Why is KYC and AML compliance critical for fintech in 2026?
Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) are essential in the upcoming years as they act as a defensive wall against surging AI-driven financial crimes.
Whatever be your pain points, fraud attempts, non-compliance, or increased digital onboarding times, AML KYC regulations fintech is your ultimate savior.
In 2026, you are going to witness a smooth shift of fintech regulation from reactive mandates to a predictive, data-backed model, where compliance will be directly embedded into system architecture.
Fintech founders, CEOs, Risk & Fraud Managers, chief compliance officers (CCOs), CTOs & technology leaders, financial institutions & banking partners, CTOs, technology leaders, and RegTech & compliance solution buyers should ensure they follow KYC best practices and meet the AML compliance checklist.
How fintech should implement KYC and AML to make the most of them?
The fintech compliance guide will address all your relevant queries, like what is AML and KYC in fintech, crucial KYC and AML compliance for fintech, the role of AI in AML and KYC, and more.
Let’s get the ball rolling!
Understanding KYC and AML in the Modern Fintech Ecosystem
In the modern fintech space, compliance is not a one-time process but a consistent, tech-driven discipline.
What is AML and KYC in fintech?
Let’s dive deeper to know.
What Is KYC (Know Your Customer) in Fintech?
Know Your Customer (KYC) is a process that fintech firms opt for to assess risk levels, verify customers’ identity, and guarantee that users are exactly who they assert to be before and during the business journey.
Simply put, KYC in fintech takes charge, ensuring digital financial platforms assess risk, verify customer identities, and consistently monitor users to avoid regulatory violations and fraud.
Key Objectives of KYC in Fintech
- KYC ensures regulatory compliance across distinct jurisdictions
- It keeps away fraud, identity theft, and impersonation
- KYC fosters trust in digital financial services
- It enables risk-based customer onboarding
Core Components of Fintech KYC
- Identity Verification: Government-issued ID checks, liveness detection, and biometric verification
- Ongoing Monitoring: Ongoing evaluation of customer activity rather than one-time checks
- Customer Risk Profiling: Assessing risk based on user type, transaction behavior, and geography
What Is AML (Anti-Money Laundering) in Fintech?
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) is a set of regulations, processes, and laws created to pinpoint, avoid, and report financial crimes, incorporating terrorist financing, money laundering, and sanctions evasion.
In other words, AML in fintech focuses on recognizing suspicious behavior, monitoring transactions, and reporting financial crimes to regulators, utilizing the strength of intelligence-based systems.
Objectives of AML in Fintech
- AML detects dubious financial activity in real time.
- It meets every global and local regulatory requirement.
- AML discourages the misuse of fintech platforms for illegal purposes.
- AML safeguards the financial ecosystem from systemic risk.
Core AML Activities in Fintech
- Sanctions & Watchlist Screening: AML checks customers against global sanctions, PEP (Politically Exposed Persons), and unfavorable media lists.
- Transaction Monitoring: It identifies high-risk or unusual transaction patterns.
- Suspicious Activity Reporting (SAR): Anti-Money Laundering (AML) report flagged moves to regulators within specified timelines.
KYC vs AML: Key Differences and Interdependencies
KYC and AML are generally discussed together as they serve an interconnected purpose within fintech compliance frameworks, but are distinct.
Let’s check it out through a comparative study between these two.
Key Differences Between KYC and AML
| Aspect | KYC | AML |
| Primary Focus | Customer identity verification | Transaction and behavior monitoring |
| Timing | At onboarding and constantly | Continuous throughout the relationship |
| Scope | Who the customer is | What the customer does |
| Tools Used | ID verification, risk profiling, and biometrics | Transaction monitoring, fintech, and sanctions screening |
| Objective | Prevent fraud and impersonation | Prevent money laundering and financial crime |
By 2026, regulators expect fintechs to implement integrated KYC-AML frameworks to ease the identity verification, transaction monitoring, and risk scoring as a single, consistent compliance system.
Together, KYC and AML form a complete compliance framework that supports fintechs and lets them stay safe from fraud and financial crime.
Why KYC and AML Compliance Is More Challenging for Fintechs in 2026
With the transformation of financial services, the complexity of KYC and AML compliance for fintech firms is also increasing.
Next year, fintech institutions are going to operate in more interconnected, faster, and regulated environments, so compliance is technically demanding and mission-critical in 2026.
