirement 4.1 requires that merchants use strong encryption to protect all transmission of cardholder data over open, public networks. This means that merchants should use industry-standard encryption methods to protect cardholder data whenever it is transmitted over the internet or other public networks.
4.2: Use Strong Encryption for Non-Console Administrative Access
Here, merchants use strong encryption to protect all non-console administrative access. This means that merchants should use encryption and other security measures to protect administrative access to their systems, including remote access.
► PCI Development Requirements 6: Secure Systems and Applications
PCI DSS Requirement 6 focuses on developing and maintaining secure systems and fintech applications.
6.1: Protect Systems and Software from Known Vulnerabilities
Requirement 6.1 requires that merchants ensure that all system components and software are protected from known vulnerabilities. This means that merchants should have a process in place for identifying and patching known vulnerabilities in their systems and software.
6.2: Securely Configure Systems and Software
Moving on, in this level of standard merchants ensure that all system components and software are securely configured. This means that merchants should ensure that all default passwords and configurations are changed, unnecessary services are disabled, and other security measures are implemented to reduce the risk of exploitation.
6.3: Develop and Maintain Secure Applications
Requirement 6.3 requires that merchants develop and maintain secure fintech applications. This means that merchants should use secure coding practices and implement security measures to protect their applications from exploitation.
6.4: Test Applications for Vulnerabilities
Requirement 6.4 requires that merchants test their applications for vulnerabilities. This means that merchants should conduct regular vulnerability scans and penetration tests to identify any weaknesses in their applications.
6.5: Protecting Web-Facing Applications Against Known Attacks
Requirement 6.5 requires that merchants ensure that all web-facing applications are protected against known attacks. This means that merchants should implement security measures to protect their web applications from common attacks, such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS).
6.6: Review and Assess Custom Code
Requirement 6.6 requires that merchants implement a process for reviewing and assessing custom code before it is implemented. This means that merchants should have a process in place for identifying and mitigating security risks associated with custom code, such as code injection attacks.
With this out of the way, let’s see why is PCI compliance actually important for
Why PCI Compliance is Important for Fintech Apps?

So, is how is PCI compliance for software developers? Well, this is inarguably one of the most important compliance in the tech world. Why? Let’s see:
♦ Protecting Sensitive Financial Information
Fintech apps have revolutionized the financial industry, providing users with convenient and efficient ways to manage their finances anytime, anywhere. However, with this convenience comes the need for strong security measures to protect users’ sensitive financial information. This is where PCI compliance comes in.
By complying with PCI mobile payment acceptance security guidelines, fintech apps or any other PCI compliance mobile app can assure their users that their data is safe and secure.
♦ Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with PCI standards can result in severe consequences, including fines and legal liability. Additionally, a security breach can result in the loss of trust among users, potentially damaging the reputation of the app and causing users to switch to competitors.
This is why it is crucial to build PCI compliance mobile app and invest in robust security measures to protect their users’ financial information.
♦ Building Trust and Loyalty
As such, PCI compliance mobile apps can set themselves apart from competitors and establish themselves as trustworthy and reliable platforms for managing finances. This can help build trust and loyalty among users, ultimately leading to increased usage and revenue for the app.
All in all, PCI compliance is not just important, but essential for fintech apps that deal with sensitive financial information. It not only ensures the security of user data but also helps build trust and loyalty among users. By prioritizing PCI compliance, fintech apps can provide their users with peace of mind and establish themselves as leaders in the industry.
How To Make A Fintech Mobile App PCI Compliant?
