Fintech has truly revolutionized the way people interact with their finances. While several trends like open banking, instant payments, use of IoT, etc. are responsible for this change, embedded finance is also at the forefront of this revolution.
More than users, businesses are inclined towards investing in an embedded finance solution as it offers a lot of benefits to them.
It allows a user to directly access services like payments, loans, buy now, pay later, etc. Reducing the hassle of navigating to a different app just to use financial services.
Interesting, right? Embedded finance is one of the most fascinating trends of fintech that has become a part of the digital transformation in fintech.
In this post, we are going to take a closer look at the factors that make this trend so fascinating. What are the benefits & challenges of implementation? What is the impact of embedded financial services on the overall market?
Without further ado, let’s start by understanding the concept in more detail.
Embedded Finance: An Overview
Embedded finance allows a user to access financial services faster while being in the same application where they plan to spend. This way, a user can easily finish the entire process faster which leads to more conversions for a business as well.
One of the most common examples of embedded finance can be seen in real-time cab booking applications that offer in-app payments.
Some apps even embed a Buy Now Pay Later feature, which is a direct implementation of embedded finance.
There are many other examples of embedded finance that people use in everyday life. Embedded finance is used in different applications by integrating an API offered by a financial institution.
Once the integration is done, users can access the embedded financial services by simply verifying their identity and banking details.
This information is often crucial for the service providers as it helps in risk assessment while offering credit limits for BNPL services.
The implementation of embedded financial services helps all the involved parties in different ways.
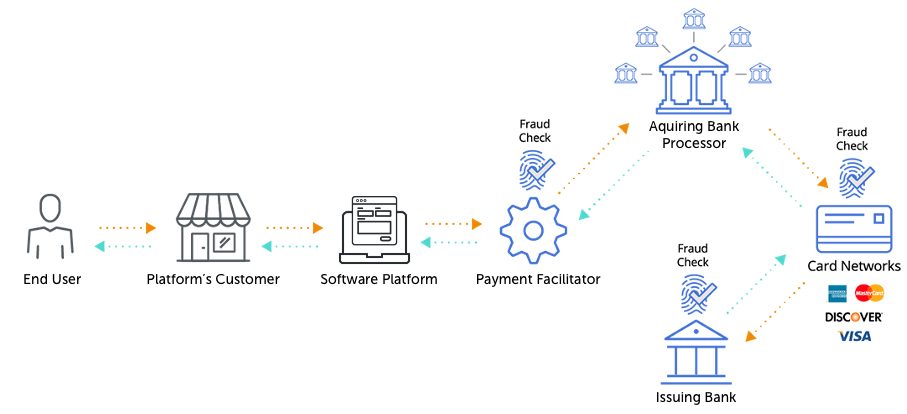
How? Well, here’s how:
- A user gets direct access to financial services, without having to switch between apps or services.
- A business gets more conversions as sometimes a user may change their mind when the steps are complicated.
- A bank or financial institution that is offering a BNPL or e-wallet service gets more customers onboard easily.
Overall, the entire concept of embedded finance is proving to be a game-changer in terms of the way financial services are being used in e-commerce and other areas.
It is quite easy to understand how embedded finance works if you are familiar with online payments and other fintech solutions.
Embedded Finance Market Stats
Embedded finance has seen a long journey as it was first introduced way back in 1920 by Ford, offering a Ford Credit Bank for its car buyers.
While it was not all digital, the concept remained the same, i.e., integration of a financial service into a different service.
However, with the rise of technology, the entire concept of integrated financial services has gone through a digital transformation, making it easier to implement and access.
If we talk about the current status of this fintech market, the embedded finance market was valued at $82.7 Billion in 2024 and is a growing one set to reach $570.9 Billion by 2033, at a CAGR of 21.3%.