Key reasons why KYC and AML compliance are tough to attain:
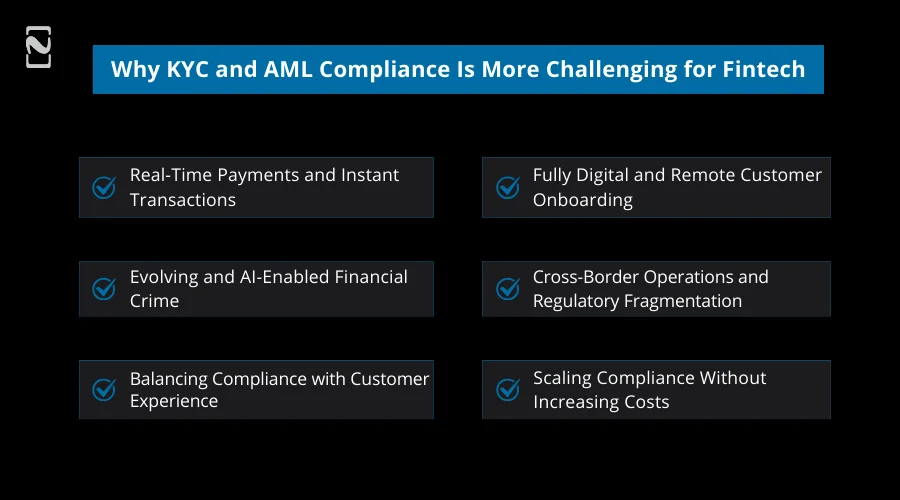
1. Real-Time Payments and Instant Transactions
The increasing demand and execution of instant lending, real-time payments, and embedded finance are leaving minimal to no time for manual compliance checks.
Challenges Include:
- Locating suspicious activity in milliseconds
- Balancing pace with regulatory accuracy
- Monitoring increased transaction volumes with no delay
Necessity: Fintech companies should operate real-time AML systems that pinpoint risk before funds are permanently moved.
2. Fully Digital and Remote Customer Onboarding
Fintech institutions depend entirely on 100% digital onboarding, eliminating the need for face-to-face verification or physical branches.
No doubt, it boosts customer experience and scalability, but it also increases the exposure to:
- Document forgery at scale
- Synthetic identities
- Deepfake risks and identity fraud
Necessity: Regulators want fintech firms to resist such risks with biometric KYC solutions, continuous monitoring, and advanced identity verification, increasing the complexity for compliance.
3. Evolving and AI-Enabled Financial Crime
To combat the traditional controls, financial criminals are increasingly using AI, synthetic data, and automation.
Core emerging threats are:
- Swift funds move through complex networks
- Transaction laundering across distinct platforms
- AI-generated identity fraud
Necessity: Fintech should stay compliant, and for that, they must adopt intelligence-driven AML models, not just static rule sets.
4. Cross-Border Operations and Regulatory Fragmentation
From day one, various fintech companies have served a global clientele across multiple jurisdictions.
They encounter the following challenges:
- Diverse definitions of risky customers
- Distinct data privacy and reporting needs
- Conflicting KYC and AML regulations
Necessity: Fintech should craft region-aware compliance frameworks that internationally scale without breaching local laws.
5. Balancing Compliance with Customer Experience
Customers expect minimal documentation, smooth digital journeys, and instant onboarding.
However, regulators want complete risk assessment, constant monitoring, and powerful verification.
Necessity: Companies should provide trusted compliance experiences, or risk regulatory penalties and customer churn.
6. Regulatory Scrutiny of AI and Automation
As fintech firms leverage the power of AI to scale compliance, regulators are now closely investigating how AI decisions are made.
Key challenges:
- Upholding human oversight in risky cases
- Keeping away from bias in automated decisions
- Guaranteeing the explainability of AI models
Necessity: Fintech must strike a balance between innovation and robust AI governance, accountability, and documentation.
7. Scaling Compliance Without Increasing Costs
With the expanding fintech companies, the compliance costs also rise rapidly than revenue.
Challenges are:
- Integrating compliance across new partners and products
- Handling huge volumes of false positives and alerts
- Retaining and hiring skilled compliance experts
Necessity: Successful fintech firms should acknowledge compliance as a scalable technology function, not as a manual overhead.
