Digital banking and mobile banking are two transformative forces.
As technology continues to advance, the lines between these two concepts have become increasingly blurred, leading to confusion among many users.
In this blog post, we will explore the digital banking vs mobile banking landscape, delving into the key differences, features, and benefits of each approach.
With the proliferation of smartphones and the growing demand for convenient, accessible financial services, both digital banking and mobile banking have seen significant growth in recent years.
However, while these terms are often used interchangeably, there are distinct differences between the two.
Understanding these nuances is crucial for consumers looking to make informed decisions about their banking preferences and for financial institutions seeking for development of a mobile banking app that meets the evolving needs of their customers.
Throughout this blog, we will provide a comprehensive comparison of digital banking vs mobile banking, examining their respective use cases, advantages, drawbacks, and real-world examples.
By the end of this post, you will have a clear understanding of the difference between digital banking and mobile banking and be better equipped to navigate the digital financial landscape.
What is Digital Banking?
Digital banking is a broad term that encompasses a wide range of financial services and transactions conducted through digital channels.
It represents a significant shift from traditional banking methods.
This typically involves physical interactions at bank branches. Digital banking has revolutionized the way consumers manage their finances, offering unparalleled convenience, accessibility, and efficiency.

Let’s take a closer look at the various aspects of digital banking.
► Use Cases
Digital banking offers a plethora of use cases for consumers, catering to a wide range of financial needs and preferences:
- Account management: With digital banking, users can easily view their account balances, transaction history, and statements online. This allows for real-time monitoring of financial activities and helps users stay on top of their spending and budgeting.
- Money transfers: Digital banking enables users to send and receive funds between their own accounts or to other individuals seamlessly. Whether it’s splitting a bill with friends or sending money to family members, digital banking makes money transfers quick, secure, and hassle-free.
- Bill payments: Gone are the days of writing checks or visiting physical payment centers. Digital banking allows users to pay their utility bills, credit card balances, and other recurring expenses with just a few clicks. This not only saves time but also helps users avoid late payment fees and maintain a good credit score.
- Loan applications: Applying for loans has become much more convenient with digital banking. Users can easily fill out loan applications online, provide necessary documentation, and receive quick decisions from their financial institutions. This streamlines the process and eliminates the need for multiple visits to bank branches.
- Investment management: Digital banking has opened up new avenues for investment management. Users can access online investment platforms, monitor their portfolios, and make informed decisions based on real-time market data. This empowers individuals to take control of their financial future and grow their wealth.
► Advantages
Digital banking offers several compelling advantages that have made it an increasingly popular choice among consumers:
- Convenience: One of the most significant benefits of digital banking is the unparalleled convenience it provides. Users can access their banking services 24/7 from anywhere with an internet connection, be it from the comfort of their homes or on the go. This eliminates the need to visit physical bank branches during limited business hours, saving valuable time and effort.
- Time-saving: Digital banking significantly reduces the time spent on banking activities. Transactions that once required filling out forms and waiting in long queues can now be completed within minutes using online platforms. This allows users to focus on other important aspects of their lives while still managing their finances effectively.
- Efficiency: Digital banking leverages automated processes and advanced technology to streamline financial transactions. This results in faster transaction times compared to traditional banking methods. Whether it’s transferring funds, paying bills, or applying for loans, digital banking ensures that these tasks are completed swiftly and efficiently.
- Eco-friendly: By embracing digital banking, users can contribute to a greener environment. Electronic statements, paperless documentation, and online transactions significantly reduce paper waste associated with traditional banking. This not only helps conserve natural resources but also aligns with the growing trend of eco-consciousness among consumers.
► Drawbacks
While digital banking offers numerous benefits, it’s essential to consider some potential drawbacks:
- Security concerns: As with any online activity, digital banking is not immune to cyber threats, hacking attempts, or online fraud. While financial institutions invest heavily in robust security measures, users must also remain vigilant and follow best practices, such as using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and avoiding suspicious links or emails.
- Technical issues: Digital banking relies on technology, which means that occasional system outages or glitches can occur. These technical issues can temporarily disrupt access to banking services, causing inconvenience and frustration for users. However, financial institutions generally have contingency plans in place to minimize downtime and ensure prompt resolution of any issues.
