Transactions of all sorts have become an integral part of the common man’s daily life.
Every business and entity uses a transaction processing system, from a basic grocery store to an online portal.
You see, every exchange you make seems super easy, as all you have to do is make the payment instantly and get your goods. However, that is not what happens in the background.
Every business transaction has a set flow that follows different parameters to fulfill the expected outcome. And all of it happens in a matter of seconds, thanks to modern technology.
Several robust software programs are being used today to ensure that backend processes are flawless.
One such software is the Transaction Processing System. In this post, let us take a closer look at Transaction Processing Systems, what they are, and how they function. We will also be exploring types of TPSs and their components.
What is a Transaction Processing System?
A Transaction Processing System (TPS) is a computer-based system designed to handle an organization’s business transactions. It mainly deals with data-related tasks such as collecting, storing, updating, retrieving, and processing information.
For instance, placing an order, recording the sale, checking, updating, and managing inventories, taking payable accounts, and ensuring the smooth financial operations, are all part of a single transaction.
Now, dedicating human resources to manage all of them is neither feasible nor productive, as completing these steps manually will take a lot of time. This is where Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) come into play.
These are high-speed, secure, and multi-tasking systems that take care of all the aspects involved in a transaction and complete them seamlessly.
A key player in this system is the database that is being used to power the transaction processing system.
Now talking about Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) is also a type of TPS that focuses on managing internet-based transactions, such as online banking or order placements, and enables real-time processing across banking, fintech, and retail industries.
Since there are different tasks that these systems have to perform, they have different components attached to them.
Components of a Transaction Processing System
A well-functioning Transaction Processing System is built based on 4 components. These components take care of different aspects to fulfill the requirements of the users.
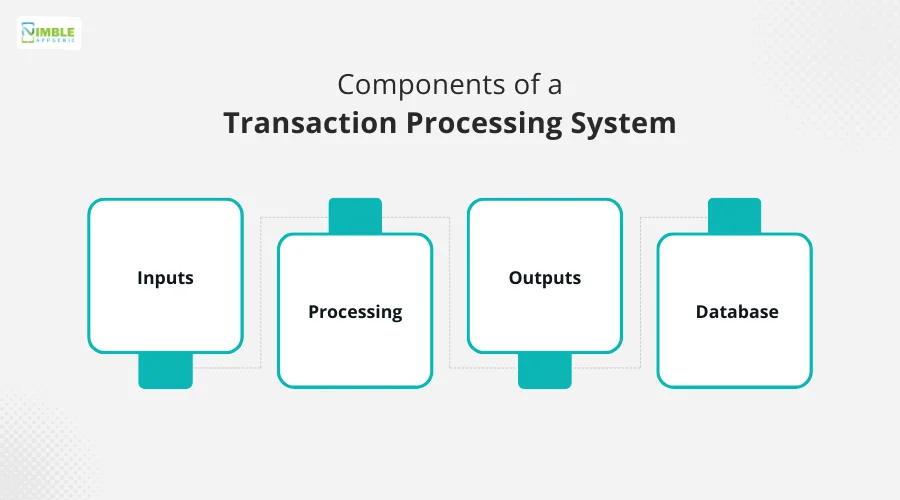
Here are the components that make up the entire functionality of the Transaction Processing System-
♦ Inputs
For every transaction that you need to process, there has to be some information that you feed to the system. This information can be anything from an order, inventory information, or payment details.
Inputs may come in several forms, such as:
- Customer purchase details
- Payment and billing information
- Supplier order entries
- Product return requests
- Customer feedback forms
- Account balance inquiries
♦ Processing
All the information that you feed to the TPS is then processed based on your requirements.
For instance, if the input is related to a customer order, the system will help you calculate the order value along with the required discounts that can be offered. All of it is done instantly.
The system performs a variety of operations to handle transactions efficiently, including:
- Total Order, taxes, and applicable discounts
- Validating customer details and financial transactions
- Updating stock and inventory records in real-time
- Creating invoices, receipts, and billing statements
- Processing returns, refunds, and exchanges
- Applying loyalty points or promotional offers
- Monitoring transaction errors and exceptions
♦ Outputs
Once your input is processed, the transaction processing system (TPS) shows the information generated. It can help you generate invoices, show order status, trigger notifications, and more.