In 2026, fintech will likely find KYC and AML compliance more challenging because of real-time transactions, digital-only onboarding, AI-driven financial crime, boosted regulatory scrutiny, and cross-border operations.
Global KYC and AML Regulatory Landscape for Fintech in 2026
Next year, the global KYC and AML regulatory landscape for fintech is anticipated to move from completely technical compliance to notable effectiveness, harnessing advanced technologies, like AI, for continuous risk-based monitoring.
Fintech companies running across borders should adhere to international standards while switching to regional regulatory nuances.
International Standards Shaping Fintech Compliance

1. Financial Action Task Force (FATF)
The major global authority, the FATF, sets AML and KYC standards. Its recommendations underscore:
- Risk-based compliance models
- Accountability for automated and AI-driven decisions
- Real-time transaction monitoring
- Ongoing customer due diligence
2. Basel AML Principles
Yes, Basel guidelines have been banking-focused traditionally, but they boost the impact of fintech regulations by:
- Demanding senior management accountability,
- Supporting robust governance frameworks, and
- Promoting integrated risk management across channels and products.
3. Global Force for Digital Identity
Besides, international identities are embracing interoperable digital identity frameworks, leading to:
- Powerful fraud prevention,
- Diminished duplication of KYC checks. and
- Rapid cross-border onboarding.
Regional Regulatory Expectations
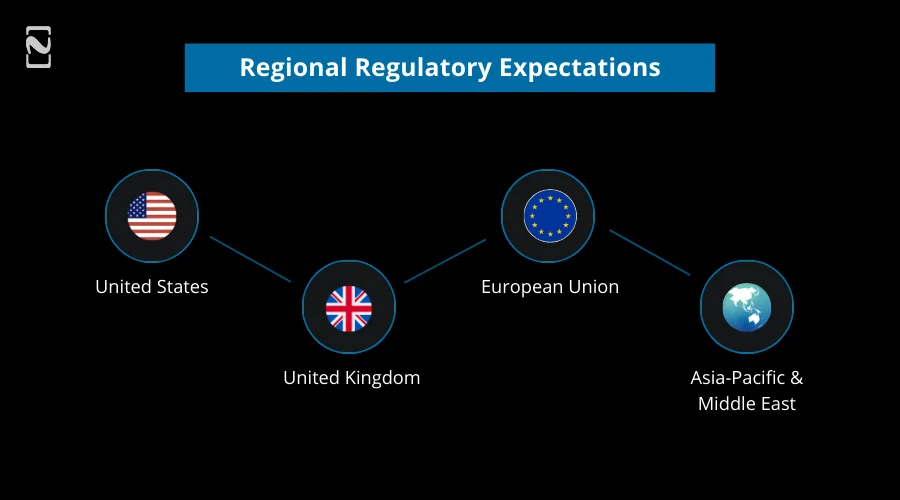
1. United States
- Supervision by FCEN (Financial Crimes Enforcement Network) under the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) and AMLA (Anti-Money Laundering Authority).
- Increased inspection of AI-based transaction monitoring, crypto and digital asset fintechs, and real-time payment platforms.
- Strong projection for suspicious activity reporting (SAR) precision and timeliness.
2. United Kingdom
- FCA (Financial Conduct Authority) supports tech-powered compliance.
- The emphasis is on consumer protection, governance of AI and automation, and unbiased onboarding practices.
- Presumptions for fintechs to showcase proactive risk management.
3. European Union
- Seamless implementation of the EU Anti-Money Laundering Authority (AMLA).
- Severe oversight on risky fintechs.
- Increased harmonization across different member states.
- Increased focus on data privacy (GDPR alignment) and explainability of automated decisions.
4. Asia-Pacific & Middle East
- Swift adoption of fintech-friendly yet firm regulatory models.
- Rising penalties for AML failures with scaling fintech adoption.
- Robust support for National digital identity systems and digital onboarding.
What Regulators Expect from Fintechs in 2026
Regulators envision fintech firms to implement AI-governed and auditable KYC and AML systems that maintain an equilibrium between transparency, innovation, and customer protection.
Regulatory is expected to surpass the boundaries of basic compliance checklists.
