Cryptocurrency has become significantly more accessible for investment. Thanks to easily accessible crypto wallets, any user can manage, invest, and transfer their digital assets.
Crypto wallets are usually thought of as an e-wallet that stores cryptocurrency. However, it is not that simple. These wallets work directly with blockchain to ensure that your digital assets are secure.
If you believe that your crypto wallet stores your crypto assets, then you are wrong as the wallet simply holds a public key that allows you to set up a transaction and a private key that is used to authorize transactions.
Knowing that there are keys involved that enable the transactions, there are different types of wallets that are available in the market. These include Custodial Wallets and Non-Custodial Wallets.
There are significant differences when it comes to both of these. In this post, let us take a closer look at how they differ and which one is a good option for you.
We will also try to understand how each of these works so that if you are an entrepreneur planning to enter the fintech market for crypto, you know where to invest your money.
Without further ado, let’s begin!
Custodial vs Non Custodial Wallets: An Overview
Managing your crypto assets through a blockchain wallet is all about managing the public and private keys associated with your crypto assets.
Based on how these keys are managed and by whom, the wallets are classified as custodial and non-custodial.
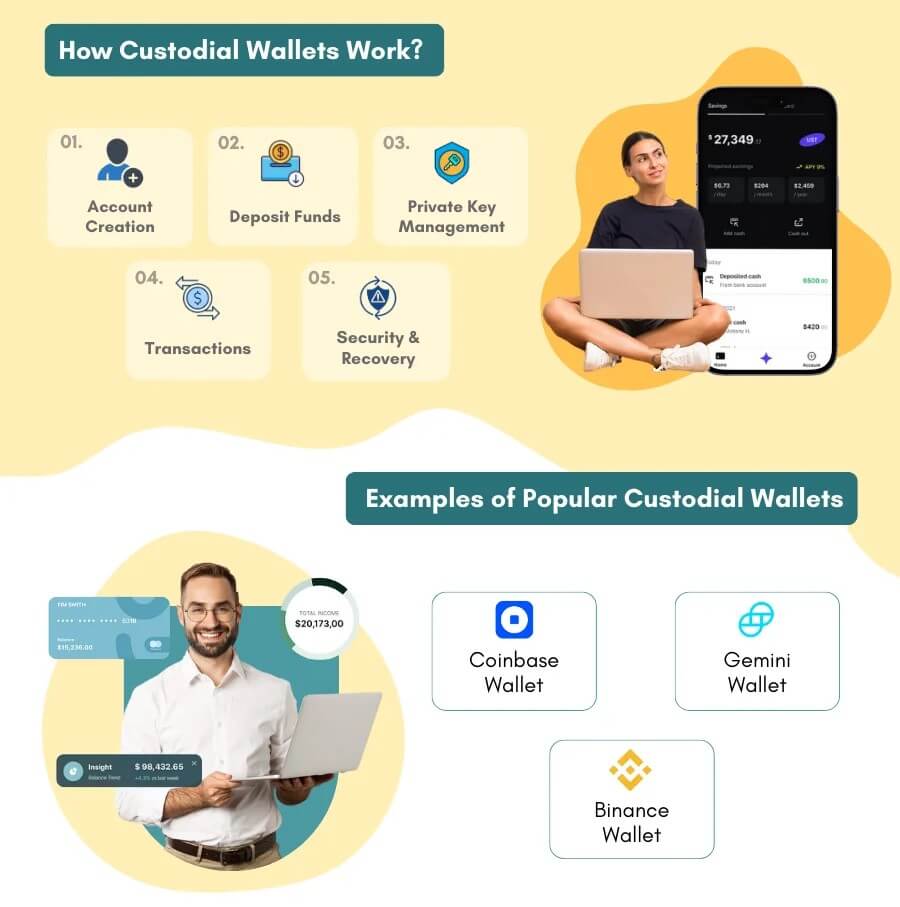
What is a Custodial Wallet?
A custodial wallet is one in which a third party is responsible for managing the private keys of crypto assets for a user.
These third parties are crypto exchange platforms and companies that can manage your private keys. Users usually prefer opting for custodial wallets as it is typically difficult to manage your private keys.
These keys are the fundamental requirements to access your funds, and in case these are lost, all your crypto funds can no longer be accessed.
Allowing a third party to manage these keys helps a user stay stress-free while using the crypto assets at their disposal.
