APIs are an integral part of every online service you use today. They fetch data from the source in real time, making it appear that the platform is directly fetching the results. APIs can magically save developers a lot of time and add a lot of value for users.
RESTful APIs, or REST API’s, are some of the most commonly utilized components while developing an app or website. There are multiple ways APIs make the app development process smoother and faster.
But do you know how these APIs are built? How do they work? If not, then don’t worry, as in this post, it’s all about APIs. In this one, let us discover everything there is to know about APIs, their functionalities, tools used to build an API, the features it offers, and more.
Without further ado, let’s get started!
What is an API?
As you may be aware, an API is a set of rules and protocols that enable software to communicate with one another and share data as required.
You see, when you want to check the weather from the convenience of your home screen, you open the weather app or widget. However, that app is not the direct source of the current temperature stats. It is connected to a central website that shares its data with your app.
This sharing of data requires a certain level of communication between the two using specific methods and data formats. These methods and data formats are defined by APIs, which allow a website to access data from a server or an app to fetch data from a database.
Types of APIs & Their Classification
Different types of APIs are being used. These types are also defined based on different factors. There are 3 classifications commonly referred to when looking for APIs.
They are:
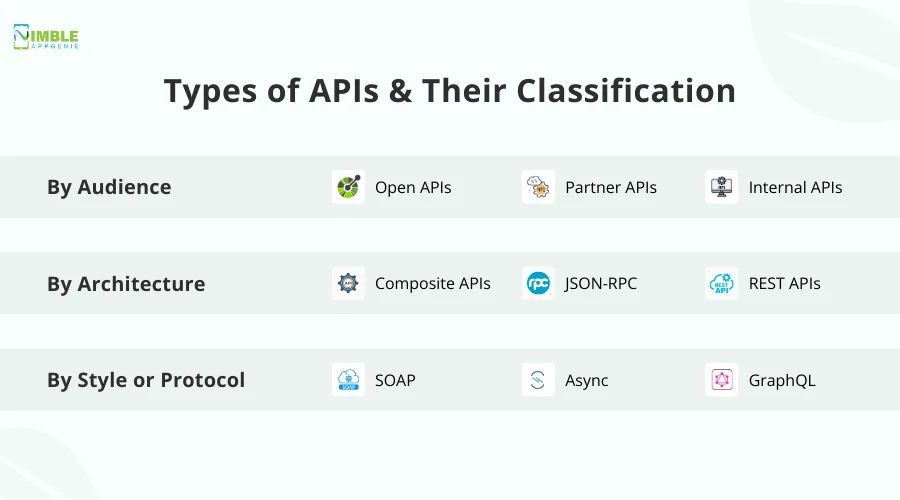
➤ By Audience
This classification is based on the availability of the APIs. These include:
- Open APIs
- Partner APIs
- Internal APIs
➤ By Architecture
This defines differences in APIs based on the architecture they use.
- Composite APIs
- JSON-RPC
- REST APIs
➤ By Style or Protocol
Since there are different protocols used by APIs, this becomes a great classification factor for APIs.
- SOAP
- Async
- GraphQL
Other than these, you can also classify APIs based on where they are used, what type of technologies it is being used for, and what type of vertical it is being used in.
Understanding APIs Used in App/Web Development
Different types of APIs are used to exchange data in different ways. Out of all the types shared in the previous section, the most commonly used APIs are Representational State Transfer APIs, commonly known as RESTful APIs or REST APIs.
REST defines the architecture used to design APIs that work over a network to enable the transfer of data. Mobile applications use REST APIs because it is extremely easy to integrate and enables instant data fetching.
REST APIs use a client-server architecture. Resources that are to be shared are identified with the help of Unique Resource Identifiers or URIs. The interaction between the client and server is stateless.
There are several operations that RESTful APIs can apply to the data that is being fetched and shown to the user. These operations include:
- GET: Used to retrieve data from a server.
- PUT: Used to replace/update existing data.
- POST: Used to create new resources.
- DELETE: Used to remove existing resources.
Other than these, RESTful APIs also offer basic Create, Read, Update, and Delete operations, often referred to as CRUD.
How Does an API Work?
After understanding the definition of an API and what it does, you might have an idea of how it works.