- Limited personal interaction: Digital banking has reduced the need for face-to-face interactions with bank representatives. While this is seen as a convenience by many, some users may prefer the personal touch and expertise provided by in-person banking experiences. It’s important for financial institutions to strike a balance between digital efficiency and human connection to cater to diverse customer preferences.
- Learning curve: For some users, particularly those who are less tech-savvy, adapting to new digital tools and interfaces can present a learning curve. Financial institutions must prioritize user-friendly design, clear instructions, and readily available customer support to ensure a smooth transition and positive user experience for all customers.
► Examples
The digital banking landscape is vast and diverse, with numerous platforms and services catering to different user needs and preferences. Some prominent examples include:
- Online banking portals: Traditional banks such as Chase, Bank of America, and Wells Fargo offer comprehensive online banking portals. These platforms allow users to manage their accounts, transfer funds, pay bills, and access a range of financial services from their computers or mobile devices.
- All-digital banks: Innovative all-digital banks like Ally Bank and Chime have emerged to provide a complete online banking experience. These banks operate entirely online without physical branches, offering competitive rates, low fees, and user-friendly interfaces that appeal to tech-savvy consumers.
- Personal finance management tools: Platforms like Mint and Personal Capital have gained popularity by providing users with a holistic view of their finances. These tools aggregate financial data from multiple sources, including bank accounts, credit cards, and investment portfolios, allowing users to track their spending, set budgets, and make informed financial decisions.
- Peer-to-peer payment apps: Apps such as Venmo and Cash App have revolutionized the way people transfer money to each other. These platforms enable users to easily split expenses, send money to friends and family, and even make purchases directly from their mobile devices, making peer-to-peer transactions seamless and convenient.
As we delve deeper into the digital banking vs mobile banking comparison, it’s crucial to recognize that the best banking apps often incorporate a wide array of digital banking features to provide a comprehensive and convenient user experience.
In the next section, we will focus on the specific characteristics and benefits of mobile banking, shedding light on how it differs from the broader scope of digital banking.
This will provide a foundation for thorough digital banking vs mobile banking analysis and help readers make informed decisions about their banking preferences.
What is Mobile Banking?
Mobile banking is a specific subset of digital banking that focuses on delivering financial services and transactions through mobile devices.
Such as smartphones and tablets.
It leverages the ubiquity and convenience of mobile technology to provide users with on-the-go access to their banking needs.
Mobile banking has transformed the way people interact with their financial institutions, offering a seamless and intuitive experience tailored to the mobile lifestyle.
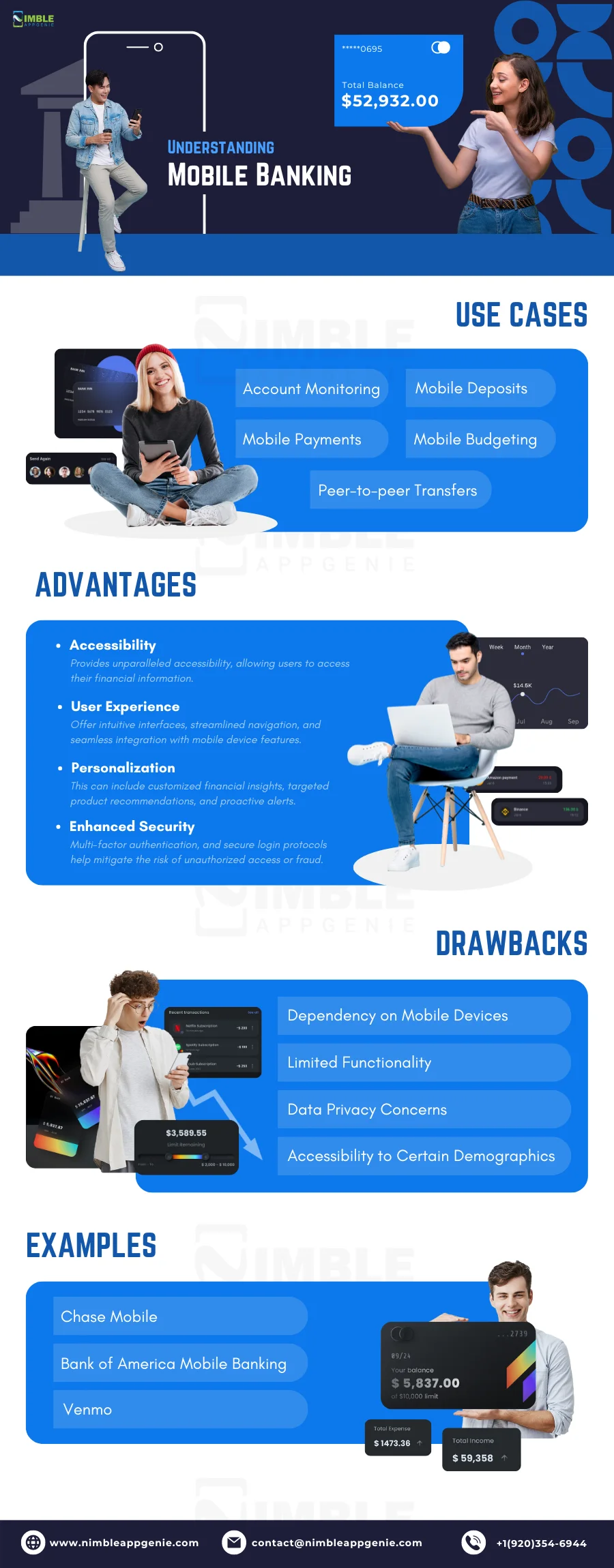
Let’s explore the various aspects of mobile banking in detail.