The results of transaction processing can be displayed in multiple ways, including:
- Show transaction history or alerts to the user
- Generating printed or digital invoices, bills, and receipts
- Updating records in customer or financial databases
- Sending SMS or push notifications for transaction status
- Producing reports for management or accounting purposes
- Exporting data to external systems or partners
- Providing confirmation messages via chatbots or web portals
♦ Database
This is the component where all the magic happens. All the transaction information, be it the order value, final order payment, customer information, payment details, and every other detail related to the transaction, is saved.
This helps in automating bulk processes such as payroll, maintaining sales records, etc. All these components work together like a well-oiled machine to bring the best results out of a TPS.
-
Supplier information: contact details and order history
-
Marketing data: campaign results, customer preferences, and engagement metrics
-
Service requests and support tickets: issue details and resolution status
-
Loyalty programs: points earned, redemption history, and membership tiers
-
Regulatory compliance records: tax filings, audit logs, and certifications
-
Inventory movement logs: stock transfers, returns, and adjustments
-
Pricing and discount policies: current offers, promotions, and historical changes
When all of these aspects are sorted for a transaction, you can rely on the accuracy and efficiency in data management & operations.
Types of Transaction Processing Systems: Pros & Cons
Knowing how crucial the system is, you might have become curious about what type of solutions are implemented in the form of a TPS.

There are two types of Transaction Processing Systems-
► Real-time Processing
As the name implies, it helps with processes that are real-time and require instant output.
These systems are more useful in everyday transactions for online banking, making reservations, and more.
- Pro: It takes less time to respond and is highly efficient for real-time accuracy.
- Con: Significantly more expensive to implement.
Real-time processing systems are best suited for scenarios where immediate data updates and instant responses are critical, including:
- Online banking and financial transactions
- Stock market trading and securities exchanges
- Airline and travel reservation systems
- Point-of-sale (POS) systems in retail
- Emergency response and hospital monitoring systems
- Traffic management and smart city control systems
- Live auctions and bidding platforms
- IoT device monitoring and industrial automation
► Batch Processing
Highly recommended for grouped transactions, batch processing systems are used more in the corporate world, especially for payroll processing and generating weekly/monthly reports. Automated invoices are also a great use case.
- Pros: Highly cost-effective solution, can help in simplifying and automating build transactions.
- Con: Delayed processing & higher waiting times.
Batch processing systems are ideal for situations where large volumes of data need to be collected and processed together at scheduled intervals, such as:
- Data Backup: Securing large datasets in scheduled intervals
- Billing Cycles: Processing monthly bills for multiple customers at once
- Inventory Updates: Refreshing stock records in bulk
- Payroll Tax Filing: Calculating and submitting taxes for all employees together
- Customer Statements: Generating account summaries in batches
- Order Processing: Handling multiple purchase orders simultaneously
- Financial Reconciliation: Balancing accounts for large transaction sets
- Subscription Renewals: Updating memberships and payments in bulk
Based on the requirements of a business, one can easily choose a transaction processing system. Both of these simplify the work in different industries.
However, the core objective of implementing a TPS is the same, which is adding convenience to complex processes involved in any exchange or transaction.
Benefits of Opting for a Transaction Processing System
The biggest advantage of using a TPS for your business is that it frees your manpower to do better things.
Several manual tasks, such as making invoices, checking and managing inventory, and more, can be done easily through a transaction processing system, as it automates the entire process.