When an API is put to task, there is a series of steps that it follows. While it may seem like a simple transfer of data from server to client, there’s a lot more to the process.
Here are the steps involved in working on an API:
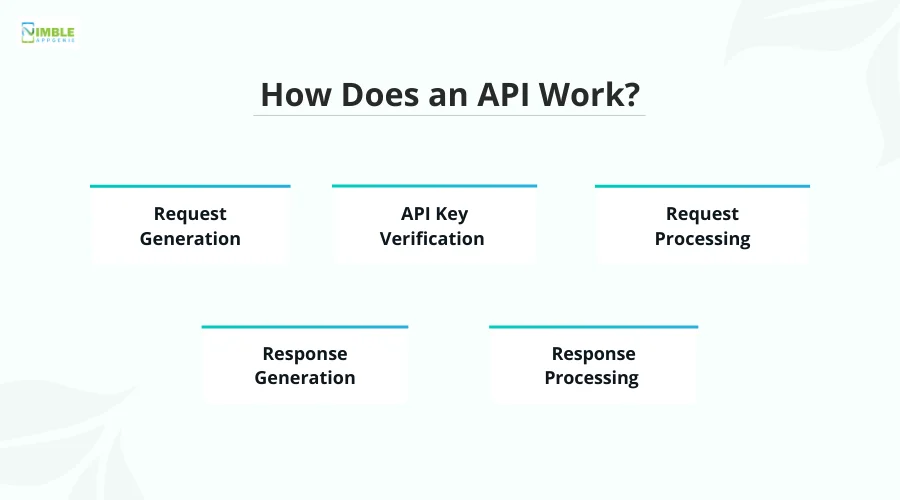
Step 1: Request Generation
The very first step is the generation of data requests. The client application interface is used to initiate a request to fetch specific data from the server and send it over.
Step 2: API Key Verification
When the request is received by the server, it first tries to verify the API key that was used to invoke the information. This verification is to ensure that the API uses the correct protocols to handle the data.
Step 3: Request Processing
Once the API key is authenticated and authorized by the server, the request is processed, and the required data is shared. The processing involves querying the database for required data, calculating the results, etc.
Step 4: Response Generation
After the request is processed, all the data is ready with the server to be sent. This response has all the information that was demanded by the API in the request to be processed.
Step 5: Response Processing
The response after being generated is processed, and the data is shared as requested. Once these steps are completed, the user interface of the app/website is updated, and the required data is shown.
While the process seems lengthy, all of it happens in a matter of seconds, making it feel seamless.
Tools to Develop an API
Now that you are aware of how an API works, the types of API, and the most commonly used type of API, let’s try and understand what tools are used to develop APIs that you can deploy.
You see, for every type of development process, there are dedicated tools, programming languages, and other resources that are used. Similarly, when it comes to API development, there are dedicated tools.
The tools are as follows:
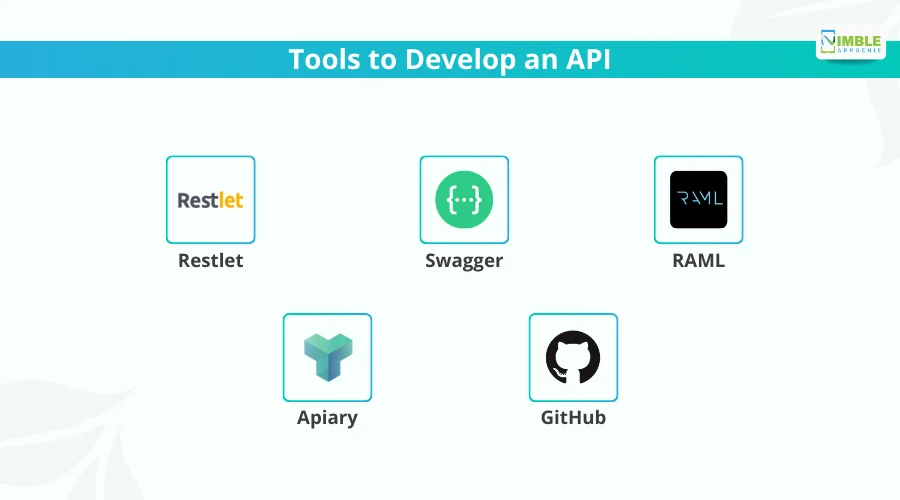
1. Restlet
An Integrated Development Environment (IDE) for API development, where Java developers can develop their REST architecture-based web APIs (REST APIs).