► Use Cases
Mobile banking offers a wide range of use cases that cater to the diverse needs of modern consumers:
- Account monitoring: With mobile banking apps, users can easily check their account balances, view transaction history, and receive real-time notifications about account activity. This allows for better financial management and quick detection of any unauthorized transactions.
- Mobile deposits: Many mobile banking apps offer the convenience of mobile check deposits. Users can simply take a photo of a check using their smartphone camera, and the funds are deposited into their account, eliminating the need to visit a physical bank branch or ATM.
- Mobile payments: Mobile banking apps often integrate with digital wallet services like Apple Pay and Google Pay, enabling users to make payments using their smartphones at participating retailers. This provides a secure and convenient alternative to carrying physical credit or debit cards.
- Peer-to-peer transfers: Mobile banking apps have made it easier than ever to send and receive money from friends and family. Users can quickly transfer funds to other individuals using their mobile device, often with just a phone number or email address, making splitting expenses or sending money a breeze.
- Mobile budgeting: Many mobile banking apps offer built-in budgeting tools that help users track their spending, set financial goals, and receive personalized insights and recommendations. This empowers users to make informed financial decisions and develop better money management habits.
► Advantages
Mobile banking offers several distinct advantages that have contributed to its rapid adoption and popularity:
- Accessibility: Mobile banking provides unparalleled accessibility, allowing users to access their financial information and perform transactions anytime, anywhere, using their mobile devices. This is particularly valuable for individuals with busy lifestyles or those who frequently travel.
- User experience: Mobile banking apps are designed with user experience at the forefront. They offer intuitive interfaces, streamlined navigation, and seamless integration with mobile device features like biometric authentication (e.g., fingerprint or facial recognition). This makes mobile banking easy to use and enhances overall customer satisfaction.
- Personalization: Mobile banking apps often leverage data analytics and machine learning to provide personalized experiences for users. This can include customized financial insights, targeted product recommendations, and proactive alerts based on individual spending patterns and goals.
- Enhanced security: Mobile banking apps employ advanced security measures to protect user information and transactions. Features like multi-factor authentication, encryption, and secure login protocols help mitigate the risk of unauthorized access or fraud, providing users with peace of mind.
► Drawbacks
While mobile banking offers numerous benefits, there are some potential drawbacks to consider:
- Dependency on mobile devices: Mobile banking relies heavily on the availability and functionality of mobile devices. If a user’s smartphone is lost, stolen, or experiences technical issues, it can temporarily hinder access to banking services, causing inconvenience.
- Limited functionality: Although mobile banking apps strive to provide a comprehensive range of services, some complex banking transactions or specialized features may still require visiting a physical branch or using a desktop computer. This can be a drawback for users who heavily rely on mobile banking for all their financial needs.
- Data privacy concerns: As mobile banking involves transmitting sensitive financial information over wireless networks, some users may have concerns about data privacy and the potential for cybersecurity breaches. It’s crucial for financial institutions to prioritize robust security measures and educate users on best practices for protecting their information.
- Accessibility to certain demographics: While mobile banking has gained widespread adoption, some demographics, such as older individuals or those with limited access to smartphones or reliable internet connectivity, may face barriers to fully embracing mobile banking services.
