The collection of user data has become a common practice for applications to offer a personalized experience.
While businesses are working to make the most of the available information, using this data irresponsibly can cause serious risks related to individual privacy.
These privacy concerns are the reason that, when building any application, there are several compliance requirements and regulations that businesses have to follow.
General Data Protection Regulation is one of the most important and compliant applied regulations that directly deals with the data protection rights of the user.
The idea behind imposing this regulation is to make sure that all the data shared by a user is accounted for and no organization misuses it in any way.
If you are planning to launch any sort of mobile application of your own, you should keep GDPR compliance at the top of your list.
With that said, it is also a fact that people building any sort of application for the first time are not completely aware of what GDPR is and why it is an important regulation to comply with.
If you, too, are on the same page and want to learn more about this compliance, then this is the blog for you!
In this post, let’s explore GDPR compliance and understand everything about it.
What is GDPR?
General Data Protection Regulation, commonly referred to as GDPR, is a data privacy law enacted by the European Union on May 25, 2018, replacing the previously used 1955 Data Protection Directive.
With the help of GDPR, the EU government plans to put stricter data protection policies so that every EU citizen can enjoy privacy, and organizations working in the region take data privacy seriously.

But how? Well, usually people give up all their information without even knowing where and why it will be used. GDPR allows users from EU countries, as a right, to know how an organization is using their information and user-generated data.
The General Data Protection Regulation defines the basic requirements that a business or an application must comply with to process the information legally, without having to worry about any consequences.
These requirements should be met by all businesses, public authorities, and organizations.
GDPR is designed to protect different data subjects and the personal data of people living in the European Union region. Anyone residing in the region, irrespective of their nationality.
That means if someone is present in the EU and is using a service that is protected by GDPR, they have all the rights that GDPR implies.
Who Does the GDPR Apply To?
The GDPR applies to all organizations that are involved in public businesses in the EU/EEA region.
This implies that the regulations have extraterritorial reach, allowing them to be imposed on all types of organizations, even if they are foreign to the EU region, if they are involved with the people of the region, directly or indirectly.
To understand the application of GDPR more clearly.
Here is the classification of entities that it directly applies to:
- Services Originating from the EU/EEA Region: The guidelines are directly applicable to organizations that are based in the EU/EEA.
- Services Targeting EU/EEA Population: If the organization is foreign, i.e., based in another country, but still offers its services to the EU/EEA region, the GDPR guidelines are directly applicable.
- Apps/Services/Organization Monitoring EU/EEA Behavior: Any specific app, service, or organization that is designated to monitor, control, or process data in any way, irrespective of where they originate from.
Other than these, any individual who processes personal data other than for personal or household activities. In simple words, any person who is involved in data processing related to professional, commercial, or public activities. The idea is to keep the general data of any individual secure.
What Rights Does the GDPR Grant to Individuals?
The GDPR applies to all organizations that deal with data, giving individuals direct access to data privacy norms that they can claim.
With the rise in the digitization of everything, accessing user data through their online footprint has become significantly simpler.
In such cases, users often overlook the cost in terms of privacy when a single click allows them to sign in and explore the service/app they want.
This is why the implementation of GDPR is crucial, as it offers rights to the individuals using a service so that their data is safe, privacy is intact, and they can take action if any of these is violated.
- Right to Information: A user should be able to be informed.
- Right of Access: A user should be able to access their data.
- Right to Rectification: A user should be able to rectify and make changes to their data.
- Right to Erasure (Right to Be Forgotten): If a user wants, they should be able to erase their presence from the platform easily.
- Right to Restriction of Processing: A user can object to the processing of data whenever required.
- Right to Data Portability: A user should be able to request and receive their data from a data controller in a structured, commonly used, and machine-readable format.
- Right to Object: If data is misused, the user has the right to object.
- Rights concerning Automated Decision Making and Profiling: If the service offers automated decision making, users should be able to see the decisions and deny them when necessary.