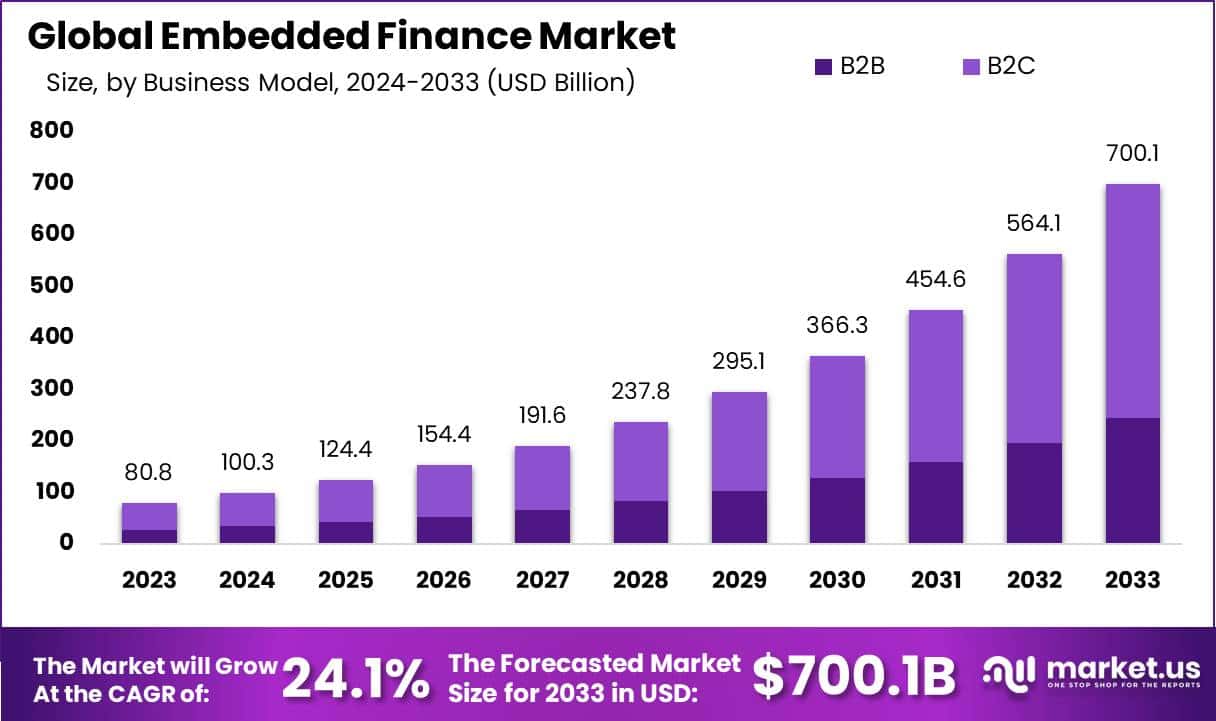
Embedded finance has surely made it to the forefront of fintech implementation in different services.
From basic shopping applications to delivery apps and from delivery apps to travel and booking applications, the concept is widely accepted by users.
Types of Embedded Finance
As you might have guessed, embedded finance offers different types of services. These services also define the types of embedded services that you integrate into your application.
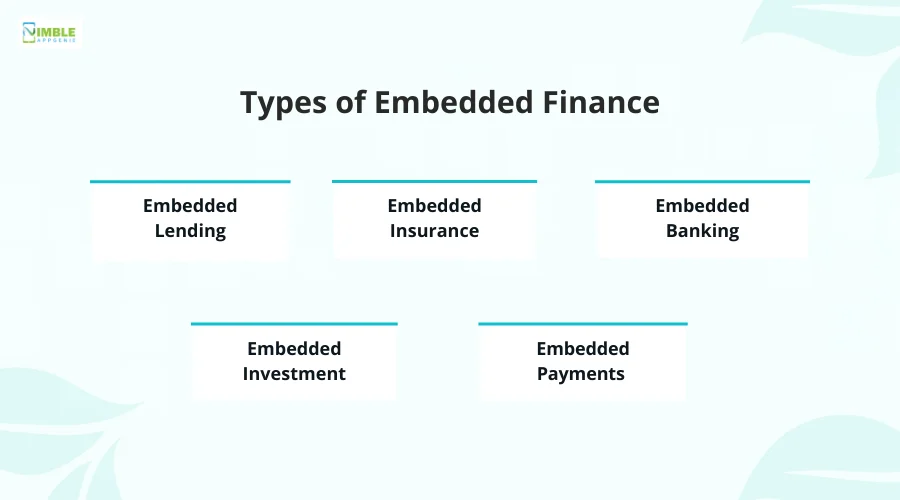
These different types of financial offerings include-:
Type 1: Embedded Lending
One of the most common types of embedded finance services that is integrated into applications is embedded lending.