RESTlet API development framework is compatible with HTTP, HTTPS, JSON, and XML. It can be downloaded for free under an Apache license.
2. Swagger
An open-source API development framework that allows developers to create RESTful APIs. Swagger is a series of tools for API development. It starts with Swagger Editor, used to edit API specifications in YAML.
Swagger UI allows developers to dynamically generate documentation and a sandbox for the API. Lastly, Swagger Core is used for the implementation of Swagger in Java.
3. RAML
RESTful API Modeling Language (RAML) facilitates API lifecycle management, from design and development to third-party accessibility, including testing and documentation.
RAML allows developers to build APIs in various syntaxes, including Node.js (JavaScript), Java, Python, and .NET.
4. Apiary
It sounds more like a gimmick, but Apiary promises tools that allow developers to build their APIs in 30 minutes. Apiary provides developers with mock servers that allow them to run tests and mock-ups before encoding an API (like wireframing for user interfaces).
5. GitHub
An open-source git repository hosting service that allows developers to easily manage code files, control versions, pull requests, and comments, all of which will be distributed across the groups. Developers can also save their code in private repositories.
Other than these, API science and AuthO are also helpful in API development. These tools enable developers to curate their APIs as they see fit. Different developers prefer different tools as per their convenience.
API Development: Components & Steps
Before we begin with the API development process, let us quickly take a look at all the components that you have to deal with. The API development components include –
- API Specification
- Authentication & Authorization
- API Documentation
- API Security
When developing your API, make sure all these components are touched and justified. Failing to fulfill the requirements of any of these components may lead to failure in app development.
To develop an API, you need to follow these steps:
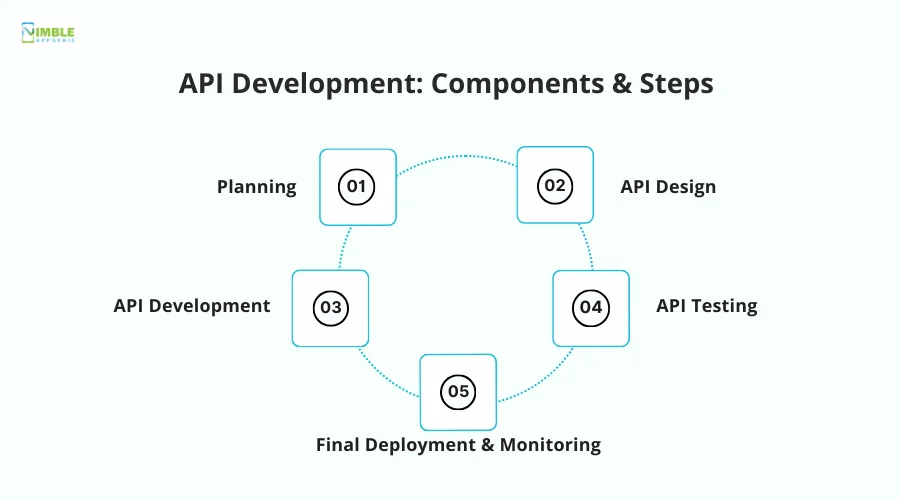
Step 1: Planning
The first step is to plan what your API will look like. It addresses the specifications you want in the API. What functionality do you want it to have, who is the intended user, and which apps will leverage its use?
As an API developer, you have to look at things from the perspective of a user who will be deploying your API solution to resolve their data fetching.
Step 2: API Design
After identifying the use cases and audience that you want to address, it’s time you start with the design of your API. To ensure that the API you are building is reliable, secure, and scalable, you need to create an architecture that suits your concept.
The design of an API includes a choice of architecture along with the API’s endpoints, methods, data formats, and other parameters.
Step 3: API Development
Once you have figured out all the elements of your API design, it’s time to develop the functionalities. In this step, you need to work on the code that will bring the functionality to life.
This is the step where you integrate with other systems or services. This is one of the core steps, as the performance of your app will depend on the accuracy of your code.
Step 4: API Testing
When you have completed the development process, you should now test all the necessary functionalities to ensure that the API is working properly.