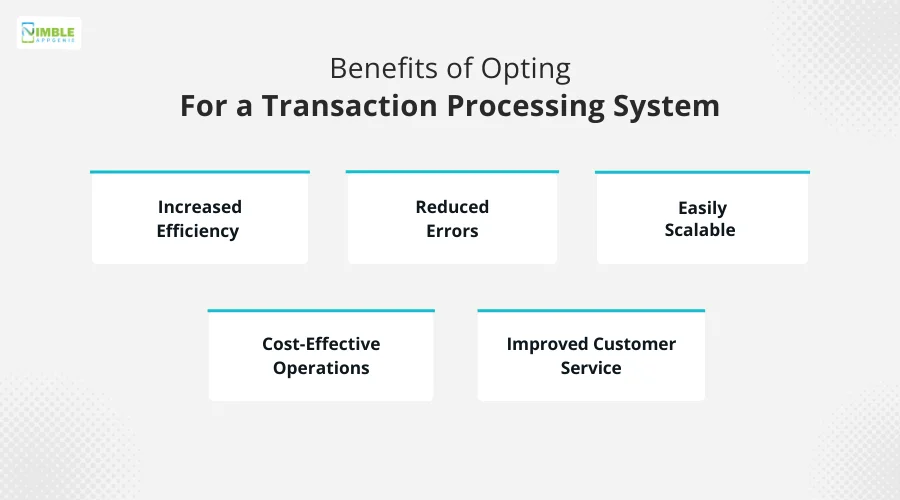
Other than that, here are some of the key benefits that it offers –
- Increased Efficiency
- Reduced Errors
- Easily Scalable
- Cost-Effective Operations
- Improved Customer Service
With all these advantages that Transaction Processing Systems bring along, it is understandable that using a TPS is a vital decision.
However, it is not easy to implement as it requires a lot of expertise to build a Transaction Processing System of your own.
Check out the steps that you can use to build a process of your own.
How to Develop a Transaction Processing System?
Transaction Processing Systems are used in different industries, and a customized system is built for each industry.
Some opt for ready-made solutions and manage their day-to-day transactions, while others go the extra mile and build one from the ground up.
In case your business requires a custom solution, you can follow the given steps –
Step 1 – Identify Your Use Cases
Developing a Transaction Processing System can be simplified and fruitful when done based on what you want it to do for you.
What is the niche of your business? What type of TPS will work best for your business? What are the tasks you will be performing on the system regularly?
Identify the answers to these questions by discussing your vision with the experts to start the process.
Step 2 – Select the Features You Require
Based on the answers and discussion, choose the features you need. Identifying the exact features can help you stay focused on why you want the system instead of cluttering your TPS with unnecessary gimmicks.
Choose the features that you would want today and in the future when you plan to scale your business. This way, you need not worry about changing the existing features and system, as it makes it future-proof.
Step 3 – Let the Experts Develop the Solution
Once you have pre-planned the system with the help of the development team, it’s time you leave the rest of the process to the experts.
Based on the requirements, our highly qualified developers will build and develop every functionality as you want it to be.
Usually, experts choose the financial tech stack for a Transaction Processing System, including APIs and security considerations, based on the software requirements.
Step 4 – Testing & Deployment
Once the development team is through with the transaction processing system, it is delegated to the testing experts.
They ensure that the application performs as expected and there are no issues in the final build.
Several test cases are designed to check the efficiency of the system before deploying it for implementation.
With all these steps, you get yourself a customized TPS. Working on a Transaction Processing System helps your business stay streamlined and automated.
With this time-saving system, you can allocate your resources better and do more with the available bandwidth.
Functions of a Transaction Processing System That Make it Worth It!
You may be wondering how a single Transaction Processing System can help you save all the resources and make your business more efficient. Well, the answer to that lies in the functions that it offers.
Here are some primary functions that a TPS helps you with –
- Data Input: Entering data in different formats as required.
- Data Processing: Processing the data transactions faster and accurately.
- Data Output: Generating desired output in the form of a calculation, reports, estimates, etc.
- Data Storage: All the storage entered in the system is stored for future use and calculations.
- Data Validation: Saved transaction data can be used to validate information entered in the system.
- Data Integrity: A set of rules is implemented to ensure that errors and inconsistencies in the data can be regulated easily.
- Reports & Analytics: Your TPS can easily help you generate reports for all the data that it houses.
Other than these, several additional functions can be made available depending on your requirements and the development team you hire. It is crucial to find the right partner to get the job done.
Transaction Processing Systems – Examples Explained!
Transaction Processing Systems have found their way into every sector of the business realm. These highly efficient systems ensure that the volumes of transactions do not affect the quality of service and can be managed easily.
Needless to say, having a Transaction Processing System in place is a game-changer for every field.
Here are some real-world examples of TPS in action:
1. Retail
-
Online Retail Order Processing: E-commerce websites like Amazon and Flipkart use TPS to manage online purchases. When a customer places an order, the system processes payment, updates stock levels, generates invoices, and triggers shipping notifications.