What are the GDPR Principles for Businesses?
Since the compliance regulates every data point, it requires the services to be catered out in a certain way, under certain circumstances, and fulfill some contractual obligations.
These contingencies of implementation are also the mandatory requirements of GDPR that any business has to follow.
In hindsight, these requirements are also considered GDPR compliance principles.
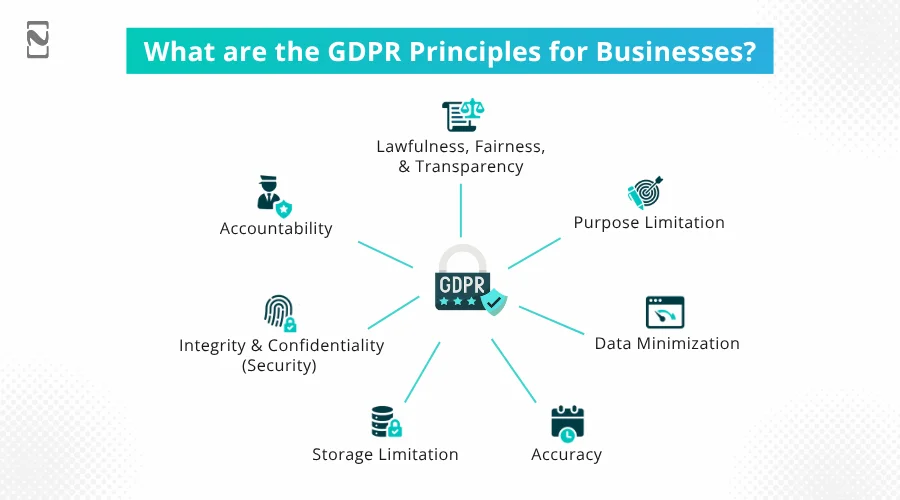
Here are the principles:
-
Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency
Every organization should have a legally valid reason to collect and process personal data. The mode of data collection should be fair, legal, consistent, and consensual.
-
Purpose Limitation
This principle refers to limiting the usage of personal data to the purpose for which it was collected. It should not be used for anything other than what it is intended for unless consent is taken.
-
Data Minimization
GDPR requires applications to minimize the collection of personal data and limit it to only necessary details, specific to a function, and nothing else should be collected.
-
Accuracy
All the information that a business collects should be accurate and kept up to date. There should be specific provisions to ensure that older data is removed or rectified timely.
-
Storage Limitations
Personal data that a business collects should be stored securely and should only be stored until the data is required.
-
Integrity and Confidentiality(Security)
The integrity and confidentiality of the data that a business collects should be properly protected, and security measures must be put in place.
-
Accountability
Every business in the EU/EEA should be accountable towards GDPR compliance, and most have all the provisions to impose it properly.
Other than these principles, there are some additional GDPR requirements that every business should pay attention to.
These include:
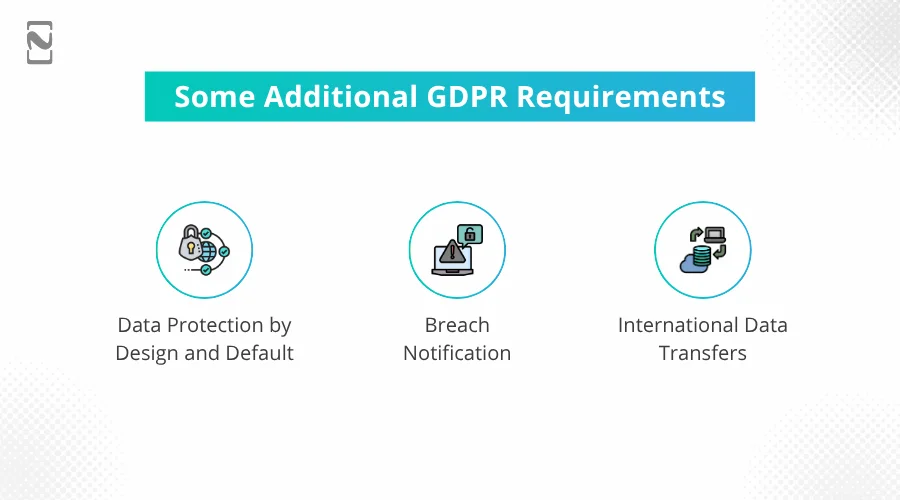
-
Data Protection by Design and Default
Data protection by design and default is a GDPR compliance requirement that states that the data any business collects should be, by default, used and processed only when a specific feature is invoked.