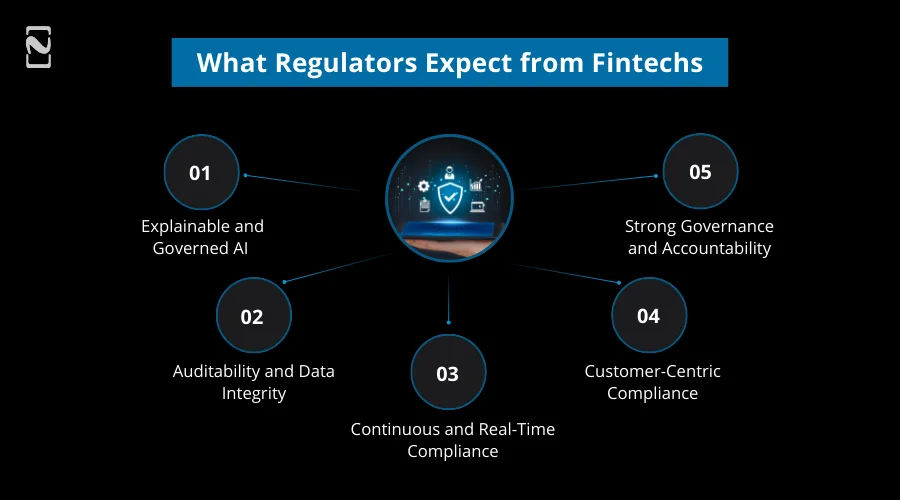
- Explainable and Governed AI
- Auditability and Data Integrity
- Continuous and Real-Time Compliance
- Customer-Centric Compliance
- Strong Governance and Accountability
Core KYC and AML Compliance Requirements for Fintech Companies
Fintech companies looking to operate sustainably and legally should implement continuous, powerful, and auditable KYC and AML frameworks.
Regulators no longer go for static, checklist-backed processes. Instead, they want compliance programs to be technology-powered, risk-based, and outcome-oriented.

1. Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) in fintech includes customer identity verification, risk assessment, and monitoring level confirmation needed throughout the customer lifecycle.
It is the base of fintech compliance that ensures fintech brands comprehend who their customers are, what risk level they bear, and how that risk needs to be managed.
Key CDD Requirements in 2026
- Identity Verification: CDD performs digital verification utilizing government-issued IDs, biometrics, and liveness detection.
- Risk-Based Onboarding: It applies diverse verification levels based on customer risk.
- Customer Profiling: CDD classifies according to geography, customer type, risk indicators, and transaction intent.
2. Ongoing Monitoring and Continuous Risk Assessment
Fintechs should implement continuous monitoring to ensure real-time updation of customer risk profiles with behavioral change.
Key Elements of Continuous Monitoring
- Behavioral Analysis: Continuous monitoring identifies variations from normal customer behavior.
- Transaction Monitoring: It detects unusual transaction patterns across channels.
- Dynamic Risk Scoring: Ongoing monitoring automatically adjusts customer risk levels based on new activity.
3. Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD)
EDD applies to transactions and customers that pose fraud risks or increased money laundering.
When to Choose EDD?
- Complicated ownership structures
- Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs)
- Unusual or high-value transaction behavior
- Customers from sanctioned or high-risk jurisdictions
EDD Requirements for Fintechs
- Ongoing and intensified monitoring
- Deeper identity verification and source-of-funds checks
- Senior management approval for onboarding or continuation
4. Sanctions, Watchlists & Adverse Media Screening
Sanctions and watchlist screening come under a non-negotiable requirements list for fintech brands running globally.
Screening Requirements
- Identification of Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs)
- Screening against global sanctions lists (like UN, OFAC, and EU)
- Adverse media screening for reputational and financial crime risk
5. Suspicious Activity Reporting (SAR) and Regulatory Filings
Fintech institutions are essential to legally pinpoint, survey, and report suspicious activities to associated authorities.
Suspicious Activity Reporting needs fintech firms to potentially report illegal transactions to regulators, backed by in-depth documentation and investigation.
SAR Requirements in Fintech
- Detailed documentation of investigation results
- Timely identification and surge of suspicious behavior
- Submission of SARs within regulatory timelines
End-to-End KYC and AML Compliance Workflow for Fintechs
KYC and AML compliance in fintech functions as an automated and continuous lifecycle, not as a linear onboarding job.