- Point-of-Sale (POS) Systems: When you purchase at a supermarket like Walmart using a card, the POS system (such as Square or similar platforms) acts as a TPS. It records your purchase, updates inventory, and completes the payment transaction.
- Self-Checkout Kiosks: At stores like Target or Costco, self-checkout machines allow customers to scan items, pay, and complete transactions independently. The TPS handles item scanning, calculates totals, processes payments, and updates inventory automatically.
2. Banking & Financial Services
-
Mobile Banking Apps: Applications like HDFC Bank Mobile or Paytm use TPS to process fund transfers, bill payments, and account updates in real time, ensuring secure and accurate transactions.
-
Credit/Debit Card Processing: Whenever you make a purchase using a credit or debit card, TPS verifies the card, checks the available balance, approves the transaction, and updates both the merchant’s and customer’s accounts instantly.
-
ATMs: Withdrawing cash or checking your balance at an ATM involves a TPS. It verifies your identity, retrieves account information, updates balances, and dispenses cash securely.
3. E-commerce
- Inventory and Fulfillment Management: When customers place orders online, the TPS updates inventory in real time, triggers warehouse operations, and schedules shipments to ensure timely delivery.
-
Shopping Platforms: Adding products to your cart and completing a purchase on sites like Amazon or Flipkart relies on a TPS. It processes your order, validates payment details, and updates stock levels instantly.
4. Stock Markets & Investment Platforms
-
Trading Systems: Every trade on exchanges like the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) or Nasdaq is handled by a sophisticated TPS. It matches buyers and sellers, updates stock prices, and electronically settles transactions.
5. Travel & Aviation
- Online Flight Booking Systems: Airline websites and apps like Indigo or Emirates use TPS to check seat availability, process payments, issue tickets, and send confirmation emails instantly.
- Hotel Reservation Systems: Platforms like Booking.com and OYO rely on TPS to manage room availability, confirm bookings, process payments, and update property records in real time.Airline Reservation Systems: Booking a flight online uses a TPS. The system checks seat availability, verifies payment, and generates tickets and confirmation emails in real time.
TPS is integrated across diverse industries, ensuring accurate, efficient, and often real-time transaction processing to support smooth business operations.
If you are thinking that having a TPS means having software that adds to the complexity of your everyday tasks, then you are mistaken.
Looking for a Transaction Processing System? Nimble AppGenie Can Help!
While a TPS can be customized to fit the needs of a business, it is crucial to find a development partner who can understand your requirements and execute the plan as you want it done.
There are several Transaction Processing System developers available in the market; some offer pre-built systems, while some offer custom-built solutions.
If you want to go for a customized solution, look no further and start talking to our experts. With a decade of experience in fintech app development services, our developers understand the market needs quite well.
Which makes them the perfect companions to help you find the right fit for your business.
One of the core mistakes that people make while choosing a Transaction Processing System is that they go for one that is more complex and offers tons of unnecessary features.
While the ability of these features seems extraordinary, there’s hardly any practicality involved.
This is where Nimble AppGenie can guide you. Share your requirements with us and we will build a dedicated system tailored to your requirements and convenience.
Reach out today and let us help you out!
Conclusion
Getting your work done faster and better is a dream for every business. A Transaction Processing System not only enables you to get things done quicker, but also makes it more efficient and always available.
These scalable solutions are highly responsive and give you the best experience to finish the process easily.
Needless to say, it is a management system that helps you process things faster and keep a record of them.
It is vital to hire an experienced team of developers to help you understand the components, types, and attributes of the system and help you build the most suitable solution for your business.
Hopefully, this post gives you enough insights into what a Transaction Processing System is.
FAQs
There are 2 ways you can get your Transaction Processing System-
1. Get one built from scratch.
2. Choose a pre-built system.
If you want to build one from scratch, you need a proper partner to guide you with the TPS development services. Whereas you can simply pay a subscription fee or a one-time charge for a pre-built system.

Niketan Sharma, CTO, Nimble AppGenie, is a tech enthusiast with more than a decade of experience in delivering high-value solutions that allow a brand to penetrate the market easily. With a strong hold on mobile app development, he is actively working to help businesses identify the potential of digital transformation by sharing insightful statistics, guides & blogs.
Table of Contents



No Comments
Comments are closed.