-
Breach Notification
If a business finds that its data is being breached or personal information of the user is being shared or used outside of their knowledge or the rights that GDPR gives the user, the business is obligated to notify the user.
-
International Data Transfers
GDPR strictly restricts personal data transfers outside the EU/EEA to ensure that the users are protected from unnecessary data leaks.
All in all, the focus of GDPR is always on keeping personal data safe and secure. If an organization does not comply with them, they are penalized.
Find out about GDPR compliance penalties for violating the GDPR in the next section.
Penalties & Consequences for Violating the GDPR
The penalties for violating the GDPR are categorized into two tiers. These tiers depend on the type of violation that a business commits or the issue that leads to these violations.
Here are the fines associated with the tiers:
- Tier 1 Fines: 2% of the organisation’s global annual revenue or €10 million, whichever is greater..
- Tier 2 Fines: 4% of the organization’s global annual revenue or €20 million, whichever is greater.
Other than these fines, there are some severe consequences.
These consequences include:

- Reputational Damage: Since these are public organizations and businesses, the reputation of the firm is severely affected, which further destroys the reputation of the company.
- Legal Action: If the data breach has affected an individual, it can lead to legal action, landing the business in severe trouble. Lawsuits related to GDPR often convert into class actions as the data is of hundreds or thousands of users, which can directly cause severe financial damage to the business.
- Corrective Orders: If the damage is not severe and can be corrected with any measures, the business can be directed to implement them, irrespective of what impact those actions may have on the business.
With all these penalties and consequences, it should be clear to all businesses that it is better to stay compliant with GDPR rather than looking for a shortcut.
However, the majority of businesses are not aware of all these consequences because they are not guided properly.
If you own a business and are planning to develop an application for the same, make sure you hire developers who know how to build an app that is GDPR compliant.
How Nimble AppGenie Can Help You in Obtaining GDPR Compliance
Nimble AppGenie has years of experience in offering Secure Software Development that not only offers robust solutions but also takes compliance and regulations into consideration.
While building a GDPR compliant solution, your developer needs to take care of several things, such as Consent Management Integration, Data Minimization and Anonymization, Robust Data Security, Data Subject Request (DSR) Facilitation, GDPR-Compliant Analytics, and Implementation Support.
Not all app development services can deliver on all these fronts, especially without going over budget.
Hence, we recommend that you connect with our experts and let us develop an ideal solution for you that is GDPR compliant and gets the job done!
Hope you find all the information you were looking for on GDPR compliance. If you have any doubts, feel free to connect with our experts. Thanks for reading, good luck!
FAQ
Organizations that fail to comply with GDPR can face fines of up to €20 million or 4% of their annual global revenue, whichever is higher.
Key principles of GDPR compliance include obtaining consent for processing personal data, ensuring data accuracy and security, and providing individuals with the right to access, correct, and erase their data.
GDPR came into effect on May 25, 2018.

Niketan Sharma, CTO, Nimble AppGenie, is a tech enthusiast with more than a decade of experience in delivering high-value solutions that allow a brand to penetrate the market easily. With a strong hold on mobile app development, he is actively working to help businesses identify the potential of digital transformation by sharing insightful statistics, guides & blogs.
Table of Contents


No Comments
Comments are closed.