► Examples
The mobile banking landscape is diverse, with numerous financial institutions and fintech companies offering innovative and feature-rich mobile banking apps. Some notable examples include:
- Chase Mobile: The mobile banking app from JPMorgan Chase offers a comprehensive suite of features, including account management, mobile check deposits, bill payments, and personalized spending insights. The app also integrates with Chase’s rewards program, allowing users to easily redeem and track their points.
- Bank of America Mobile Banking: Bank of America’s mobile app provides users with a seamless banking experience, offering features like account balances, money transfers, mobile check deposits, and ATM locator. The app also includes Erica, an AI-powered virtual assistant that helps users with tasks and provides financial guidance.
- Venmo: While not a traditional banking app, Venmo has revolutionized peer-to-peer payments and become an integral part of many users’ mobile financial experience. That’s why so many people want to create an app like Venmo.
As we compare Digital Banking vs Mobile Banking, it’s evident that mobile banking is a critical component of the broader digital banking ecosystem.
The best banking apps combine the convenience and accessibility of mobile technology with the comprehensive features and services offered by digital banking platforms.
This involves understanding the unique needs and preferences of mobile users, incorporating banking app features that streamline common tasks, and ensuring a high level of security and reliability.
Mobile Banking vs Digital Banking
While mobile banking and digital banking are closely intertwined, there are some key differences between the two that are worth exploring. In this section, we will compare and contrast digital banking vs mobile banking across various parameters to provide a comprehensive understanding of their similarities and distinctions.
| Parameter | Mobile Banking | Digital Banking |
| Access | Primarily accessed through mobile devices like smartphones and tablets | Encompasses a broader range of digital channels, including desktop computers, laptops, and mobile devices |
| Functionality | Offers a more streamlined and focused set of features tailored to mobile users | Provides a comprehensive suite of banking services and features across multiple digital platforms |
| User Experience | Prioritizes simplicity, ease of use, and mobile-specific features like biometric authentication | Offers a broader user experience that may vary across different digital channels and platforms |
| Convenience | Provides unparalleled convenience and accessibility, allowing users to bank on-the-go | Offers convenience through 24/7 access to banking services, but may require more time and effort compared to mobile banking |
| Security | Employs mobile-specific security measures like biometric authentication and two-factor authentication | Implements a range of security measures across digital channels, including encryption and secure login protocols |
| Adoption | Has seen rapid adoption, particularly among younger generations and tech-savvy users | Enjoys widespread adoption across various age groups and demographics, with increasing popularity among all user segments |
| Innovation | Focuses on mobile-specific innovations like mobile wallets, payments, and location-based services | Encompasses a broader scope of innovation, including artificial intelligence, big data analytics, and open banking APIs |
| Integration | Seamlessly integrates with mobile device features and third-party apps, enhancing the overall mobile experience | Integrate with various digital tools and platforms, enabling a more comprehensive and interconnected banking ecosystem |
1] Access and Functionality
One of the primary distinctions between mobile banking and digital banking lies in the way users access and interact with banking services. Mobile banking is specifically designed for mobile devices, offering a streamlined and optimized experience tailored to smaller screens and touch-based interactions. The functionality of mobile banking apps is often more focused, prioritizing essential features like account balances, money transfers, and mobile deposits.
In contrast, digital banking encompasses a wider range of digital channels, including desktop computers and laptops, in addition to mobile devices. This broader scope allows for a more comprehensive suite of banking services and features, catering to the diverse needs of users across different platforms.
2] User Experience and Convenience
Mobile banking excels in providing a user-friendly and intuitive experience, leveraging the native capabilities of mobile devices to offer features like biometric authentication, push notifications, and geolocation services. The convenience of mobile banking is unparalleled, allowing users to access their accounts and perform transactions anytime, anywhere, with just a few taps on their smartphone.
Digital banking, while offering 24/7 access to banking services, may require more navigation and effort compared to the streamlined experience of mobile banking. However, digital banking platforms often provide a more comprehensive set of tools and resources, enabling users to manage their finances holistically across multiple devices and channels.
3] Security and Adoption
Both mobile banking and digital banking prioritize security, employing various measures to protect user information and transactions. Mobile banking apps often incorporate mobile-specific security features like biometric authentication and two-factor authentication, leveraging the built-in security capabilities of mobile devices. Digital banking, on the other hand, relies on a range of security protocols across different channels, such as encryption and secure login processes.