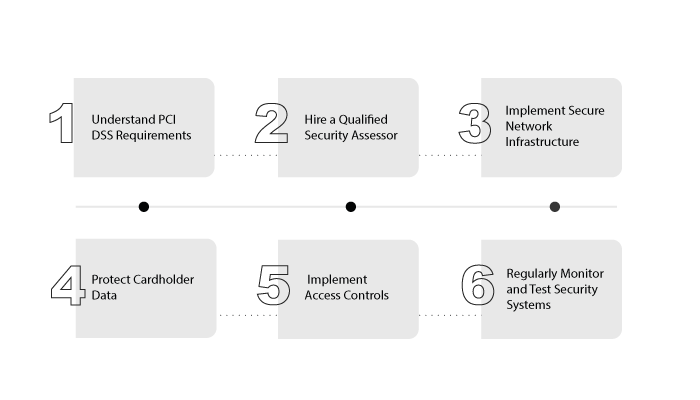
So, how do you create a PCI compliance mobile app or fintech app? Well, it’s not all that difficult. Let’s see why are the steps to do so.
Step 1: Understand PCI DSS Requirements
The first step to making your fintech mobile app PCI compliant is to understand the PCI DSS requirements. There are twelve requirements that businesses must follow to be PCI DSS compliant. These requirements cover areas such as network security, data protection, and access control.
Step 2: Hire a Qualified Security Assessor
To ensure that your fintech mobile app is PCI compliant, you should hire a qualified security assessor. A qualified security assessor is a professional who has been certified by the PCI Security Standards Council to assess and validate PCI compliance.
Step 3: Implement Secure Network Infrastructure
One of the key requirements of PCI DSS is to have a secure network infrastructure. This includes using firewalls, encrypting data in transit, and segmenting networks. You should also ensure that your app is hosted on a secure server and that access to the server is restricted.
Step 4: Protect Cardholder Data
Another key requirement of PCI DSS is to protect cardholder data. This includes encrypting cardholder data when it is stored and transmitted, limiting access to cardholder data, and regularly monitoring and testing your security systems.
Step 5: Implement Access Controls
Access controls are essential to ensuring that only authorized individuals have access to cardholder data. This includes using strong passwords, two-factor authentication, and limiting access to cardholder data on a need-to-know basis.
Step 6: Regularly Monitor and Test Security Systems
Regularly monitoring and testing your security systems is essential to ensuring that your fintech mobile app remains PCI compliant. This includes performing regular vulnerability scans, penetration testing, and system audits.
Making your fintech mobile app PCI compliant is essential to ensuring the security of your users’ credit card information. By understanding the PCI DSS requirements, hiring a qualified security assessor, implementing a secure network infrastructure, protecting cardholder data, implementing access controls, and regularly monitoring and testing your security systems, you can ensure that your fintech mobile app is PCI compliant.
PCI Compliance Checklist
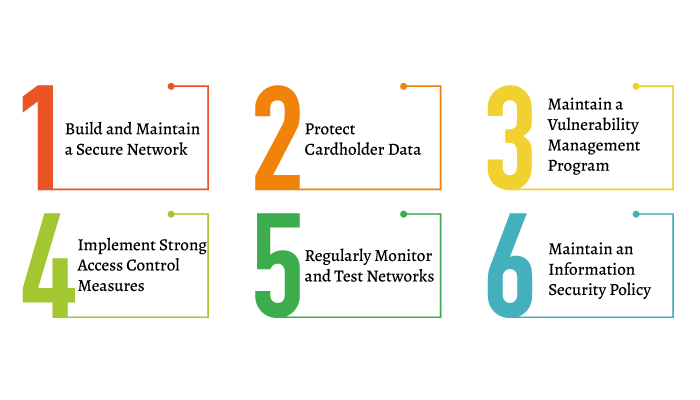
Do you want to create a fintech app that is PCI complaint? Well, it’s a good idea to read through the PCI compliance check list first. We can then go through of actually making an app compliance in the next step.
Therefore, these are, as mentioned below:
1. Build and Maintain a Secure Network
- Install and maintain a firewall configuration to protect cardholder data.
- Do not use vendor-supplied defaults for system passwords and other security parameters.
2. Protect Cardholder Data
- Protect stored cardholder data.
- Encrypt transmission of cardholder data across open and public networks.