Below, we will discuss the modern workflow that fintech leaders follow:
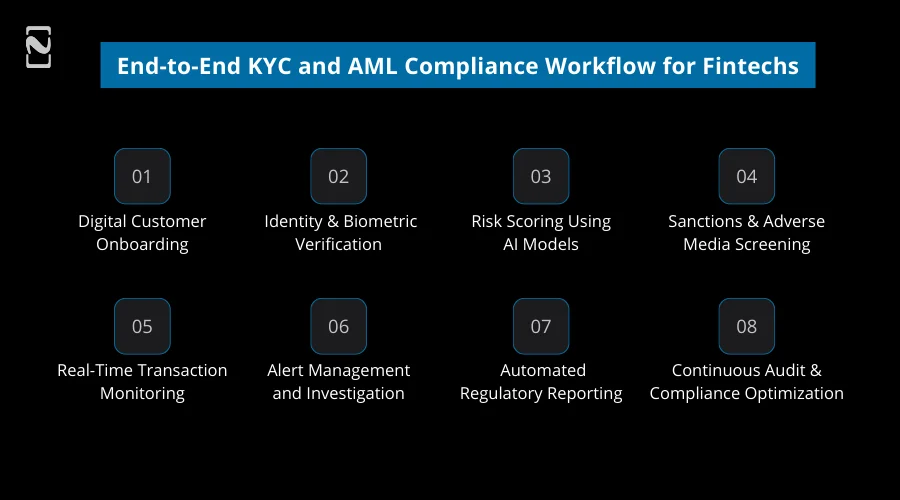
1] Digital Customer Onboarding
The very first compliance touchpoint, digital onboarding, sets the base for risk assessment.
Key Activities
- Jurisdiction and product eligibility checks
- Privacy and consent management
- Safe customer data accumulation
2] Identity & Biometric Verification
Fintech companies then verify customer identities leveraging fraud-resistant and digital-first methods.
Verification Methods
- Government-issued ID validation
- Liveness detection and anti-spoofing controls
- Biometric checks (face, fingerprint)
Strategic Benefits
- Enables scalable and remote onboarding
- Controls identity theft and impersonation
- Reinforces trust in digital financial services
3] Risk Scoring Using AI Models
Post identification, fintech institutions allot initial and ongoing risk scores utilizing AI-driven models.
Risk Factors Assessed
- Geography and jurisdiction
- Customer type and profile
- Historical and external risk signals
- Anticipated transaction behavior
4] Sanctions and Adverse Media Screening
At this edge, customers are screened against PEP databases, global sanctions, and adverse media sources.
Screening Scope
- Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs)
- Sanctions and embargo lists
- Negative news and reputational risk indicators
Best Practices
- Real-time screening at onboarding
- Decreased false positives utilizing intelligent matching
- Continuous rescreening throughout the customer lifecycle
5] Real-Time Transaction Monitoring
The core of AML compliance in fintech is transaction monitoring.
Monitoring Capabilities
- Behavioral pattern detection
- Real-time analysis of transactions
- Network and relationship analysis
6] Alert Management and Investigation
When a suspicious move is caught, investigation alerts are generated.
Investigation Workflow
- Case management with complete customer context
- Automated alert prioritization
- Human-in-the-loop review for high-risk alerts
Regulatory Expectations
- Constant investigation procedures
- Clear escalation paths
- Detailed documentation of decisions
7] Automated Regulatory Reporting
Fintech companies accurately report compliance data and suspicious activity to regulators on time.
Reporting Requirements
- Threshold-based transaction reports
- Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs)
- Periodic compliance disclosures
8] Continuous Audit & Compliance Optimization
The reporting doesn’t end with compliance. Regulators expect fintech firms to consistently assess and enhance their controls.
Optimization Activities
- Model performance testing and bias detection
- Routine compliance audits
- Policy updates based on regulatory modifications
Strategic Value
- Enhances regulator confidence
- Demonstrates compliance significance
- Decreases long-term compliance risk and cost
In 2026, KYC and AML compliance fintech follows an ongoing lifecycle, beginning with digital onboarding, backed by real-time monitoring, AI-driven risk scoring, consistent audit optimization, and automated reporting.
Major KYC and AML Challenges Fintechs Will Face in 2026 with Solutions
With the increasing dependence of fintech platforms on AI-driven systems, KYC and AML compliance for fintech is emerging with complicated operational, regulatory, and technical challenges.
Regulators expect explainable, measurable, and consistent optimized compliance results.