In terms of adoption, mobile banking has seen rapid growth, particularly among younger generations and tech-savvy users who value the convenience and accessibility of banking on-the-go. Digital banking, as a whole, enjoys widespread adoption across various age groups and demographics, with increasing popularity among all user segments as digital literacy continues to rise.
4] Innovation and Integration
Mobile banking is at the forefront of innovation, with a strong focus on mobile-specific advancements like mobile wallets, payments, and location-based services. These innovations aim to enhance the overall mobile banking experience, making it more seamless and integrated with users’ daily lives.
Digital banking, in contrast, encompasses a broader scope of innovation, including artificial intelligence, big data analytics, and open banking APIs. These advancements enable financial institutions to offer more personalized and data-driven services, improve operational efficiency, and foster collaboration with fintech partners.
Both mobile banking and digital banking emphasize integration, but in different ways. Mobile banking apps seamlessly integrate with mobile device features and third-party apps, creating a cohesive and enhanced mobile experience. Digital banking, on the other hand, focuses on integrating with various digital tools and platforms, enabling a more comprehensive and interconnected banking ecosystem.
5] Cost and Scalability
When it comes to the development cost of a mobile banking app, mobile banking apps often have a lower upfront investment compared to comprehensive digital banking platforms. Mobile banking apps can be developed and deployed more quickly, with a focus on essential features and mobile-specific optimizations. This makes mobile banking more accessible for smaller financial institutions or those with limited resources.
Digital banking, on the other hand, requires a more significant investment in terms of time, resources, and infrastructure. Building a comprehensive digital banking platform that caters to multiple channels and devices involves a larger scope of development and ongoing maintenance. However, the scalability of digital banking is a key advantage, as it allows financial institutions to expand their services and customer base across various digital touchpoints.
6] Customer Support and Personalization
Mobile banking apps often prioritize self-service features and in-app support, enabling users to resolve common issues and access help directly from their mobile devices. This includes features like in-app messaging, chatbots, and FAQs. The mobile banking experience is also highly personalized, with features like push notifications, location-based offers, and customized dashboards based on individual user behavior and preferences.
Digital banking platforms, while offering self-service options, may also provide more comprehensive customer support through various channels, such as phone, email, and live chat. Digital banking also allows for personalization, but it may be more data-driven and focused on cross-channel consistency, leveraging customer information and analytics to deliver targeted offers and recommendations.
7] Future Trends and Opportunities
The future of both mobile banking and digital banking is shaped by emerging trends and technologies. For mobile banking, the focus is on enhancing the mobile user experience through innovations like augmented reality, voice assistants, and wearable device integration. Mobile banking apps are also exploring new features like financial wellness tools, peer-to-peer lending, and cryptocurrency integration.
Digital banking, as a whole, is evolving towards a more open and connected ecosystem, with the rise of open banking APIs and partnerships with fintech startups. The future of digital banking also involves the adoption of advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT), enabling more intelligent and automated banking services.
As the digital banking vs mobile banking landscape continues to evolve, financial institutions must stay attuned to these trends and opportunities, continuously innovating and adapting to meet the changing needs and expectations of their customers. By embracing the strengths of both mobile banking and digital banking, financial institutions can deliver a holistic and seamless banking experience that combines the convenience of mobile with the comprehensive capabilities of digital.
Which One Should You Invest In?

When it comes to deciding whether to invest in mobile banking or digital banking, financial institutions must consider several key factors:
- Target audience: Understanding the demographics, preferences, and behaviors of your target customers is crucial in determining whether to prioritize mobile banking or digital banking investments.
- Business goals: Clearly defining your business objectives, such as improving customer engagement, reducing costs, or expanding market share, will guide your investment decisions.
- Budget and resources: Consider the available budget and resources for development, maintenance, and marketing of mobile banking or digital banking solutions.
- Competitive landscape: Analyze the offerings of your competitors and identify opportunities to differentiate your mobile banking and digital banking services.
- Regulatory requirements: Ensure that your mobile banking or digital banking investments comply with relevant regulations and security standards.