3. Maintain a Vulnerability Management Program
- Use and regularly update anti-virus software and programs.
- Develop and maintain secure systems and applications.
4. Implement Strong Access Control Measures
- Restrict access to cardholder data by business needs-to-know.
- Assign a unique ID to each person with computer access.
- Restrict physical access to cardholder data.
5. Regularly Monitor and Test Networks
- Track and monitor all access to network resources and cardholder data.
- Regularly test security systems and processes.
6. Maintain an Information Security Policy
- Maintain a policy that addresses information security for all personnel.
By following this checklist, you can help ensure that your business is PCI compliant and protects your customers’ sensitive credit card information.
Here’s How To Maintain PCI Compliance Mobile App
More important than creating a PCI compliance mobile app for fintech is to maintain PCI compliance. Also, there are a few things you can do to maintain compliance.
Here are a few tips to do so.
- Use a secure payment gateway: Make sure you are using a payment gateway that is PCI compliant. The payment gateway should encrypt all credit card data and store it securely. This is a must have for any and all PCI compliance mobile apps.
- Use secure coding practices: When developing your PCI compliance mobile app, use secure coding practices to prevent vulnerabilities that could be exploited by hackers. Make sure you use encryption and secure data storage practices.
- Perform regular security audits: Regularly audit your mobile app for security vulnerabilities. This will help you identify and address any potential security issues before they become a problem.
- Implement access controls: Implement access controls to restrict access to sensitive data within your mobile app. This will help prevent unauthorized access to credit card data.
- Train your employees: Train your employees on PCI compliance and security best practices. Make sure they understand the importance of maintaining PCI compliance and know how to identify and report security issues.
Conclusion
With the increasing popularity of Fintech apps and other apps which have payment gateway integration, knowing about PCI compliance is important. Now, if you are someone who wants to create a complaint app, it’s highly recommended that you consult a fintech app development company as they will be able to help you with the same.
FAQ
A PCI DSS compliant fintech mobile app is an application that adheres to the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI DSS) requirements. These standards ensure that credit cardholder data is protected from unauthorized access or theft.
It is important for a fintech mobile app to be PCI DSS compliant because it ensures the security and privacy of credit cardholder data. Compliance with these standards helps to avoid security breaches and data theft, which can result in financial losses, legal liabilities, and reputational damage.
The requirements for PCI DSS compliance include:
- Building and maintaining a secure network
- Protecting cardholder data
- Maintaining a vulnerability management program
- Implementing strong access control measures
- Regularly monitoring and testing networks
- Maintaining an information security policy
To ensure PCI DSS compliance, a fintech mobile app developer can:
- Implement encryption and tokenization methods to protect cardholder data
- Use secure coding practices to prevent vulnerabilities and ensure secure data storage
- Conduct regular security assessments and penetration testing to identify and address vulnerabilities
- Limit access to cardholder data to authorized personnel only
- Develop and enforce an information security policy that outlines security procedures and responsibilities
- Partner with a PCI DSS compliant payment gateway or processor.
Some common mistakes to avoid when developing a PCI DSS compliant fintech mobile app include:
- Failing to properly secure cardholder data
- Neglecting to conduct regular security assessments or penetration testing
- Not limiting access to cardholder data to authorized personnel only
- Failing to adhere to PCI DSS requirements
- Not partnering with a PCI DSS compliant payment gateway or processor.
To maintain PCI DSS compliance, a fintech mobile app developer can:
- Regularly review and update security procedures and policies
- Stay up to date with changes to PCI DSS requirements
- Conduct regular security assessments and penetration testing
- Train employees on security best practices and procedures
- Partner with a PCI DSS compliant payment gateway or processor.

Udai Singh is a senior content writer with over 6 years of experience in creating content for FinTech, eWallet, EdTech, and App Development. He is an expert in simplifying complex concepts and creating engaging content that resonates with the audience.
Table of Contents











No Comments
Comments are closed.