Below, we will talk about the most common challenges fintech can predict in 2026, with proven solutions to combat them.
1. Managing Compliance Across Fintech Partnerships
Challenge: Open banking, embedded finance, and partnerships with banks, third-party platforms, and PSPs raise visibility gaps and shared compliance responsibilities.
Solution:
- Execute ongoing due diligence on vendors and partners.
- Create clear compliance ownership models across partners.
- Leverage centralized KYC and AML frameworks with standardized data sharing.
- Uphold unified audit trails across entire ecosystems.
2. Handling Compliance at Scale
Challenge: Increased transaction volumes, swift customer growth, and multi-product expansion burden traditional compliance models.
Also, as static rules and manual reviews fail to scale efficiently, it leads to increasing costs and operational bottlenecks.
Solution:
- For low-risk cases, choose automation, and for complex scenarios, reserve human review.
- Implement AI-powered risk scoring to prioritize high-risk transactions and customers.
- Choose cloud-native, API-first compliance platforms that hold the caliber to expand with transaction volume.
3. Diminishing False Positives Without Raising Risk
Challenge: Increased false-positive rates flood compliance teams, escalate costs, and slow the investigations, as extremely relaxed controls raise regulatory risk.
Solution:
- Constantly fine-tune thresholds according to performance metrics.
- Utilize contextual data to boost alert accuracy
- Divide customers by risk to enforce proportional controls.
- Replace strict rules with behavioral and pattern-based AI models.
4. Regulatory Scrutiny of AI Decision-Making
Challenge: Regulators increasingly investigate how AI models make compliance decisions, specifically in risk scoring, transaction monitoring, and onboarding denials.
Solutions:
- Implement human-in-the-loop controls for borderline or high-risk cases.
- Conduct bias testing and regular model validation.
- Utilize explainable AI (XAI) for AML and KYC decisions.
- Maintain detailed documentation of data sources, models, and assumptions.
5. Balancing Privacy Laws with Compliance Obligations
Challenge: Fintech companies should comply with AML needs while being compliant with rigid data protection regulations, like GDPR and regional privacy laws.
Solution:
- Leverage privacy-by-design architectures
- Ensure transparent data retention and consent management policies.
- Apply purpose limitation and data minimization principles.
- Implement robust encryption and access controls.
Fintech institutions encounter KYC and AML challenges relevant to partnerships, false positives, scalability, privacy, and AI governance. But these can be addressed via explainable AI, intelligent automation, privacy-first design, and centralized compliance.
Role of RegTech and Automation in Fintech Compliance
In fintech, RegTech, and automation play a significant role in scalable KYC and AML compliance.
Manual processes fail to match the steps with global regulations, increasing fraud sophistication, and real-time transactions.
With RegTech, fintech firms directly embed compliance into their digital workflows, ensuring precision, regulatory alignment, and speed.
How RegTech Supports KYC and AML Compliance
Let’s check out how RegTech appears to be helpful for KYC and AML compliance.
- RegTech is best at AI-driven transaction monitoring and risk scoring.
- It automates KYC by performing digital identity verification, document validation, and biometrics.
- RegTech is used for Sanctions and PEP screening, where it conducts constant watchlist and adverse media checks.
- It is chosen for automated SAR filing and compliance documentation
- It’s useful for automated alert prioritization with complete audit trails
RegTech strengthens fintech to automate KYC and AML processes while upholding auditability, regulatory transparency, and real-time risk control.
AI in KYC and AML Compliance: What Changes by 2026
By 2026, AI in KYC and AML will help in several ways, despite just automating operations.
Banks, auditors, and regulators want fintech firms to leverage AI responsibly and transparently.
So, AI is not judged by speed, but by explainability, governance, and accuracy.
How AI Changes KYC by 2026
AI-driven KYC surpasses static identity checks and helps with continuous identity assurance.
Besides verifying customers once at onboarding, Fintech companies harness AI to:
- Locate identity fraud during onboarding utilizing biometric and behavioral signals.
- Diminish manual reviews while enhancing onboarding approval quality.
- Consistently reassess customer risk as context and behavior change.
The outcome is rapid onboarding with fewer risky customers barely passing through.
How AI Changes AML by 2026
Traditionally, AML was dependent on fixed rules that create high false positives. AI empowers context-aware transaction monitoring.