This allows a user to unlock a credit limit that they can use while checking out of the service and smoothly finish their purchase.
Buy Now Pay Later is the most visible form of embedded lending. With the help of financial institutions backing a service, a user is more likely to use their credit limit as it offers an easy way to pay.
Generally while paying, you either have to use funds from your savings account, or enter your credit card information on the platform.
However, thanks to embedded lending, people today have access to a payment method that does not require a lot of details.
It presents a great opportunity for fintech businesses as they directly offer access to funds to their customers, enhancing their purchasing power leading to more conversions.
Type 2: Embedded Insurance
Buying insurance while you are shopping for something else is an older institution that has been practiced offline for a long time now. The best examples include buying a car from a showroom, getting your new laptop from an outlet, etc.
However, these cases have found their way into the digital world through online commerce and embedded finance applications.
You may have seen an add-on insurance service while making bookings for a hotel room, or a flight. These add-on services are offered by insurance companies that are integrated with the booking platform.
These services can be introduced in any purchase that may require insurance. The best part is that the user does not have to engage in any sort of communication with the insurance company or an agent.
Type 3: Embedded Banking
Often referred to as banking as a service, embedded banking is the integration of banking services directly into a platform that is not conventional banking.
Embedded banking offers all the benefits of using a bank without directly interacting with a financial institution.
One of the best examples of embedded banking, or banking as a service, can be seen at Shopify, which offers Shopify Balance.
What it does is that it offers an entire account with direct access to a bank account that reduces the time of account settlement.
Through these accounts, you can easily access all the funds that you have collected instantly.
Type 4: Embedded Investment
Investments have seen massive growth over the past few years, thanks to the digitization of investment platforms and embedded investments.
Generally, this type of embedded finance service is integrated in an e-wallet or an instant payment platform.
Investments in cryptocurrency and other types of online assets like NFTs are a good example of embedded investments. A user can access a payment app to find various ways to invest your money where you see fit.
Your investment can be as simple as keeping your money in an account that bears interest.
Embedded investments, though do not have a lot of use cases, are surely an up-and-coming trend that will take over the entire realm of embedded finance.
Type 5: Embedded Payments
Embedded payments or payment methods are the most common type of embedded finance that has been used for ages now.
Offering payment methods that can be used directly from the platform that you are using, embedded payments enable a user to finish transactions faster.
Basically, embedded payments tend to integrate payment methods and save your information securely so you need not go through the same steps again and again. This also helps you access your cards and accounts for payments instantly.
The best examples of embedded payments are your existing applications such as Starbucks, Amazon, etc. that can save your card for easy checkout.
Other than these, embedded finance can also be categorized based on the types of services that can simplify the experience of spending online for a user.
Categories such as Embedded Fintech, Embedded Finance Marketplaces, and B2B Marketplaces are the latest financial trends that you can utilize.
Benefits of Embedded Finance
There are several benefits of implementing embedded finance in your business.
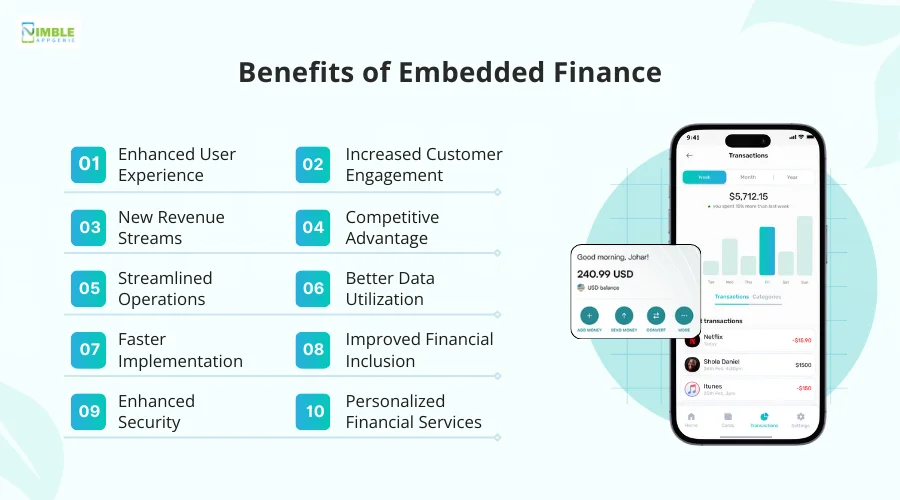
Some of these benefits include-:
1. Enhanced User Experience
Using embedded finance in your business can help in enhancing the entire user experience. How?