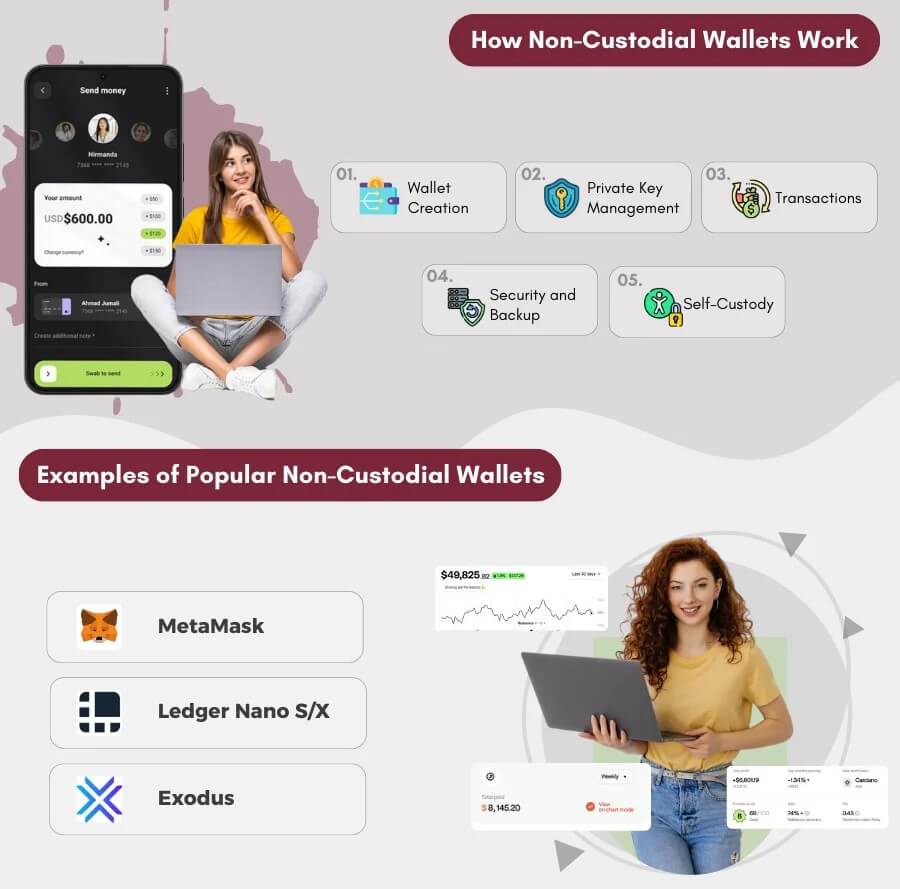
What is a Non-Custodial Wallet?
Non-custodial wallets are those where no third party is liable for managing your private keys.
All your public and private keys are managed by you, making the entire system reliant on you. It is you who is responsible for managing your private keys.
Users who have access to a non-custodial wallet gain round-the-clock access to their funds as they are essentially their own banks.
Generally, experienced traders prefer using a non-custodial wallet as the funds are accessible. But, using a non-custodial wallet poses a risk of you losing, misplacing, or forgetting your private key.
This reduces the chances of your funds being stolen or becoming a target in a data breach, considering your keys are not exposed to any other party.
Custodial & Non-Custodial Wallets: Key Differentiating Factors
The key difference between these two wallets is based on the access to the private key or “Custody” of the private key.
Custodial wallets are those that have a third-party bank managing your key, only allowing you to send or receive requests for funds using your public key.
Non-custodial wallets are those where a user is the managing authority and can access their crypto assets any time they want with full control.
While the management of your crypto asset’s private key is the ultimate point of difference between custodial and non-custodial wallets.
Some significant factors also describe the differences between the two.

These factors include:
1. Scope of Usage
This refers to the availability of usable features for an individual. Usually, a custodial wallet has a limited scope of usage as all it allows is to initiate a transaction for sending or receiving a payment. Whereas, in non-custodial wallets, everything is up for access!
2. Security Features
The security features in an ewallet are the ones that your third party offers. The entire value of your assets is dependent upon the hardware and software that the custodian provides.
And since these are companies that offer multiple crypto assets for different users, they have to create a dedicated data bank to keep all the keys safe.
While it surely makes a lot of sense, what people often overlook is the fact that at the end of the day, your private key has been shared with others and is kept in a place from where it might be subjected to a data breach.
On the other hand, the security for a non-custodial wallet is considered more secure as it is less prone to be leaked or breached unless a user has shared their data with someone else, for which they have to stay extra vigilant.
3. Transaction Updates
The update of transactions depends on the infrastructure of the third-party crypto asset manager and the time they take to update your account.
However, in a non-custodial wallet, the transactions are updated in real time as there is no mediator between the two parties involved in the transaction.
This makes a significant difference as traders who regularly update their crypto assets need to have real-time information on their balance.
This is one of the key reasons why traders prefer using a non-custodial wallet for crypto transactions and management.
4. Recoverability
All your crypto assets rely on the private key that is generated when you acquire them. Backup and recoverability is better in a custodial wallet when compared to a non-custodial wallet.
That is because since there is a third party involved in a custodial wallet, you need not remember your private key to the assets.
The involved party does it for you, hence your keys are always backed up. In case you forget, you can simply ask the mediator to give you the key, provided you prove your identity.
But when it comes to recovering a non-custodial wallet, you do not have a lot of options as you are the responsible party.
Since only you have access to the private key, it can be impossible to recover your assets if you happen to lose the key due to any reason.
5. Offline Access
When you are using a custodial wallet for your crypto assets, you have a third party that you need to connect with. Hence, there is a necessity to stay connected to the internet.
However, when you are using a non-custodial wallet, you can access these wallets completely offline.