Modern AI-powered AML systems:
- Prioritize alerts according to real financial crime risk
- Learn general customer behavior over time
- Accommodate new laundering patterns with no continuous rule updates.
- Pinpoint subtle anomalies instead of threshold breaches.
This notably lowers alert fatigue while enhancing detection precision.
Real Benefits of AI-Driven Compliance
If implemented properly, AI delivers:
- Rapid scrutiny and case resolution
- 40-60% less false positives
- Mitigated compliance operating costs at expansion
- Enhanced banking partner and regulator confidence
Besides being an efficiency tool, AI becomes a risk control enhancement.
AI Governance: The Line Fintechs Cannot Cross
Regulators now don’t accept “black-box AI”.
Fintech firms are required to:
- Uphold human direction for critical outcomes
- Describe why AI made a compliance decision
- Document AI for regulatory reviews and audits.
- Monitor models for performance issues and bias,
With governance, AI reduces regulatory risk rather than increasing it.
How Fintech Companies Should Implement KYC and AML in 2026?
You are eager to know what the best way is to set up KYC AML in fintech. Or how should fintechs implement KYC and AML?
This section will help you out.
To implement KYC and AML, fintech brands should move ahead of basic compliance checklists and go for a continuously monitored, risk-based, and technology-driven framework.
Now, regulators expect compliance programs to be auditable, explainable, scalable, and embedded into key fintech operations.
Below are the KYC AML implementation steps for fintech you should consider:

1. Set Robust Compliance Governance
While you initiate KYC and AML implementation, you should begin with clear ownership and accountability.
How?
Best Practices:
- Define roles across product, compliance, and engineering teams.
- Allot a designated senior compliance executive
- Ensure board-level supervision of financial crime risk
- Keep up with documented escalation paths and compliance policies.
Note: Powerful governance is important for audit readiness and regulatory trust.
2. Adopt a Risk-Based Compliance Approach
Based on customer risk, fintech brands must tailor KYC and AML controls, despite applying the exact checks to all.
Key Actions:
- Constantly update risk scores according to behavior
- Categorize customers based on risk level
- Activate Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) for high-risk users
- Enforce proportionate KYC needs at onboarding
Note: This approach boosts precision while mitigating excess friction.
3. Implement Digital Identity Verification and Onboarding
Modern fintech institutions should depend on safe, digital-first identity verification.
Implementation Steps:
- Leverage biometric checks and document verification
- Get data privacy acknowledgements and consent
- Activate anti-spoofing controls and liveness detection
- Ensure onboarding procedures are traceable and auditable
Note: The target is to stabilize swift onboarding with robust identity assurance.
4. Harness AI Responsibly for Risk Scoring and Monitoring
AI is crucial for scaling compliance, but you should meticulously govern it.
How to leverage AI effectively?
- Utilize explainable AI models that regulators can understand.
- Integrate AI for transaction monitoring, risk scoring, and alert prioritization.
- Frequently test the model for accuracy, drift, and bias.
- For high-risk cases, keep a human-in-the-loop review.
Note: AI should not replace accountability, but support compliance teams.
5. Trigger Continuous Monitoring and Real-Time AML Controls
After onboarding, compliance doesn’t end.
Core Demands:
- Dynamic customer risk reassessment
- Real-time transaction monitoring
- Continuous sanctions and watchlist screening
- Behavioral pattern analysis
Note: Always-on monitoring is crucial for embedded finance models and instant payments.
6. Implement Efficient Alert Management and Investigation Workflows
Fintech should respond rapidly and consistently when risks are detected.
Best Practices:
- Detailed documentation of outcomes and decisions
- Centralized case management systems
- Standardized investigation procedures
- Clear alert prioritization rules
Note: This step ensures operational efficiency and regulatory defensibility.
7. Streamline Regulatory Reporting and Recordkeeping
Timely and precise reporting is a legal obligation.
Implementation Steps:
- Automate Suspicious Activity Reporting (SAR)
- Sustain safe, tamper-proof audit logs
- Match reports with regional regulatory formats
- Ensure seamless retrieval during inspections or audits
Note: Automation decreases compliance workload and errors.
8. Consistently Audit, Test, and Enhance Compliance Programs
Regulators envision fintech firms to not only design compliance, but also prove their effectiveness.