Well, while making payments online, there are a lot of steps that you have to complete. For instance, you have to select the product/service that you want to buy, then head to the payment app to make payments, add your information, etc.
However, with embedded finance, the entire process is constrained to a single app and hardly takes a few seconds to finish the transaction. This makes the entire process more simplified, improving the user experience.
2. Increased Customer Engagement
When customers do not have to worry about the availability of funds or keeping their cards handy every time they have to buy something, it can help in gathering more active users.
These active users clearly lead to a more engaging experience as now a user is not hesitating in using the platform. On the contrary, a user is spending more time on the platform.
Not to mention, when users start using an embedded finance service they get used to the convenience and hence keep returning.
3. New Revenue Streams
When you integrate a service on your platform, you are allowing a third party to access your users. This integration opportunity is a game-changer for many service providers and hence they are more than happy to pay for this integration to work.
Also, added benefits like transaction fees, service charges, interest on offered credit limits, etc. can be a way for your platform to generate revenue.
In some cases, you can keep a commission for providing the integrated service to your customers. All in all, it can be said that through embedded finance, you can unlock new revenue streams for your business.
4. Competitive Advantage
Embedded financial services can also serve as the X factor for your business.
When you have an embedded system for payments that offers ease of access, all the users are inclined towards a platform.
This is because no individual has time to re-enter their payment information on any platform every time they want to place an order.
What it means is with the help of an embedded platform you can gain a competitive edge over your competitors.
Platforms that offer more customer-oriented services are mostly preferred over other platforms from the same industry.
5. Streamlined Operations
Implementing embedded finance in your application can help streamline several operations both for you and your users.
For you, the hassle of tracing every transaction from different sources is reduced. The integrated embedded finance system directly yields that data for you. Whereas, a user has to go through fewer steps to make a payment.
The entire process is completed in a single app, which leaves no need for switching to another application to make payments.
6. Better Data Utilization
Offering an additional service can help you generate more user data, which can be further used for better decision-making.
Data such as a user’s creditworthiness, their buying patterns, how much time they spend on your application, which payment method they prefer, etc. can help you in the long run.
All this information usually allows assessment of the user, along with decision-making about which features to implement next.
Being able to identify what type of user you have can help you introduce new features and fix the existing ones better.
7. Faster Implementation
Implementing embedded finance, unlike any other financial technology, does not take a long time. Since it uses APIs to be integrated with the existing applications, the entire solution can be implemented instantly.
This ease of integration reduces time to market. For any application, embedded finance services of any type, be it lending, payments, insurance, or investment can be easily integrated.
Embedded finance offers a major convenience to its customers and, hence, can be a great addition to your application.
The best part is you need not go through a complete development process to integrate it. Simply integrate an API and you are good to go!
8. Improving Financial Inclusion
Several constraints stop several users from being able to use online financial services. Some may not have access to a credit card, some may not have access to a bank account. The problem appears due to a lack of financial inclusion.
Thanks to embedded finance, people can access these services without having to depend on another financial institution. If they can access your business, they can easily access the solutions that you offer.
Embedded finance helps more and more people to access financial services such as lending, investment, insurance, etc., making the entire realm more and more inclusive.
9. Enhanced Security
One of the key factors that the use of embedded finance helps in reshaping the future of fintech security that it brings along. You see when a user has to enter his details along with banking information, there is a chance that it may not be safe.
However, with embedded finance applications, there’s no need for that. You get access to a dedicated payment option that can only be used for that particular platform or a set of platforms from the list of eligible ones.
You need not create a dedicated account, and, more importantly, your savings account is not involved. Making the entire transaction useful.
At the same time, it is secure for businesses as well. That is because an embedded payment method can serve as a closed-loop payment system, reducing the chances of being hacked or compromised.
10. Personalized Financial Services
While fintech has tried to personalize the service for its customers as much as it can, embedded finance takes it a step further.
Since embedded finance works on the platform where the user is spending, they have more insights on what a user prefers, and hence personalization is far superior.
Knowing if a person can afford a credit limit or not is also easy for banks. This helps them create a personalized financial plan for every customer, offering different payment options, limits, and offers respectively.