Other than these, factors like user experience, availability of support, cost of access, and privacy also create a contrast between custodial vs non custodial wallets.
For a quick comparison of both of these wallets, based on all the factors mentioned, refer to the table below:
| Parameter | Custodial Wallet | Non-Custodial Wallet |
| Control | Third-party controls your private keys and assets. | You have full control over your private keys and assets. |
| Security | Security is dependent on the service provider’s measures. | Security depends on how well you manage your private keys. |
| User Experience | Generally more user-friendly, especially for beginners. | May require more technical knowledge and hands-on management. |
| Recovery Options | Service providers can help recover lost access. | No recovery option if you lose your private keys or seed phrase. |
| Privacy | Requires KYC and compliance with regulations. | Greater privacy, often no KYC required. |
| Support | Customer support is available for issues and recovery. | No customer support; you are responsible for troubleshooting. |
| Cost | may include service fees or custodial charges. | Typically lower costs, with no custodial fees. |
| Accessibility | Accessible through web platforms and mobile apps. | Accessible via apps, hardware wallets, or browser extensions. |
| Trust | Requires trust in the service provider. | Trustless: you rely on yourself for security and management. |
| Transaction Speed | Dependent on the provider’s processing times. | Transactions are usually faster as they’re directly on the blockchain. |
How to Choose Between Custodial & Non-Custodial Wallet? Pros & Cons
Knowing about the differences, based on all the crucial factors, you might have got clarity on how both of these wallets work.
If you are unable to decide on which one to choose, you should try and identify the pros and cons of using both of these wallets.
This way you might be able to identify which one will be the best for you.
To make it simpler, here are the pros and cons of using custodial wallets and non-custodial wallets laid out for you!
Pros of using Custodial Wallets
- A custodial wallet is highly user-friendly, which means even a beginner can easily use it.
- A custodial wallet implies no additional transaction fees, making it pocket-friendly for a user.
- A custodial wallet has less lethal effects of losing a key as the third party can easily help in gaining access.
- Restoring previous versions and undoing a transaction is a possibility that makes it easier and adaptive to use it.
- Offers dedicated customer care support that gives a user the ability to stay on top of everything, even if something goes wrong.
Cons of using Custodial Wallets
- A custodial wallet gives major control of your crypto assets to the third party that is managing your private key.
- When using a custodial wallet, you have to verify your identity to gain access to your crypto assets. This defeats the purpose of using cryptocurrency as the whole principle is based on anonymity in making transactions.
- A custodial wallet requires you to follow a timeline for accessing your own crypto assets. These are not instantly available funds as you are reliant on a service provider to access them.
Pros of using Non-Custodial Wallets
- Instant availability of your assets as you are the authority that manages the private key for access.
- Since you are the only one with access to the private key, the chances of data breaches are significantly reduced. This makes it more secure.
- With a non-custodial wallet, you are not reliant on any third party to gain access, reducing the time taken to liquidate your funds or make any transactions.
- Non-custodial wallets offer real-time updates of transactions, allowing traders to be prompt while trading.
- Allows easy offline access as you need not interact with a third party, which usually requires an internet connection.
Cons of Non-Custodial Wallets
- No recovery/backup solution in case you lose access to your private keys.
- The advanced user interface is tough for a user to navigate through.
- No customer support is available in case you get stuck, leading to higher chances of losing money if you are a novice.
Based on these pros and cons, you can further analyze which approach is better for you. Accordingly, you can choose whether to opt for a custodial wallet or a non-custodial wallet.
Nimble AppGenie: Building Crypto Wallets for All!
Choosing the correct type of wallet is definitely a crucial decision for any crypto enthusiast. But, this decision is not limited to a user only.
Being a crypto wallet company, you also need to identify the features that you resonate with, what will be beneficial for your users, and more importantly, what can help you reach the masses.
Once you are aware of all the differences between custodial and non-custodial wallets, you will be able to create an ewallet application that drives more users.
While this blog can help you identify the differences, we at Nimble AppGenie can help you identify the exact opportunity in the market. Not only that, we can help you with e-wallet app development services, offering the finest solutions, customized to your requirements.
Reach out to our experts today and let us help you create a robust cryptocurrency wallet that becomes the next big thing!
Conclusion
Knowing what you are looking for is the best thing to happen to you in this uncertain market of cryptocurrency.
Choosing the right wallet as per your requirements and experience in dealing with crypto can be highly beneficial.
Both custodial and non-custodial crypto wallets have their pros and cons. Based on those, you can simply decide on which is the best type of wallet for cryptocurrencies.
Hope this blog helps you identify the pros and cons and make an informed decision on whether to choose a custodial wallet or a non-custodial wallet. That will be all for this post.
Thanks for reading, good luck!
FAQs

Niketan Sharma is the CTO of Nimble AppGenie, a prominent website and mobile app development company in the USA that is delivering excellence with a commitment to boosting business growth & maximizing customer satisfaction. He is a highly motivated individual who helps SMEs and startups grow in this dynamic market with the latest technology and innovation.
Table of Contents





No Comments
Comments are closed.