This testing and analysis is to ensure that all the endpoints are working fine and the data requirements are being fulfilled as expected.
Step 5: Final Deployment & Monitoring
If no issues are found in the testing phase, the API is deployed for regular use. However, the job is not yet finished. You have to monitor the performance of your API.
All the metrics such as uptime, requests per month, monthly unique users, response time, resource usage, etc. Monitoring these will help you identify the core gaps that you can address and refine the API.
Once all these steps are complete, you have a well-developed API. These steps to create an API can be easily used by any professional to build an API.
However, the majority of users are not familiar with the code. Hence, they often look for API developers who can assist in finishing the process.
Features of a Well-Built API
A well-built API offers a plethora of features to its users. Some of those features are just for convenience, while some features are considered a must-have for an API as they allow it to be user-friendly, secure, and fully optimized for usage.
These features include:
♦ Search By Criteria
A feature that allows a user to search for required data based on particular criteria. The most common one is the date.
♦ Sorting
When data is fetched through an API in bulk, the API should offer a custom sorting mechanism so that when it sends the data, it is received by the user in the desired format.
♦ Paging
Your API should be smart enough to create pages of the data to be displayed as required. For instance, if a user has requested limited data, your API should share only that and show other pages with a similar number of results.
♦ Authorization via OAuth
If you are familiar with the development norms, OAuth is the fastest way to securely authorize access to the data. Implement this feature to improve the speed with which your program interface fetches data.
♦ JSON Support/REST
While it is not necessary to create an API that follows REST or JSON, it improves the user experience and enhances the use cases of your API.
The majority of API users are mobile app developers or web developers. If you offer a RESTful API, a developer is more likely to use your API.
If you can develop an API that has all these features, you can deploy an API that gets the job done easily for the developer.
There are many other features that you can incorporate, however, they depend on what type of API you are developing.
Best Practices to Help You Develop APIs
Now, how to get a well-developed API? Well, there are a few practices that can help you create an API that is secure, efficient, scalable, and user-friendly. The idea is to create an API that can easily meet the requirements of modern-day applications/websites.
- Ensure clarity in naming conventions to reduce confusion between endpoints. This makes your API more user-friendly for the developers.
- Make sure you have used the proper HTTP methods to establish crystal-clear communication.
- Incorporate authentication mechanisms such as SSL/TLS and other data encryption methods that keep your API secure from unauthorized access and ensure that the data on your API is intact.
- Design APIs that have limited but necessary functionalities, as they are more accurate in getting the job done and simplifying the complications for a developer.
- Pay attention to the documentation as a well-documented API simplifies the integration process for a developer, enhancing the overall experience.
If you can incorporate these practices into your API development, the outcome will be nothing short of a well-designed API.
Keep in mind that all of these best practices will only come in handy when you have justified all the key components of an API development.
How Nimble AppGenie Simplifies API Development?
With the entire process of API development unfolding right in front of you, you may be wondering if there is a simpler way to build an API. Well, there is! We at Nimble AppGenie, a leading mobile app development company can help you create an API in no time.
Thanks to our expert developers, you can simply state what you want the API to do, and they will simply implement it for you.
Our developers have years of experience in delivering quality API development services. Reach out to the experts today and give your business the convenience of an API.
A well-built API can simplify the functionality of your application by a huge margin. Not to mention it boosts your service visibility as if you own a website that has a lot of data that others might need. You can develop an API of your own, offering access to your database for monetization.
Conclusion
Knowing how things work when it comes to API development, you should have gotten clarity on whether you want to make an API of your own or want to delegate the task to someone else. Either way, APIs will always be a crucial part of any application to manage and fetch data.
Implementation of APIs brings a completely new outlook to the way things are done in an app. It saves a lot of time for developers and hence is of high importance.
Hopefully, this post helps you understand the process behind developing an API and the best practices to incorporate into it.
That will be all for this blog. Thanks for reading. Good luck!
FAQs

Niketan Sharma is the CTO of Nimble AppGenie, a prominent website and mobile app development company in the USA that is delivering excellence with a commitment to boosting business growth & maximizing customer satisfaction. He is a highly motivated individual who helps SMEs and startups grow in this dynamic market with the latest technology and innovation.
Table of Contents





No Comments
Comments are closed.