The list of benefits can go on and on, considering embedded finance is easily executable, scalable, and offers instant growth. However, being from the field, it is you who has to identify which benefit will boost your business.
Top Embedded Finance Providers/Companies
You may be wondering if embedded finance can be implemented through an API, and who is offering these services? Well, some of the major fintech companies have started offering embedded finance services.
Some of the key players that are making waves in the market are:
♦ Plaid
Plaid provides APIs that enable apps to connect with users’ bank accounts, facilitating seamless integration of financial services.
Key Features: Plaid’s technology is widely used to enable embedded payments, financial data aggregation, and lending solutions.
Clients: Venmo, Robinhood, and Coinbase leverage Plaid’s APIs to offer seamless financial services within their apps.
♦ Stripe
Stripe is a leading payment processor that offers extensive APIs for integrating payment processing into various platforms.
Key Features: Stripe supports embedded payments, billing, and financing options, making it a versatile solution for many businesses.
Clients: Shopify, Amazon, and Instacart use Stripe payment solutions to enhance their platforms.
♦ Square
Square provides comprehensive financial services, including payments, POS systems, and small business loans.
Key Features: Square’s embedded finance solutions are designed to help businesses manage payments and access financing seamlessly.
Clients: Square’s services are used by small businesses and retailers worldwide to streamline their financial operations.
♦ Solarisbank
Solarisbank is a BaaS provider that offers banking services through APIs, enabling companies to embed financial services.
Key Features: Solarisbank’s platform supports embedded banking, payments, and lending solutions, allowing businesses to offer branded financial products.
Clients: Companies like Samsung and Vivid Money utilize Solarisbank’s infrastructure to provide financial services.
♦ Adyen
Adyen is a global payments company that offers a single platform for managing payments across different channels.
Key Features: Adyen’s embedded payment solutions enable businesses to integrate seamless payment experiences into their apps and websites.
Clients: eBay, Spotify, and Uber rely on Adyen’s payment infrastructure for their global operations.
♦ Finix
Finix provides payment infrastructure as a service, enabling businesses to own and manage their payment processing.
Key Features: Finix’s APIs support embedded payments, allowing companies to build customized payment experiences and manage transactions efficiently.
Clients: Finix serves a range of businesses, including SaaS platforms and marketplaces, helping them integrate financial services.
♦ Railsbank
Railsbank offers a global platform for embedding banking services, including issuing cards, managing accounts, and processing payments.
Key Features: Railsbank’s flexible APIs allow businesses to integrate financial services and expand their offerings quickly.
Clients: Companies like Yolt and Sync use Railsbank’s services to provide integrated financial products to their users.
All these services have created a mark for themselves when it comes to offering embedded financial services.
If you plan to develop a fintech application, you can rely on your developer to integrate embedded fintech services offered by these companies.
How Can Fintech Startups (or Startups to be) Leverage Embedded Finance?
If you are planning to step into the realm of fintech or any sort of online platform, you can use embedded services to enhance your performance.
Embedded finance offers so many options and solutions that a young startup can leverage.
The issues that embedded finance can help you address and resolve are-:
-
Integrating Seamless Payments
One of the key issues that users face while shopping online is the complicated steps they have to go through while making purchases.
With the correct implementation of embedded finance, you can easily integrate seamless payment options in your startup, attracting more customers.
-
Offering Embedded Lending
If you plan to reach the masses, offering embedded lending can be a great step for you. Users often find themselves short of funds while purchasing online.
Not to mention, some users do not prefer using their savings. Offering a payment method where they can pay later, and access funds instantly, changes everything, making funds more accessible to a user.
-
Providing Insurance Solutions
If you are a startup that offers any sort of bookings or purchases, you can offer insurance and purchase protection plans bundled with your service.
This way, you have added value to your products and services, attracting more users easily. Not to mention, this also uplifts your offerings, making your services more value for money.
-
Utilizing Data for Personalization
As a startup, data is your best asset as it will help you understand user behavior and make better decisions. You can try things like offering a small discount on your services when people use your embedded finance service.
This way you get access to a lot of data that can be utilized for creating a personalized experience for the user.
-
Expanding Market Reach
By offering embedded financial services through your service, you enable every user to make online payments.