Ultimately, the decision to invest in mobile banking or digital banking should be based on a comprehensive evaluation of your business needs, customer expectations, and long-term strategic goals. In many cases, a holistic approach that encompasses both mobile banking and digital banking investments may be the most effective strategy for financial institutions seeking to remain competitive and meet the evolving needs of their customers.
For consumers, the choice between mobile banking and digital banking largely depends on personal preferences, lifestyle, and banking needs. Those who value on-the-go convenience and a streamlined user experience may gravitate towards mobile banking, while those who require a more comprehensive set of financial tools and resources may prefer digital banking.
Nimble AppGenie, Your Partner in Financial Innovation
When it comes to developing a cutting-edge mobile banking or digital banking solution, partnering with an experienced mobile banking app development company like Nimble AppGenie can make all the difference. With a deep understanding of the fintech landscape and a track record of delivering innovative banking apps, Nimble AppGenie is well-equipped to help financial institutions navigate the complexities of digital transformation.
Whether you’re looking for the creation of a mobile banking app from scratch or enhance your existing digital banking platform, Nimble AppGenie brings the technical expertise and industry knowledge needed to drive success in the competitive world of digital finance.
Conclusion
The digital banking vs mobile banking debate is not about choosing one over the other but rather understanding the unique strengths and capabilities of each approach. As we have explored throughout this blog post, mobile banking and digital banking are closely intertwined, with mobile banking being a key component of the broader digital banking ecosystem.
Mobile banking has emerged as a game-changer in the financial industry, offering unparalleled convenience, accessibility, and user experience to customers on-the-go. With its focus on mobile-specific features and innovations, mobile banking has transformed the way people interact with their finances, making banking more seamless and integrated with daily life.
On the other hand, digital banking encompasses a wider range of channels and platforms, providing a comprehensive set of financial tools and services that cater to the diverse needs of customers across various devices. Digital banking platforms leverage advanced technology and data analytics to offer personalized experiences, streamline operations, and foster innovation.
FAQs
Mobile banking refers specifically to banking services accessed through mobile devices like smartphones and tablets, while digital banking encompasses a broader range of digital channels, including desktop computers, laptops, and mobile devices.
Both mobile banking and digital banking employ various security measures to protect user information and transactions. Mobile banking often incorporates mobile-specific security features like biometric authentication, while digital banking relies on a range of security protocols across different channels, such as encryption and secure login processes.
Yes, most financial institutions offer both mobile banking and digital banking services, allowing customers to access their accounts and perform transactions through multiple channels and devices seamlessly.
Mobile banking offers unparalleled convenience, accessibility, and user experience, enabling customers to manage their finances anytime, anywhere, with just a few taps on their smartphone. Mobile banking also provides mobile-specific features like biometric authentication, push notifications, and geolocation services.
The choice between mobile banking and digital banking largely depends on your personal preferences, lifestyle, and banking needs. If you value on-the-go convenience and a streamlined user experience, mobile banking may be the best fit. If you require a more comprehensive set of financial tools and resources, digital banking may be the way to go.
Some of the key challenges in building a banking app include ensuring robust security, delivering a seamless user experience across different devices, complying with regulatory requirements, and integrating with existing banking systems and third-party services.
To find the best banking apps for your needs, consider factors such as the app’s user interface, range of features, security measures, customer support, and user reviews. It’s also essential to choose a banking app from a reputable financial institution that aligns with your banking needs and preferences.
Some of the latest banking app trends include the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning for personalized experiences, the adoption of blockchain technology for secure transactions, the rise of open banking APIs for enhanced collaboration and innovation, and the incorporation of financial wellness tools and budgeting features.
The cost for development of a banking app can vary widely depending on factors such as the app’s complexity, features, security requirements, and the development team’s expertise. On average, the cost can range from several thousand to several hundred thousand dollars, with ongoing maintenance and updates adding to the overall investment.
When choosing an app development company, consider factors such as the company’s experience and expertise in the fintech industry, their portfolio of successful banking app projects, their development process and methodology, their communication and collaboration approach, and their ability to deliver high-quality, secure, and scalable solutions that align with your business goals and customer needs.

Niketan Sharma is the CTO of Nimble AppGenie, a prominent website and mobile app development company in the USA that is delivering excellence with a commitment to boosting business growth & maximizing customer satisfaction. He is a highly motivated individual who helps SMEs and startups grow in this dynamic market with the latest technology and innovation.
Table of Contents





No Comments
Comments are closed.