Continuous activities:
- Model performance and bias testing
- Internal and external compliance audits
- Compliance awareness and staff training programs
- Policy updates lined up with regulatory changes
Note: Constant enhancements keep fintech institutions adaptable and regulator-ready.
Fintech firms must implement KYC and AML through risk-based controls, robust governance, AI-driven monitoring with human supervision, digital identity verification, and continuous optimization and audit.
KYC and AML Compliance Checklist for Fintech Companies

- Digital identity verification
- Continuous monitoring
- Risk-based onboarding
- AI-driven transaction analysis
- Automated SAR reporting
- Sanctions and adverse media screening
- Compliance governance and audits
How Nimble AppGenie Can Help Fintechs Stay KYC and AML Compliant?
Nimble AppGenie, recognized as a top-tier fintech app development company, builds and scales regulatory-ready KYC and AML systems aligning with dynamic global compliance requirements.
Our team of fintech developers focuses on automation, practical implementation, and lasting compliance maturity.
Check the scenarios below where our team excelled and helped our clients overcome the fintech compliance challenges.
Real-Time Case Study 1: Digital Payments Fintech
Challenge: A fintech firm faced a sudden surge in fraudulent transactions and late detection, leveraging rule-based AML systems.
Our Approach:
We implemented AI-driven AML monitoring with
- Real-time transaction analysis,
- Dynamic risk scoring, and
- Intelligent alert prioritization.
Outcome:
- Swift detection of suspicious activity
- Diminished financial losses from fraud
- Better compliance response times
Real-Time Case Study 2: Embedded Finance Platform
Challenge: A fintech institute encountered issues managing KYC and AML compliance across multiple products, partners, and jurisdictions.
Our Approach:
Our developers crafted a unified compliance architecture with shared risk controls, centralized KYC, and standardized regulatory reporting access partners.
Outcome:
- Constant compliance across the ecosystem
- Easy audits and reporting
- Scalable regulatory alignment as the platform expands
Nimble AppGenie helps fintech companies to implement AI-enabled KYC and AML frameworks that mitigate risk, support regulatory growth, and ease audits.
Looking to make your fintech firm KYC and AML compliant? Collaborate with Nimble AppGenie.
The Future of KYC and AML Compliance Beyond 2026
In 2026 and beyond, KYC and AML compliance will no more a regulatory requirement; instead, it will be a native ability integrated within fintech platforms.
All across the financial ecosystem, the focus will shift toward interoperability, intelligence, and collaboration.
-
Continuous and Invisible Compliance
Compliance will run consistently in the background with risk assessments revised in real-time based on context and customer behavior.
-
Real-Time Global Compliance Networks
Fintechs, regulators, and banks will depend more on real-time, shared compliance signals and interoperable frameworks to fight cross-border financial crime more efficiently.
-
Increased Regulator – Technology Collaboration
Regulators will collaborate with RegTech providers and fintech firms to mold the standards, validate AI models, and trigger proactive compliance, instead of reactive enforcement.
-
Rise of Decentralized and Reusable Digital Identities
Reusable digital identities will mitigate onboarding friction, boost privacy controls, and permit customers to verify on their own for once across various financial services.
-
Compliance as a Built-In Fintech Capability
In the upcoming years, KYC and AML will not be acknowledged as external layers. Instead, they will be integrated into the core fintech architecture.
So, the future of KYC and AML lies in ongoing, tech-driven compliance models that balance privacy, smooth customer experiences, and security.
Conclusion: Preparing Fintechs for a Compliance-First Future
So, why is AML compliance important, and Fintech KYC best practices are explained in this Fintech compliance guide, with AI trends in AML KYC compliance in 2026.
Are you ready for KYC and AML compliance for fintech to boost customer experience and empower risk management?
This is the time! Investing early in automated workflows, implementation frameworks, RegTech integration, and explainable AI will help your firm meet regulatory predictions and gain a competitive edge.
Let’s create your compliant-first fintech infrastructure. Contact our consultants to discuss architecture, AI implementation, compliance, or strategic tech decisions.
FAQs

Niketan Sharma, CTO, Nimble AppGenie, is a tech enthusiast with more than a decade of experience in delivering high-value solutions that allow a brand to penetrate the market easily. With a strong hold on mobile app development, he is actively working to help businesses identify the potential of digital transformation by sharing insightful statistics, guides & blogs.
Table of Contents


No Comments
Comments are closed.