There are a lot of users who do not have access to conventional banking services; however, with embedded finance, they can access fintech services easily.
This opens a new door of opportunity for your services, improving market reach.
Common Challenges in Embedded Finance Adoption
While there are many benefits and leverage that embedded finance offers, there can be some challenges that you might have to face in integrating embedded finance.

Common challenges in the adoption of embedded finance include:
Challenge #1 – Security Concerns
When you offer financial services in any way, there is a significant security risk involved. That is because the exchange of personal information between the embedded APIs and your application is prone to breaches.
Privacy and data security are one of the prime concerns of a company. Especially when you have used embedded finance services offered by a non-banking platform.
That is because, unlike a banking institution that has multiple security standards in place, a non-banking service can lack security.
Challenge #2 – Regulation & Compliance Issues
When any company plans to integrate a financial service on its platforms, there are several regulations and compliance that come into play. These regulations can often be difficult to manage and follow.
These regulations also bring a lot of concerns related to the implementation of new initiatives, which may cost more. Managing regulations is not easy, as you have to face different limitations.
Not to mention, there are several costs associated with this regulatory compliance. You may be required to keep up with the ever-changing technologies, costing you more and more.
Challenge #3 – Risk of Customer Profiling
When offering services like embedded lending, you need to profile existing customers properly. Identifying creditworthiness without taking into account their past banking history can be difficult.
This means if the customer is not profiled properly, they may default on payments, making it difficult for you to recover. This can hamper the entire system and lead to a major loss.
Customer profiling will require access to the creditworthiness of a user, which will cost you more, increasing your investment.
These challenges are not a hindrance to implementation but can pose an issue in adapting the technology.
Impact of Embedded Finance on Fintech
The realm of fintech is in for another revolution with the introduction of embedded finance in different sectors.
It is evident how users have accepted embedded finance in various forms.
The embedded finance market alone is worth billions of dollars and is all set to bring some new trends in the market.
These new trends may include:
1] Technological Collaborations
In the growing embedded finance market, a lot of collaborations have already emerged successfully. Technological collaborations, such as bringing financial and non-financial technology together, offer ease of access and convenience to the users.
2] Involvement of Non-Financial Services
With embedded technology, more and more nonfinancial services will be able to enter the market, expanding fintech services to their customers. This involvement will help in the growth of embedded finance and fintech in general!
3] Revenue Opportunities for Businesses
Businesses can garner a lot of revenue by offering embedded financial services. If you have a large volume of transactions, the fees can be a good and consistent source of revenue. Also, allowing access to unbanked users can be a good way to reach new customers.
4] Competition from Existing Financial Institutions
You don’t have to be a legacy banking institution to offer embedded financial services.
This means embedded finance will bring new competition for existing financial institutions.
Embedded financial services are making a huge impact on how fintech is implemented and used.
It won’t be long before every non-financial platform has an embedded financial system.
Needless to say, if you are a business, you must have an embedded finance platform integrated with your app, as it is definitely the future!
Nimble AppGenie: Driving Innovation With Embedded Finance Solutions
You may be wondering how exactly you can benefit from the rise of embedded finance.
Well, you will require a team of professionals to help you understand how exactly you can make the most of this technology.
And who better to guide you than some of the finest fintech professionals from Nimble AppGenie?
Our experts can help you identify all the use cases of your platform where embedded finance services can be helpful and integrate them for you instantly.
Schedule a call today to identify how exactly you can get the most out of finance app development services.
Conclusion
Embedded finance is definitely one of the most popular, useful, and impactful solutions that are contributing to the rise of fintech in different industries.
The benefits of implementation are really lucrative as they offer some great opportunities to grow. With proper implementation, embedded finance can help in improving the user experience of your app, keeping customers more engaged and satisfied.
But, it surely depends on the way that you implement these services. Hence, you need the support of professional developers and fintech experts to help you carry out embedded finance properly.
So make sure you get the best aid and implement embedded finance as it is the future of fintech!
Good luck.
FAQs

Niketan Sharma is the CTO of Nimble AppGenie, a prominent website and mobile app development company in the USA that is delivering excellence with a commitment to boosting business growth & maximizing customer satisfaction. He is a highly motivated individual who helps SMEs and startups grow in this dynamic market with the latest technology and innovation.
Table of Contents




No Comments
Comments are closed.